

A Trusted Source For Boating Information Since 2019
Catamaran hulls- everything you need to know.
- Post Written By: Boater Jer
- Published: July 17, 2022
- Updated: July 19, 2022

Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product.
We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end.
Advertisement

Catamaran hulls are not like normal boats but provide increased stability. Let’s take a look at these incredible boats and how their hulls create one of the most versatile watercraft available today.
The Tamil Cholas used catamarans to ferry their troops to invade Malaysia, Indonesia, and Burma. The early paravars or fishing communities in the southern part of Tamil Nadu used two-hulled boats to fish. Polynesian seafarers were also early users of the catamaran, utilizing the watercraft to get to hard-to-reach islands. ( source )
Although the catamaran hull concept is a relatively new introduction to modern boat design , the boat has been in use since the 5th century. It was used for fishing, traveling, and transporting people and supplies.
Parts Of A Catamaran
Here are the basic parts of the modern sailing catamaran:
- Hulls are what sets this boat apart from the rest. The catamaran has two hulls, while the monohull, as the name suggests, has only one hull. Most of the advantages of this boat are hinged on these two hulls.
- The bridge deck connects the two catamaran hulls.
- On top of the catamaran hulls and the bridge deck is the deck . It is where owners attach most of the equipment in a boat.
- You can locate the berth, the galley, and other living amenities in the cabin .
- The cockpit is where you find the navigation equipment of the boat . It is where you control the catamaran’s rudder, sails, and engine.
Types Of Catamaran

The modern catamaran is far more different than its crude ancestor. Instead of tree cutouts, catamarans are now carbon fiber or fiberglass. Here are the different types of catamarans:

Based On function
Pontoons are usually present on rivers and lakes and sometimes even on oceans, but they only travel near the shore.
In a catamaran pontoon-type boat, the pontoons serve as storage areas, where you will find the onboard motors. They are useful for water leisure activities such as short water trips, tubing, wakeboarding, and water skiing.
Some pontoons may also serve as houseboats. They provide a broader, more stable platform ideal for a floating house. Plus, the space is bigger, and most of it is above water. It offers a better viewing option than a monohull. ( Source )
Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull is a catamaran-type boat that the United States Navy initially used for military purposes. They provide the water stability that is necessary when transporting heavy military equipment.
One example of a military SWATH catamaran is the Spearhead class EPF. It is as long as a World War II escort destroyer, yet it is twice as fast at 43 knots. It can reach that speed because of its two separate hulls.
Because of their innate speed, SWATH catamarans can become patrol boats in lakes and rivers. They can easily outrun and outmaneuver standard watercraft.
Nowadays, there are SWATH cruise ships and other non-military variations. ( Source )

Based On Design
- Sailing Catamaran
The smaller sailing catamarans do not have auxiliary engines, so the owner can propel the boat by harnessing the wind using the sails. It’s a popular choice for people with very little or no sailing experience because they are light and easy to use.
The larger sailing catamarans are for group charters and long-distance cruising. They have become so popular lately that they now outnumber monohulls in tropical locations all over the world. They have a last, a headsail, and a mainsail. And the twin hulls have one engine each.
- Power Catamaran
Unlike their sailing cousins, the powered catamarans do not have sails. They have massive engines which provide high speed. Their twin hulls are stronger and can carry and protect the large motors.
The smaller “powercats” are used mainly for fishing. The bigger ones are rented out for charters and cruises.
Catamaran Hulls Performance
Thanks to the catamaran hulls, the boat offers many advantages over other boat types.
- Because its dual-hull design provides a broader base, it offers more water stability than monohull boats. It makes the cat (catamaran) a popular choice for fishing expeditions and cruises.
- Riding a catamaran is ideal for people who feel seasick whenever they ride boats. The twin hulls prevent the boat from moving from side to side. The hulls allow the boat to travel smoothly, even on moderately choppy waters.
- The catamaran is the best choice when storing provisions and other household items with less heeling and bobbing.
- The twin hulls’ stability is ideal for many activities such as cooking and partying.
- Cats offer more moving space because of their broader base, thanks to dual hulls.
- With a catamaran, you have two great options on where to hang out. You can do it on the spacious deck or below the galley.
- Compared to a monohull of the same size, the catamaran can accommodate more equipment and people.
- The living area in a catamaran is above the water line. This feature provides more natural light, a greater view of the outside, and better air circulation.
- Since catamarans do not have keels, they can anchor on shallow waters, something that most monohulls will not be able to do. This ability of catamaran boats is impressive, especially if you are going around areas with many reefs and small islands.
- Catamaran hulls allow the boat to cut through the waves easier and faster. It means they require less engine power than their monohull counterparts.
- Because it has two engines and two rudders, the catamaran can easily maneuver in very tight spaces.
- Because they do not carry heavy keels, catamarans can sail faster than monohulls.
- The catamaran’s stability, speed, and weight make it a safer option than the monohull. It can sail in shallow waters, make a 360 degrees maneuver effortlessly, and carry more provisions.
Disadvantages Of A Catamaran
Like any other boat type, the catamaran also has drawbacks and limitations. Here are some of them:
- The catamaran hulls prevent the boat from sailing as fast as the monohull upwind. The two hulls cause drag, and this slows the boat considerably.
- Because of its bigger size, looking for a docking site can be more difficult and costlier than a monohull.
- For hardcore sailing fans, the experience of sailing with a catamaran will never be able to match that of sailing with a monohull. To them, the challenge of true sailing is just not there with a catamaran.
What Are The Hulls Of The Catamaran Called?
According to the Online Etymology Dictionary, the Tamil word கட்டுமரம், which is pronounced as kattumaran, is where the word catamaran takes its name. The word means “pieces of logs tied together”. Through the years, the term has evolved into what is now a catamaran in English.

What Are The Characteristics Of A Catamaran Hull?
- Both hulls of a catamaran complement each other to achieve very minimum water resistance.
- Because of this, it takes less energy to propel a catamaran, whether via an engine or sails.
- The catamaran hulls provide stability to the boat. The twin-hull significantly reduces bobbing.
- The catamaran’s ability to keep steady on the water makes it an ideal vessel for cooking, dining, and storing provisions.
Are Catamarans Good In Rough Water?
Catamarans are amazingly stable in rough water. The catamaran’s design and build, which provides stability, are factors why it is one of the best boats to use when the waters are choppy.
Yes, catamarans are relatively more expensive than monohulls. Nevertheless, since single-hull boats are less expensive, their resale value is also cheap.
If you add all the advantages that a catamaran offers – safety, comfort, and speed- it does not come out expensive.
patekphilippe.io

Share this post with your friends
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Join us in our love for all things water. And Adventure.

Can You Kayak In Rough Waters?
Advertisement Kayaking can be leisurely paddling through flat and still waters with great weather conditions and an easy route. However, kayaking can also be paddling through strong winds, strong currents, and choppy waves. Water and weather conditions can change fast, and kayakers must be ready for more challenging conditions. Kayaking in rough waters is common. The majority of kayaks are

Upgrade Your Boating Experience: Adding a Third Pontoon Made Easy!
Advertisement As the sun sets over the tranquil waters, the gentle hum of the engine and the soft lapping of waves against the hull create a symphony of serenity. Boating enthusiasts know there’s nothing like being out on the water, surrounded by nature’s beauty. But what if we told you you could take your boating

How Canoes Are Made (1 Canoe Fabrication Easy Explanation Coming Up!)
Advertisement Want to know how canoes are made? You’ve come to the best place to find out. Canoe fabrication occurs using an incredible variety of materials. Some are made of wood, while others are plastic, and some metals like aluminum. Each material has its benefits. Some are lighter, some are more durable, and others are

A Wizard of Technology – The PowerEgg X Wizard Waterproof Drone
The PowerVision PowerEgg X Wizard Drone – A Waterproof, water-landing aerial drone of the future, today. This thing is just plain awesome.

How To Clean A Kayak
Advertisement Kayaks fabrication uses several different materials that react differently to the water. These materials also respond differently to the conditions of the kayak storage. Kayaks are, in most cases, only used seasonally, which means they spend a significant time stored out of sight and out of mind. The biggest challenge to cleaning a kayak

How Long Does It Take A Canoe To Go… (Canoe Calculator Here)
Advertisement You asked, and we answered: Here’s a calculator to determine how long your canoe trip will take. The calculator uses the average speed of an average canoe in calm water. Here it is: The Canoe Trip Time Calculator: Canoe Trip Calculator Enter the distance: Kilometers Miles Calculate Advertisement Canoe Articles & Information replica rolex

Boat Information By Type
© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication.
Privacy Overview
The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)
I didn't understand anything about boat hull types. So I've researched what hulls I need for different conditions. Here's a complete list of the most common hulls.
What are the different boat hull types? There are three boat hull categories: displacement hulls, which displace water when moving; planing hulls, which create lift at high speeds; and semi-displacement hulls, which displace water and generate lift at low speeds. The most common hull types are round-bottomed, flat-bottomed, multi, V-shaped, and pontoon hulls.
But that's all pretty abstract if you ask me, so below I'll give a simple overview of what it all means. After that, I'll give a list with pictures of all the different designs.
A Simple Overview of Boat Hull Types
Your boat hull will be the biggest factor in how your boat handles or sails, how wet it is, how bumpy - absolutely everything is determined by the hull shape. So it's important to understand what different hulls will do for you, and what each hull is best for. First, let's slice it up into rough categories.
Roughly, you can divide boat hulls into three categories:
- Displacement hulls - Lie inside the water and push it away when they move
- Planing hulls - Lie on top of the water and don't push it away
- Semi-displacement hulls - Lie inside the water and push it away, but can generate lift
Everything I'll be mentioning below is one of those three, or something in between.
There are five common boat hull types:
- Round-bottomed hulls - handle well in rough water: sailboats
- Flat-bottomed hulls - very stable for calm inland waters: fishing boats
- Multihulls - very stable and buoyant: catamarans
- V-Shaped Hulls - fast and comfortable in chop: powerboats
- Pontoon hulls - fast and stable: pontoon boats
And then there's everything in-between.
Here's a quick and handy overview of the different hull types
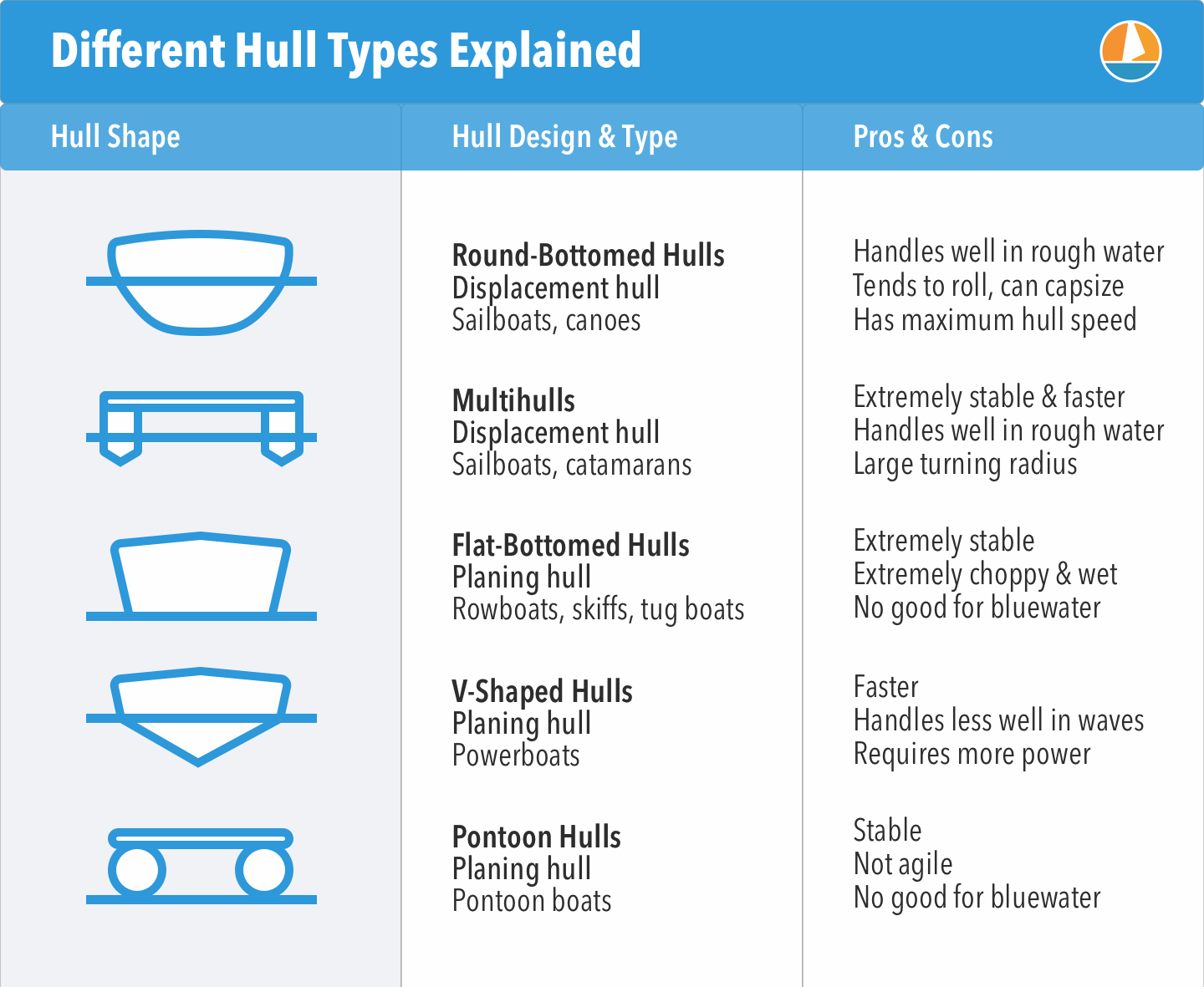
In each category, we find different designs and styles that have different characteristics. There isn't a real clear distinction between categories and styles: there are semi-displacement hulls and so on. So I thought the best way to learn you the different hull types is by simply creating a list with lots of pictures, instead of getting all theoretical about it.
So below I've listed all the different hull styles I could possibly think of, mention what category and type it is, the pros and cons of each one, and give you examples and illustrations for each one.

On this page:
Displacement hulls, round-bottom hull, catamaran hull, trimaran hull, planing hulls, flat-bottom hull, deep v-hull, modified-v hull, stepped hull, pontoon hull, semi-displacement hulls.
Examples: Sailboats, trawlers, fishing boats

Displacement hulls displace water when moving. These hulls lie in the water, instead of on top of it. The amount of water they displace is equal to the boat's weight. Displacement hulls handle way better in rough waters than flat-bottom hulls. That's why most cruisers have some sort of displacement hulls. There are actually all kinds, shapes, and forms of the displacement hull design, which we'll go over later.
The most important thing to understand about the displacement hull, is that it operates on buoyancy. This means that most of the boat's weight is supported by its capacity to float . Planing hulls, on the other hand, operate on lift instead, but we'll dive into that later.
Sailboats typically have displacement hulls, but also fishing boats, trawlers and crabbers. All in all, it's used for each boat that needs to handle well in rough conditions.
Learn everything there is to know about displacement hulls in this article . It lists all the pros and cons and really goes into detail on the nitty-gritty about how displacement hulls actually work .

But they are also slower than flat and planing hulls because the boat creates more resistance when moving. It has to push the water aside. In fact, this type of hull has a built-in upper-speed limit.
This upper-speed limit is called maximum hull speed . It means that the length of a displacement hull directly determines the maximum speed. It can't go faster, because the water-resistance increases with the boat's speed. To learn everything about calculating maximum hull speed , please check out my previous article here.

A round-bottomed hull is a type of displacement hull - it lies in the water and has to power through it. But since it's rounded, it creates little resistance and is effortless to move through the water. It's a very smooth ride and typical for any sailboat that sort of glides through the waves. In contrast, powerboats really have to eat their way through the water.
Examples: Canoes, sailboats
They are also one of the least stable. Since the bottom is rounded, your boat or canoe will rock plenty when boarding or moving around. They are also easy to capsize. That's why pro canoers learn to do a 360 in their canoes. I've never did a roll myself but came close enough a couple of times.

Almost all sailboats use a round bilge as well. This provides it its buoyancy and makes sure it handles well in waves. But since a rounded bilge is easy to capsize, a lot of sailboats have some sort of keel, which stabilizes the roll.
Nearly all ocean-going vessels use some sort of displacement hull, and the round bottom is the most common one. But our next guest is very popular as well.
The catamaran is similar to the pontoon hull (read on to learn more on that one), but it is a displacement multihull instead of a planing one. So it has two hulls, that lie inside the water and displace it. Like the pontoon, you will have to try really hard to capsize this design (and it won't work).
Examples: well, catamaran sailboats. But also this cool catamaran trawler:

Catamarans are extremely popular ocean cruisers. Their biggest pro is their extreme stability and buoyancy. And they have a very shallow draft for a displacement hull, making them very popular for sailing reefs and shallow waters, like the Caribbean.
Some cons for the catamaran are less agile than monohulls. They have a large turning radius, making them less maneuverable. Also, expect to pay high marina fees with this one.
Speaking of marina fees, our next one can go either way.
I think trimarans are incredibly cool, and especially the second type.
There are two types of trimarans:
- a catamaran with three hulls instead of two,
- or a displacement monohull with two floaters.
The first has the same characteristics as the catamaran: it's a displacement multihull, but now with three hulls:

The second can be a regular displacement monohull, with two pontoon-type floaters that provide extra buoyancy, making the total thing a hybrid between pontoon and displacement:

This last one has all the pros of a catamaran in terms of stability, but: you can simply wheel in those floaters whenever you head for port. That saves you a lot of money. And you can trailer her! Imagine that, a towing a trimaran home.
So those were the most common displacement hulls, aka what lives in the water. Let's move on to the planing hulls, aka what lives on the water.

Planing hulls are a hybrid between the flat-bottom and displacement hulls. Planing hulls displace water at low speeds , but create lift at higher speeds . The shape of their hull + speed lifts them out of the water, making them glide on top of the water. Most powerboats look like flat-bottom boats but use a shallow V-shape that helps the boat to handle better at higher speeds.
Examples: Water sports boat, powerboats
The most important thing to understand about planing hulls is that they operate mainly on lift instead of buoyancy. This means the weight of the boat is mainly supported by dynamic forces 1 . With the right amount of power, this design generates lift, which results in less resistance. This is why they are a lot faster than boats with displacement hulls, but also a lot rougher, even with mild chop.
A lot of powerboats use some sort of planing hull. Again, there are many designs and variations on the planing hull, and I'll try to mention as many as I can below.
Because the wedge of the hull runs into the water, it is much easier to handle at high speeds. At lower speeds, it is able to keep its course, even with a bit of wind. However, whenever the boat starts planing, it is prone to wind gusts, since the wedge shape no longer stabilizes the boat.
The flatter the hull, the faster it will go, but also the more poorly it will handle. Other powerboats use deep V-hulls, which I'll discuss below. But first, let's take a look at the flattest hulls you'll ever see.
A flat-bottom hull lies on top of the water and doesn't displace water (okay, very little) as it moves. Since there is no displacement, there is also little to no friction when moving. This makes it potentially fast, but it handles pretty poorly. It is one of the most stable hull design.
Examples: rowboats, (old) high-performance powerboats, small skiffs, small fishing boats, tug boats

They aren't just incredibly stable, they're also very practical. Because the bottom is practically flat, they maximize boat surface. But they are also extremely choppy in rough weather and waves. They will handle very poorly with stiff winds, as the wind can simply catch them and blow them across the water surface. That's why this design is almost exclusively used for calm, small, inland waters.
This type of hull operates mainly on buoyancy , like the displacement hull, but it doesn't require the same amount of power to propel, which is why it's faster.
Because of the uncomfortable ride, not a lot of boats use a perfectly flat bottom. Most boats nowadays use some sort of v-hull or hybrid design, like a semi-displacement hull; especially larger boats. So not a lot of boats have a real flat bottom. However, we do call a lot of boats flat-bottomed. How come?

There are two types of hulls we call flat-bottoms:
- Of course boats with an actual flat bottom
- Boats with almost no deadrise
What is the hull's deadrise? The deadrise is the angle of the front of the hull to the horizontal waterline.
As you can see, the green sailing dinghy in the picture above has a deadrise that's barely noticeable.
Let's move on to other variations of the planing hull. One of the most popular hull design for modern-day powerboats is the Deep Vee hull. And that's as cool as it sounds.

This is a type of planing hull that combines the best of both worlds.
These types of hulls are very popular on modern-day powerboats, and no wonder. With a V-shape that runs from bow to stern, deep into the water, you can handle this boat even in offshore conditions. It handles a lot better than flat-bottomed hulls, while it's at the same time extremely fast.
Examples: Most modern powerboats.
The Deep V-shape acts as a tiny keel of sorts, stabilizing the boat and making it more reliable and maneuverable. The rest of the hull acts as a planing hull, giving the boat its fast edge. Even at high speeds, the Deep V will cut into the water, making it more handleable.
The deep-V design is just one of many variants on the V-hull. Below we'll talk over another, the modified V hull.

The modified V hull is the ultimate crossover of all planing hull types. It's a mix of the flat-bottom and Deep V hull. It is one of the most popular hull designs for small motorboats. It's flat in the back and then runs into a narrow V-shape to the front. The flat back makes it more stable, and adds a little speed, while the V-shape front ensures good handling.
It is, in short, kind of the compromise-family-sedan of boat hulls. It's the fastest design that's also stable, that's also safe, and that also handles well. But it's not the best in any of those things.
Most powerboats you've seen will have some sort of Vee or Modified-V hull.
Stepped hulls are used on high-performance powerboats. It's a type of planing hull that reduces the hull surface by adding steps, or indents in the hull below the waterline. It looks something like this:
It is said to work extremely well at high speed (60 knots and up) and adds up to 10 knots to your top speed.
On to our next design. There are also planing multihulls, and they might even look like catamarans to you. Meet the pontoon hull.
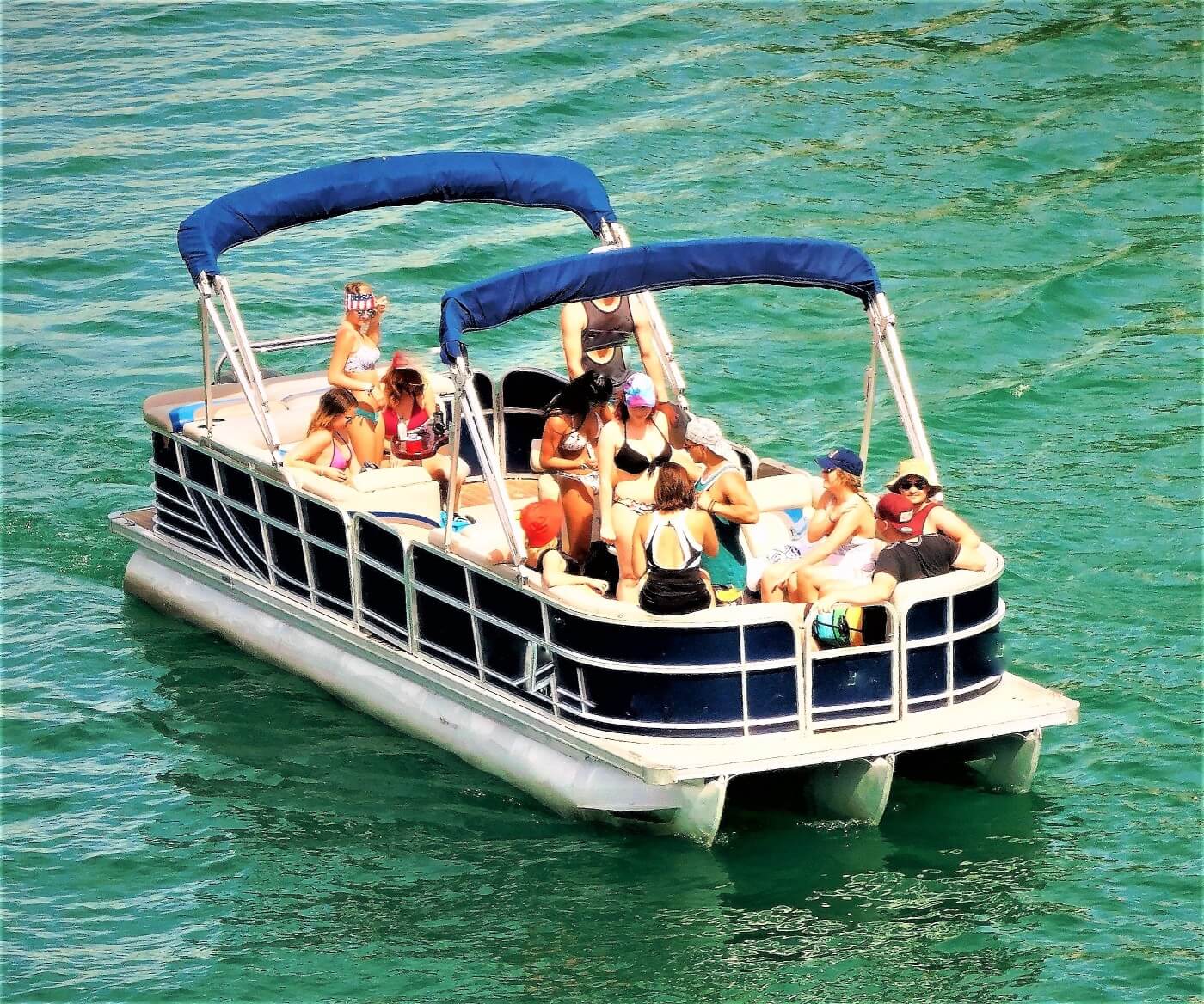

Pontoon hulls float on top of the water using pontoons or floaters that create lift. It's a type of planing multihull that doesn't lie in the water, so it doesn't displace a lot of water. They don't really handle well. As with any multihull, they aren't agile - they're not great at maneuvering. They also have a very large turning radius. But they are extremely stable: there's no chance you'll capsize this.
Examples: Cruisers, modern trawlers, motor yachts, Maine lobster boats
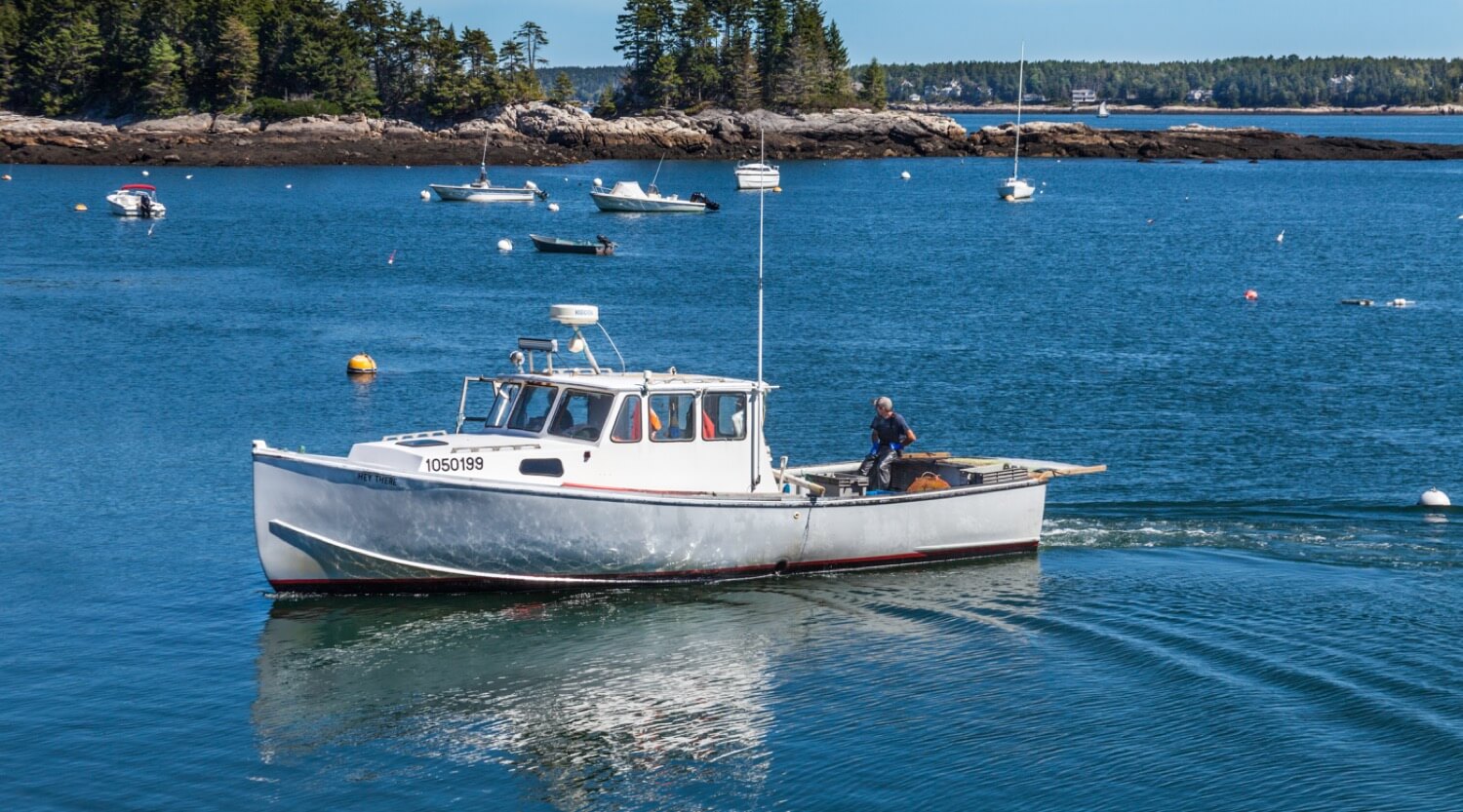

Semi-displacement hulls are smack bang in the center of planning and displacement hulls. They are a bit better for speed than displacement hulls are. They are a bit better for handling rough waters than planing hulls are. This makes them very versatile.

You can see these a bit like being 'half-planing' hulls. These hulls are designed to plane at lower speeds than normal planing hulls - somewhere in the range of 15 - 20 knots, depending on the length of the boat. It also requires less power. When the hull lifts, it reduces drag (water resistance), making it faster and more efficient.
Semi-displacement hulls are perfect for boats that need to be steady and seaworthy but fast at the same time.
For more information about semi-displacement hulls, please check out my in-depth guide to semi-displacement hulls here . It has a diagram and lists all the pros and cons.
So those were my 11 examples, and my step by step explanation of the different types of boat hulls and functions. You now have a solid basic understanding of boat hulls, and can recognize the most common ones. I hope it was helpful, and if you want more good sailing information, be sure to check out my other articles below.
https://www.soundingsonline.com/boats/how-different-hull-types-react-in-rough-water . ↩
I was wondering what your opinion would be on the ship uss Texas as far as hull type and bow type. I think it has a plumb bow and it looks to have a displacement or flat bottom hull. Im doing some research and a better trained eye would be of great help. I used images “bb-35 dry dock” to help see the hull shape. Thank you
Shawn Buckles
Hi Kirk, I don’t know about trained but here we go. I’ve checked the picture, it’s definitely a displacement hull I’d also say it’s a plumb bow.
Hahahahaa imagine liking boats hehehehehe Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water Extremely stable & faster Handles well in rough water
Leave a comment
You may also like, a complete guide to displacement hulls (illustrated).
The displacement hull is the classic go-to hull design for sailboats and one of the most recognizable ones out there. In this guide, I explain all there is to know …

Semi-Displacement Hulls Explained (Illustrated Guide)

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

How Much Does it Cost to Dock a Boat for a Year?
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Boat Hulls 101: Complete Guide to Boat Hull Types, Shapes, and Designs

Table of Contents
If you’re new to boating, then you may not have even considered a boat’s hull , its importance, and the way that it affects your time on the water. With the hull being the part of the boat in the water, it is perhaps the most important part as it gives your boat the ability to float. Not only that, but it affects every single characteristic of your boat and the smoothness of your ride. This article on boat hulls will equip you with the technical knowledge and expertise necessary to understand hulls and the way they work.
What is a Boat Hull?
First of all, we’ll go into a bit of detail on what a boat hull is. The hull is the body of the boat. It is sealed to prevent water from transmitting its way through and keeping your boat afloat. A hull can be open where you sit in it, such as a small dinghy, or a deck may cover it as you would find on a yacht.
When there is a deck placed on top of a hull, it opens up many more options for utilizing the space on your boat more appropriately as it is raised to the top of the hull, where more space is apparent. For example, on a deck, you can place a cabin -like you would find on a center console or even a mast and sail rigs to create a sailboat.
When the hull is open, options to use your space effectively are reduced as you sit at the bottom of the bowl shape. In addition to having less space, you also feel the rock of the water in a more pronounced manner as it is just the keel of the boat (the bottom) separating you from the water. Therefore, every wave and lurch in the water that rocks the boat is felt, which may cause you discomfort if you haven’t quite found your sea legs.
Why Are Hulls Important?
The knowledge of how a boat floats is fundamental if you are looking to get into boating. Without actually knowing, you put yourself at risk of compromising your boating activities and creating a danger that you cause your boat to sink. The key line to this knowledge is that the air encapsulating your boat must be denser than the water it sits upon. This not only includes the air but the items on your boat as they contribute towards the pressure that your boat’s hull puts upon the water.
The greater the amount of weight your boat holds, the further it pushes itself into the water, lowering or raising the level that your hull sits in the water. This force displaces the water to a level that is equal to the boat. If the average density of the boat is greater than the water, then the boat shall sink. You can see this in action if you have a small dinghy; the more people you place on it, you’ll notice that your boat edges itself ever so slightly more into the water as the boat’s weight is rising.
Different types of Boat Hulls
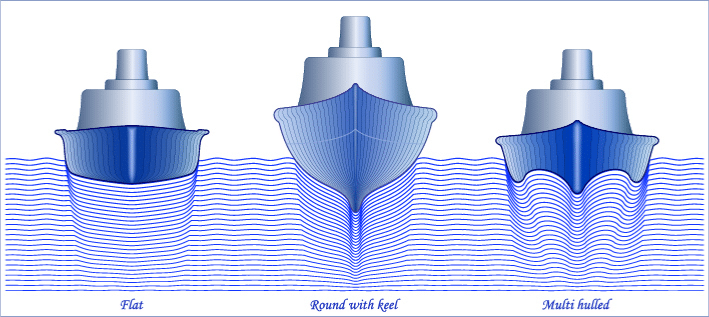
We’ll now walk you through the different types of boat hulls that you come across. The design of the boat’s hull changes the type of boat that you have. If you are browsing through our boat rentals, you’ll notice the various types of boats. Each of these boats has a different type of hull design. For example, a pontoon boat rental is designed for calm waters, whereas a giant yacht is designed for taking on the rough seas, meaning that their hulls vary greatly.
There are two main types of hull: displacement and planing. We’ll give you the rundown of both of these types and the other sub-varieties within them.
Displacement Hulls
The first variety of hulls that we shall examine are displacement hulls. These hulls are typically found on boats that need to carry a heavy load, such as a large fishing boat and big yachts. The hull sits deeper into the water, and the boat is supported by buoyancy, as opposed to its thrust.
Due to the boat sitting deeper in the water, it might be slower, but it will ride steadier. These larger boats are particularly good for the sea as they can handle stronger waves and currents as the boat can stabilize themselves better. This is why you’ll see container ships and other varieties that need to bear a heavy load using these types of hulls.
When it comes to boat rentals, you are most likely to find a sailing boat with a displacement boat hull. The hull is rounded at the bottom, allowing the sailboat to lurch strongly to one side while turning without any danger of capsizing. Thus, we can see the impact that the hull has on your boat rental as it gives your sailboat the extra capacity to lurch around sharp turns and enjoy some exhilarating fun.
Planing Hulls
The other main type of hull is the planing hull. This hull’s design allows the boat to accelerate to higher speeds due to less hull being placed in the water. When a boat with a planing hull is cruising at lower speeds, it operates similarly to a boat with a displacement. When it starts to hit around 15 knots, things start to change depending on the weight of the boat’s load. The flatter surface of the planing hull allows the boat to propel itself upwards to skiff itself across the water. This is what causes boats with planing hulls to obtain higher speeds. In addition, because the bulk of the hull is not placed below the water’s surface, there is less tension from the water holding the boat back, meaning that it can move through the water faster and using less power to obtain a speed that a boat with a displacement hull can.
There is not only one type of planing hull but instead many different varieties. We’ll look through these varieties to examine how it affects your boating experience so that you can make a more informed decision when choosing your next boat rental.
Flat Bottomed Hulls

As the name suggests, these hulls do not have the traditional curved hull that reaches a point at the bottom but has a flat surface instead. These tend to be small skiffs or fishing boats where you cast out from. Due to them having a flat hull, they are excellent for getting into shallow water where some of your favorite catches may lie. These boats don’t need much power for the planing power to come into action and reach quick speeds in no time. They also tend to handle well not just on the flats but also on the sea, with choppy water not being a big issue. So, if you’re looking for some gentle fishing on the flats or maybe out in some nearshore waters, check out our range of small flat bottomed hull boats to truly enjoy some great fishing experiences.
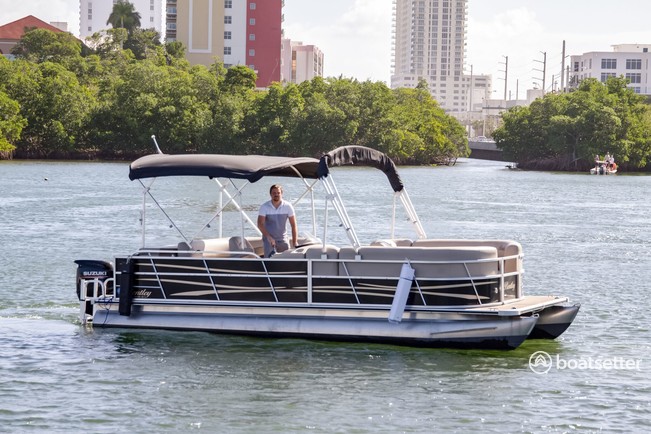

Pontoons are one of the great boat rentals for cruising around and enjoying time with friends because the design of their hulls allows for more space to be created. Pontoons have two-cylinder hulls that sit parallel to each other on the surface of the water. The deck is placed atop these two cylinders, and because they are placed on cylinders, the deck can expand beyond the cylinders, creating more space. This allows for a comfortable seating/social area to be created on the boat, allowing you to use it for parties and some relaxed exploring with the wider family. These boats are best used on inland and flat waters. This is due to waves rocking them a lot more, and a storm at sea can even put them at risk of capsizing. For some fun on a lake, however, pontoons are hard to beat.
In recent years many tritoons have started to crop up on the boat rental market. These are similar to pontoons, but they have a third cylinder that gives them some extra stability. It also means that they can handle a more powerful engine that can bring them up to higher speeds than a pontoon boat. If a pontoon has an engine that is too powerful, then its planing hull can lift it too far above the water’s surface, causing great instability. However, when it comes to tritoons, the greater speeds that you can reach allow you to expand upon other activities and add in some wakeboarding or tubing action onto your party on the water!
V Bottom Hull

The shape of a v bottom hull has a sharper decline that accumulates in having a meeting point at the bottom, creating a v shape, as stated in the name. Because of the honed hull, one of these boats can cut through the water at decent speeds and are particularly good when out on seawater. However, they require a powerful engine for the boat to go into a planing mode. One of the most common types of v bottom hull boat rentals is center consoles. These are great vessels for going for some nearshore or offshore fishing or some general saltwater exploring. Their v bottom hull allows them to cut through the waves so that you can rush to the best fishing grounds in no time at all.
The tri-hull design is a variation of the v bottom hull. It has a v-shaped hull in the center and two parallel smaller hulls on either side of the main central one. This gives the tri-hull boat some extra stability when going forward . Additionally, this also allows the boat to have more deck space as the hull covers a wider range. One of the big drawbacks of the tri-hull – also known as a cathedral hull – is that the bat rocks more when it is in choppier water because the hull is wider. Nevertheless, tri-hulls make for a great option for fishing or exploring on lakes or calm coves.
Catamaran: A Multi-Hulled Boat

Perhaps the most popular multi-hulled boat is the catamaran. This type of boat has two separate hulls that run parallel to each other. These hulls sit on either side of the boat and the deck connects them. This type of design allows forecast amounts of space onboard . Many catamarans are luxury boats that can have the space to hold swimming pools and even helipads. Because they have dual hulls, catamarans can get themselves in shallow waters and lagoons where other luxury boats cannot. This makes them the perfect boat rental if you plan to visit a location where there are multiple small islands such as Hawaii or The Bahamas. The multi-hull system also provides a lot more stability and comfort, so they are perfect boat rentals if you are prone to suffering from seasickness . Catamarans are not only luxury liners as smaller versions with a trampoline-designed deck can also be found that make for great day adventures.
As we hope you have been able to discover in this blog post, the type of hull that your boat has affects everything about your boat. By having a little bit of knowledge on how the design of a boat’s hull has an impact on your boating experience, you can begin to make more informed decisions on which boat rental is best for you. To reinforce this information a little bit further, check out this video !

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Cruise the Intracoastal Waterway and more with Melbourne Florida boat rentals

A Fishing Excursion You Don’t Want to Miss

Top 10 Spots to Boat this Labor Day Weekend

6 Best Lakes in Wisconsin for Boating
Welcome to Lake
Discover places to stay and unique experiences around the world.
- How It Works
Home - Blog - Catamarans Uncovered: The Ultimate Guide to Dual-Hulled Sailing
Catamarans Uncovered: The Ultimate Guide to Dual-Hulled Sailing

David Ciccarelli
January 27, 2024
In this article
Get started.

Understanding Catamarans
When you think of sailing through turquoise seas, what comes to your mind? If you’re picturing luxurious, spacious boats that glide smoothly over water, then you’re probably thinking of catamarans. These multi-hulled marvels are not your average boats; they’re about stability, space, and speed. Let’s set sail on understanding what makes them so unique.
Catamaran Basics
Catamarans are characterized by their two parallel hulls, which fundamentally distinguish them from the traditional monohull vessels. This twin-hull design often results in a wider beam, creating an inherently stable platform. While they boast a shallower draft compared to monohulls, catamarans generally provide more living space and less heeling. With less resistance in the water, performance catamarans can achieve greater speeds. The typical displacement of these vessels means they sit on top of the water rather than plowing through it, which adds to their efficiency.
Historical Evolution
The history of the catamaran dates back thousands of years, with its roots in the fishing and transportation crafts of the ancient Polynesians. Through generations, the design has evolved from simple canoes with outriggers to the sleek, modern vessels we see today. From rudimentary construction to high-tech materials, catamarans have adapted to become a favorite in both private and commercial sectors.
Types of Catamarans
If we list out the types of catamarans, you’d encounter various classes tailored to different sailing needs. You have your cruising catamarans, spacious and comfortable, ideal for those leisurely voyages. There’s the more agile performance catamarans, designed with speed and responsiveness in mind. And then, the luxury catamarans—think of these as floating mansions, complete with opulent amenities and furnishings.
Sailing Catamarans
Your sailing catamarans are akin to dancers on water. With sails harnessing the power of the wind, these vessels are all about eco-friendly propulsion and an authentic sailing experience . Imagine gliding past coastlines without a noise except for the wind in the sails and the water against the hulls. Brands like Lagoon and Fountaine Pajot have become synonymous with this category, providing a range of options from small day sailors to majestic cruisers.
Power Catamarans
Power catamarans, as the name suggests, rely on engines for movement. These are the go-to for those who prefer a bit more oomph in their voyage—capable of higher speeds and longer range without wind dependence. They’re perfect if you’re into coastal hopping or even deep-sea adventures.
Luxury Catamarans
Indulge yourself with luxury catamarans, the epitome of elegance on the water. These vessels come with full crews, gourmet meals, and the kind of pampering you’d expect at a 5-star resort. They represent the pinnacle in comfort and amenities , often custom-designed to meet the desires of the most discerning sailors.
Let’s pause for a breath—feeling the breeze yet? Catamarans are indeed a special breed of vessels that combine innovation, comfort, and performance. So next time you dream of sailing, think of these dual-hulled wonders and consider that perhaps your next adventure awaits on board a catamaran.
Catamaran Design and Construction

Catamarans are unique in the boating world, offering stability, space, and speed that many sailors dream of. Whether you’re an enthusiast or a prospective buyer, understanding the intricacies of catamaran design and construction is essential. Have you ever wondered what goes into making these remarkable multihull vessels?
Multihull Structure
Multihull vessels, such as catamarans, are defined by their two separate hulls. This design provides natural stability which is excellent for reducing seasickness. A significant advantage here is safety ; with two hulls, even if one becomes flooded, the catamaran can often remain afloat and upright.
The Dual-Hull Design
The dual-hull design of catamarans allows for a wider beam, which translates into more deck space. When compared to monohulls, catamarans don’t heel over, making your experience onboard more comfortable and safer. This design also means less resistance when cutting through water, increasing your speed potential.
Advantages of Multihulls
Catamarans are renowned for their spaciousness and comfort, but did you know they tend to have a shallower draft? This allows you to easily explore shallower waters where other boats can’t go. Additionally, they are often faster, making them a favorite for both racing and cruising.
Materials and Construction
When building catamarans, manufacturers often utilize lightweight materials to enhance performance without compromising strength. Composites like fiberglass are common due to their durability and ease of maintenance .
Building Catamarans
The process of building catamarans involves meticulous planning and precision. Each step, from the initial design to the final touches, aims for a blend of performance and comfort. The popularity of DIY catamaran kits has also risen, catering to those who wish to take a hands-on approach to their vessel.
Composite vs. Aluminum
Catamarans can be built from various materials, but the debate often falls between composites and aluminum. Composites are prized for their strength-to-weight ratio, while aluminum is favored for its toughness and repairability. The choice depends on the intended use and the desired balance between weight and durability.
Rigging and Sails
The rigging and sails are critical in determining a catamaran’s performance. With more sail area, catamarans capture a greater amount of wind, which can improve speed. However, the sail plan must be carefully designed to balance power and handling .
Sail Configuration
Choosing the right sail configuration depends on your sailing needs. For travelers who prefer easier handling , a simple sloop rig with one mainsail and one foresail may suffice. Alternatively, performance-oriented sailors might opt for additional sails like spinnakers for downwind speed.
Sail Handling Systems
Modern catamarans incorporate advanced sail handling systems to make sailing more manageable, even for smaller crews. Features such as roller furling for the jib and lazy jacks for the mainsail simplify sail deployment and retrieval, which can be a real back saver!
So, have you gotten a clearer picture of what goes into a catamaran’s design and construction? Whether it’s the material selection or the intricacies of sail handling, each aspect plays a part in giving you the ultimate experience on the water.
Key Features and Advantages

When you’re in the market for a boat that embodies comfort and performance, a catamaran is hard to beat. Let’s dive into what makes these vessels a standout choice for sailors and how they might just be your ticket to the ultimate sailing adventure.
Stability and Safety
Catamarans are renowned for their stability on the water, which translates into increased safety during your maritime excursions. Thanks to their wide beams, which can significantly exceed those of monohulls, moments of discomfort from rolling are minimized whether you’re at anchor or cutting through the waves.
Reduced Risk of Capsizing
The dual hulls of a catamaran are not just for show; they inherently provide a lower center of gravity and a wider base, which greatly decreases the odds of capsizing, giving you peace of mind as you navigate various sea conditions.
Safe Sailing in Rough Waters
One of the greatest perks of catamarans is their capability to handle rough waters with aplomb. The vessel’s design allows for quick and responsive movement, which is crucial when you’re miles from shore and conditions become challenging.
Spaciousness and Comfort
A catamaran is synonymous with spaciousness. Due to the dual hull construction, you’ll find ample living spaces comparable to a floating apartment, making long passages or entertaining guests a delightful experience.
Ample Deck Space
Have you dreamed of a boat where you can lounge, dine, and play without feeling cramped? A catamaran’s deck provides generous outdoor living areas, perfect for soaking up the sun or enjoying al fresco meals with a view of the ocean’s expanse.
Comfortable Living Spaces
Below deck, catamarans boast comfortable living quarters with enough headroom and sizeable cabins . The separation between sleeping areas, often located in different hulls, also ensures privacy that’s hard to come by in other vessel types.
Speed and Efficiency
With a sleek design and lighter weight, catamarans can glide through water quickly and with less effort. Their speed capability is not just great for thrill-seekers but also for those who wish to cover significant distances in tighter timeframes.
Fuel Efficiency in Power Catamarans
For power catamaran lovers, the efficiency game is strong. These cats are designed to consume less fuel while maintaining speed, leading to long-term savings and a reduced environmental footprint.
Ocean Cruising Capabilities
A catamaran truly shines when it comes to blue water cruising. The vessel’s stability and performance make this type of boat well-suited for exploring a variety of destinations across the globe.
Long-Distance Cruising Comfort
Planning an overnight or multi-day cruise? Catamarans are equipped to provide exceptional comfort during long-distance journeys, allowing you to reach far-off places like the Caribbean or South Pacific with ease and pleasure.
Catamarans for World Travel
Imagine setting sail to any corner of the world in a boat that feels like home. Catamarans offer that potential with their excellent cruising capabilities, capacity for provisions and fuel, and comfort—making them ideal for the adventurous sailor eager to chart a course for exotic destinations.
Remember, catamarans by brands like Lagoon or Fountaine Pajot are not only a statement of luxury but also showcase the pinnacle of marine engineering designed with your sailing lifestyle in mind. Ready to catch the wind in your sails?
Notable Catamaran Brands and Models

When you’re out on the open waters, the brand and model of your catamaran are as important as the wind in your sails. Let’s talk about some of the most revered names that have made waves in the world of catamarans.
Lagoon Catamarans
Lagoon is a French manufacturer that’s taken the catamaran market by storm. Known for a blend of innovation and tradition, these catamarans have a strong global presence.
Since its inception in 1984, Lagoon has become synonymous with high-quality catamaran craftsmanship. Their journey began as a segment of the illustrious Group Beneteau, sailing onto becoming a standalone brand admired by many.
Fountaine Pajot
Fountaine Pajot , another French marvel, has carved its niche in the luxury catamaran market since 1976, delivering elegance and sturdiness in every vessel.
Awarded multiple times, including ‘Boat of the Year’, Fountaine Pajot’s reputation is built on innovation, performance, and eco-friendly designs. They are a marquee name for discerning sailors looking for the French touch in boating excellence.
Leopard Catamarans
South African-built Leopard Catamarans offer a robust build quality and a luxury cruising experience that appeals to adventurers and comfort-seekers alike.
Leopard has consolidated its status in the catamaran domain with models like the Leopard 48, known for its innovative design and exceptional onboard amenities.
In your quest for the perfect catamaran, these brands and models stand as shining beacons of quality and expertise. Each one has a story to tell and a journey to offer, ready to make your seafaring dreams a reality. Which one will you choose for your next maritime adventure?
Choosing the Right Catamaran
When you’re on the hunt for the perfect catamaran, the choices can be as vast as the ocean itself. From understanding the key differences between sail and power options to considering your unique sailing style and budget, we’ve got the guidelines to help you navigate this significant investment.
Sail vs. Power Catamaran
Sail catamarans are beloved for their elegance and eco-friendly operation. You’re harnessed to the wind, often yielding better performance and lower operating costs. Power catamarans, on the other hand, offer more consistent speeds regardless of wind conditions and typically feature more living space.
Considering Your Sailing Style
Whether you’re dreaming of leisurely coastal cruises or ambitious ocean crossings, your sailing style is crucial. For example, a sail catamaran with a deep draft improves windward performance for long voyages, while a power catamaran might be the ticket for weekend jaunts and entertaining.
Pros and Cons of Power Catamarans
Power catamarans excel in ease of handling and spaciousness. However, they typically have higher fuel costs, so consider this when comparing prices.
Size and Capacity
Determining boat size.
The size of your catamaran impacts everything from displacement to comfort. Larger models above 40 feet can offer 5 cabins, ample deck space, and enough storage for extended cruising. However, bigger boats also mean higher costs.
Passenger Capacity and Comfort
A catamaran’s design optimally balances capacity and comfort. Here’s a quick reference:
- 2-3 cabins : Ideal for small families or couples.
- 4 cabins : Good for larger groups or charter businesses.
- 5+ cabins : Best for commercial use or those who entertain regularly.
Budget Considerations
Costs of catamarans.
The price of a new catamaran can range from a modest $200,000 to over a million dollars for luxury brands like Leopard Catamarans. Used models can bring significant savings, but factor in potential upgrade and maintenance costs.
Ongoing Expenses
Beyond the purchase price, be prepared for expenses such as docking fees, maintenance, insurance , and of course, fuel for power cats. The latter can significantly affect your budget, especially if you plan to log many nautical miles.
Finding the catamaran that suits your lifestyle, performance expectations, and budget is both an exciting and intensive process. Remember to weigh all factors carefully to ensure your final decision is one that brings endless days of joy on the water.
Maintenance and Care

Taking care of your catamaran not only keeps it looking great but also ensures it performs optimally for years to come. Regular maintenance can prevent costly repairs and extend the life of your boat. Let’s dive right into the nitty-gritty of keeping your cat pristine, shall we?
Essential Maintenance Tasks
“Prevention is better than cure,” they say, and it couldn’t be truer for your catamaran.
- Hull Cleaning : It’s all about the smooth sail, isn’t it? Keep the hull free from marine growth with bi-annual clean-ups.
- Electrical System: Battling corrosion is like facing the high winds at sea. Keep your electrical systems corrosion-free to prevent unexpected failures.
Maintenance Schedule
Sticking to a maintenance schedule is akin to following a treasure map – it leads you to the golden prize of a well-maintained vessel. For instance, oil should be changed at least every 150 hours of engine use.
- Routine Check-Ups: Don’t forget to schedule these with the changing seasons, folks.
- Professional Inspections: Sometimes, you need a seasoned pair of eyes. Yearly check-ups by a professional can spot issues you might miss.
Cleaning and Storage
A clean and well-stored catamaran means a ready-to-go boat when sailing season hits. Nobody likes a damp surprise onboard, right?
- Dry Storage: Whenever possible, store your beloved cat on dry land.
- Cover Up: Use a high-quality cover to shield from the elements – sun, rain, or residents of the nearby trees.
Cleaning Procedures for Catamarans
This is not just a splash-and-dash affair, my friends. Take heed of these steps:
- Freshwater Rinse: After every outing, a freshwater rinse can do wonders against saltwater’s corrosive embrace.
- Mild Soaps: Use gentle cleaners like Woolite or Dawn to keep that canvas looking dapper.
Off-Season Storage Tips
The off-season doesn’t mean rest for you. It’s prime time to ensure your catamaran rests well so it’s adventure-ready when you are.
- Ventilation: Keep air circulating to thwart the ever-creeping mildew.
- Battery Care: Don’t let your batteries go flat. Keep them charged and happy during the off-season.
From the yearly varnishing to the regular freshwater rinses, keeping your catamaran in sparkling condition is a rewarding journey. It’s not just about maintaining value; it’s about cherishing the vessel that carries you across the waters, creating memories one nautical mile at a time. So grab your maintenance kit and let’s keep those cats cruising!
Sailing Safety and Regulations
Ensuring your safety while enjoying the freedom of sailing on a catamaran involves understanding and adhering to essential safety practices and boating regulations. In this section, we’ll navigate through the crucial elements of safety onboard, understand the necessary equipment, and explore the legal requirements that keep you compliant and secure at sea.
Safety Equipment on Catamarans
Catamarans must be equipped with certain safety gear. It’s imperative that your vessel has life jackets for all passengers, fire extinguishers, visual distress signals, and other USA Coast Guard approved safety equipment. Have you checked your boat’s safety inventory recently?
Safety Guidelines for Catamaran Sailing
When you’re sailing a catamaran, it’s wise to “know before you go.” This means checking weather reports and understanding your boat’s limitations. For catamaran-specific tips, remember that while daggerboards or keels enhance performance, they should be handled with care, as they affect the vessel’s stability and maneuvering.
Boating Regulations
Did you know that boating regulations can vary by state and region? It’s not just about being legally compliant; understanding these regulations helps protect the marine environment and ensures that all boaters can enjoy shared waterways safely. Have a look at the U.S. Coast Guard Boating Safety regulations to stay updated.
Adhering to Maritime Laws
Finally, respecting maritime laws and customs is not only a legal obligation but also a mark of a responsible sailor. Here’s a compelling fact: strict adherence to maritime laws significantly reduces the risk of maritime accidents. So, keep abreast of navigation rules to ensure smooth sailing.
Remember, safety is the keel that keeps the exciting adventure of catamaran sailing stable and enjoyable – make sure it’s part of your voyage every time you cast off the lines. Now, are you ready to take the helm knowing you’re well-prepared for a safe journey?
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the advantages of sailing on a catamaran.
You’re in for a treat with catamarans — they’re like the luxury SUVs of the sea but without the fuel guzzling. Expect sheer stability, more living space, and less heeling than a monohull.
How Much Does a Catamaran Cost?
Thought about owning one of these beauties? Keep in mind, the sticker price varies wildly. We’re talking anywhere from $100,000 for a modest pre-owned vessel to north of a couple of million for a brand-spanking-new one, outfitted for luxury. Remember to factor in maintenance costs, which can set you back a few grand a year.
Are Catamarans Suitable for Family Vacations?
Absolutely, your clan will love the spacious decks and cabins that catamarans provide. It’s like a floating condo with the best ocean views.
What Safety Equipment Should I Have on Board a Catamaran?
Your catamaran should be your safe sanctuary on the seas. So gear up with life jackets, flares, VHF radios, and a dinghy for starts. Also, a solid first-aid kit and safety harnesses are invaluable.

administrator
David Ciccarelli, is the Founder and CEO of Lake. He is based in Toronto, Canada, and is an expert in management, business administration, strategy, product development, and customer experience. His educational achievements include the Owner President Management Program at Harvard Business School (2019-2022) and the QuantumShift Program at Ivey Business School in 2017, aimed at CEOs of growing businesses.
Related Posts

October 3, 2023
Lake House Rentals: Your Ultimate Getaway Guide for 2023
Lake houses are charming abodes that offer stunning waterfront views and bring a sense of ...

Boating: Your 10-Step Guide to Driving a Boat Safely
Boating is a fantastic way to take advantage of the great outdoors and create unforgettabl...
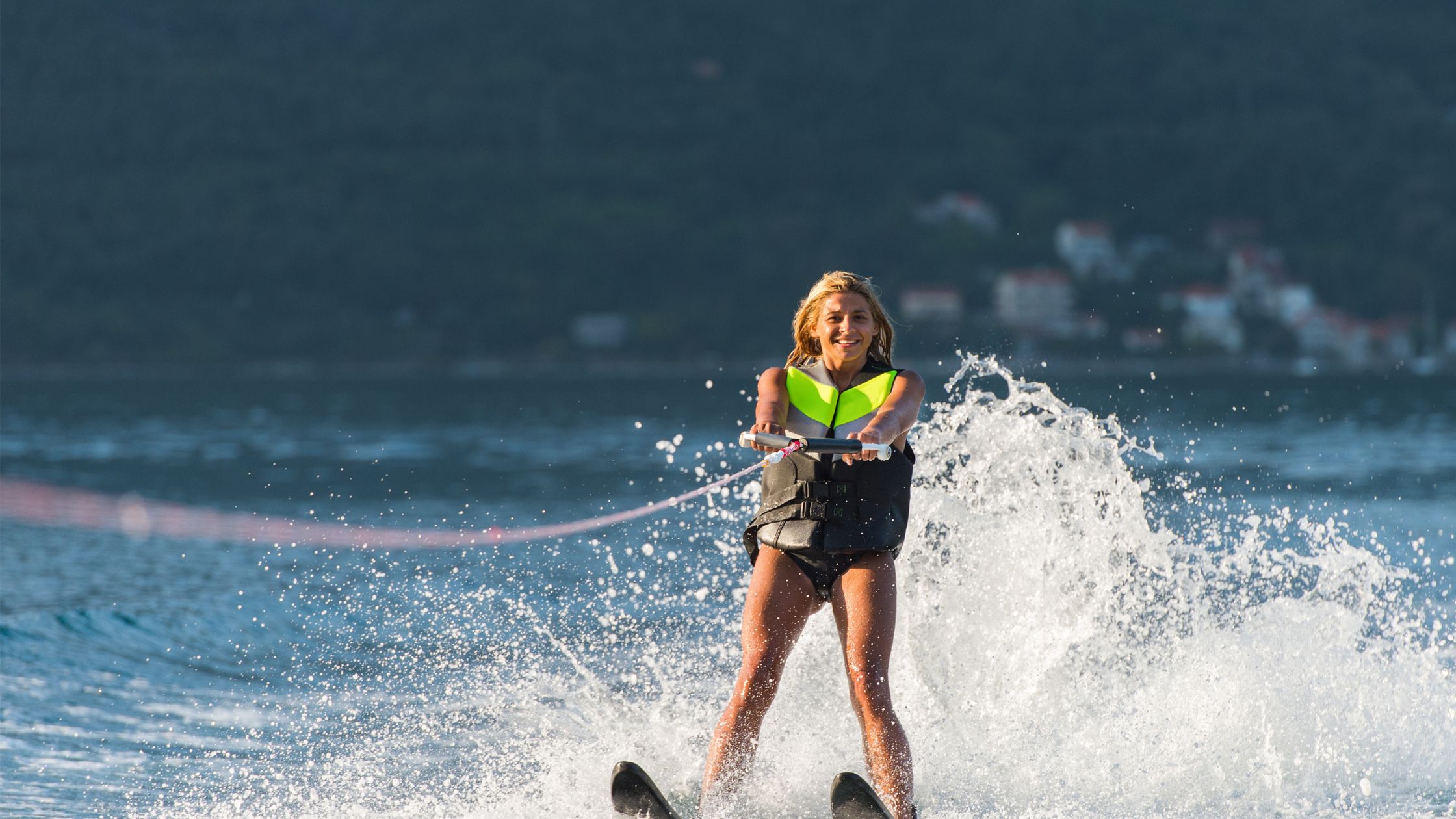

October 4, 2023
Water Skiing Essentials: Tips and Tricks for a Thrilling Experience
Water skiing is an exhilarating surface water sport where individuals ride on one or two s...
Don't have an account yet? Register
Already have an account? Sign In
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address, you will receive a link to create a new password via email.
Design Dynamics
Open Bridgedeck Catamaran
Configuration & Basic Types
Amultihull, just as any other type of boat, presents a series of compromises, and this applies to overall hull, deck and configuration as well. Concessions often have to be made because of space, performance or construction costs. In addition, the intended usage will be a significant factor in determining the shape and size of the vessel. Successful cruising designs will balance all parameters and only you, as a sailor, will know which type of catamaran will be suitable for your needs.
A monohull 's characteristics, largely determined by the beam-to-length ratio of the hull and its displacement, will vary very little from another ballasted boat, as there is only so much volume you can fit into a single hull. This will establish the amount of accommodations, which will not greatly differ from one monohull to another, setting a stark contrast to a catamaran, where intended parameters vary so much more.
Basically, we can break down the major design considerations into: overall configuration,
If one thinks of an open bridgedeck-type of catamaran, images of Hobie Cats on one end of the spectrum, and giant-open ocean racing multihulls on the extreme end, come to mind. They have no fixed coachhouse roof and some of them, especially the small beach cats, only have nets strung between the hulls. Larger examples have partial composite platforms, which stiffen the structure and allow for cockpit seats and helm stations. Since without a solid coachhouse there is less boat to build, these multihulls will be generally lighter and have better aerodynamic properties than full bridgedeck-type cats.
Although few manufacturers and designers have attempted to build open bridgedeck catamarans for cruising, only the most die-hard campers will find them useful for liveaboard applications. Typical examples are the older MacGregor 36, Stiletto 27 and 30, the French KL27 and Corneel designs, which could be sailed hard by lifting a hull (something that you try to avoid when cruising with a fully decked-out boat). Some of these vessels even featured a tiny removable doghouse which provided some shelter for the crew. On smaller open bridgedeck multihulls the only living quarters are found in the confines of the hulls. Even on larger types, they are cramped and not conducive to long-term cruising. The advantages of these sporty vessels,
Copyright © 2006, 2008 by Gregor Tarjan. Click here for terms of use.
Basic Catamaran Configurations

especially in sizes below 30 feet, is their lower cost, trailerability and lively performance. However, attention has to be paid that they not be overloaded or else one could easily turn a cat into a t they are big moneymakers and are considered the workhorses of the sea.
A large exception to the class 1 type of configuration is found in sizes above 30 feet, which could be considered as class 2. Manufacturers such as Maine Cat and a few other custom multihulls such as the Shuttleworth successfully combine an open-deck plan with a certain degree of cruising comfort. In order to provide some shelter for the crew, large semi-rigid biminis are erected. Not only are these afterthoughts unsightly and do no justice to the beauty of these boats, but they also add a considerable amount of drag, contradicting the nature of these athletic multihulls.
Large charter boats or "Day Boats," as they are called, also utilize the open bridgedeck layout to maximize cockpit space. These machines can entertain up to 80 passengers and are found in holiday resorts around the world. Correctly managed and marketed,
Partial Bridgedeck Catamaran
These are often referred to as cruising/ racing types and, unfortunately, very few existing manufacturers still make them. Designs such as the older Edel and Outremer catamarans had a rigid deck and a small coachhouse, which was completely separate from the hulls. My own Outremer 43 "Flo" was of that category. She was a great sailboat and provided ample room for our family cruises along the U.S. East Coast. Similar to the class 1 vessels, the bridge decks of these types of catamarans are also shorter fore and aft, and the accommodations are simple.
Partial bridgedeck catamarans usually place simple sitting arrangements and nav-stations on the main deck. The balance of the layout, below The Broadblue range of cruising catamarans are examples of full-length bridgedeck multihulls, providing plenty of volume for cruisers.

above The Blubay 72 is a state-of-the-art, maxi-sized racer-cruiser featuring a separate saloon pod. She will cruise at close to 28 knots.
below The Gemini 105Mc, seen here in the Patagonian channels, is a popular full bridgedeck catamaran which, in capable hands, can be taken to the world's most remote areas.
such as the galley, heads and berths are often situated in the hulls. Most of the time, these multihulls only have sitting or crouching headroom in the saloon, unless the cabin sole is dropped significantly, compromising the underwing clearance. The Edel 35 was particularly notorious for her low bridge deck, although hundreds of them were built.

Advantages are good looks and light weight overall structure, but the fact that one can only access the hull compartments via the cockpit poses limitations for serious cruising or live-aboard applications.
Some years ago when Outremer was looking for a substitute for its 40 footer, I was asked to design an open bridgedeck type and came up with a compact 38' racer/cruiser with low profile and tiller steering. Unfortunately, lack of demand prevented the project from being realized and the Outremer 42 was born. However, I feel that a properly designed class 2 multihull is a fantastic compromise for the average weekend sailor. It is unfortunate that presently no manufacturer builds one.
Bridgedeck Catamaran
Probably the majority of production and custom cruising catamarans belong to this category, which is the focus of this book. A bridgedeck multihull maximizes the use of space and features a solid deck with a coachhouse that spans the entire width of the cockpit. There is one main entrance into the boat via large sliding doors, and access into both hulls is through companionways leading down from either side of the large saloon. Bridgedeck catamarans are ideal for cruisers or liveaboard sailors. These vessels feature ample payload-carrying capacity and provide good protection for the crew. Helm locations are usually behind the coach roof bulkhead or in some rare cases on the aft end of the hulls behind the cockpit.
These class 3 multihulls contain all the comforts of home and feature a spacious

saloon, galley, and navigation station on the main deck. The coachhouse acts as a centralized core, spanning both hulls, which are usually reserved for heads, sleeping cabins and storage. Unlike any other type of boat, monohull and multihull combined, the class 3 cruising catamaran has an unrivalled "homey" feel to it. The wide cockpits are protected by biminis which integrate seamlessly into the coachroof. This not only looks good but creates an inside-outside space that is both practical and unique.
Large bridgedeck cats have the capacity and volume to carry most of the items you would find in your home. From dishwashers to the generators that power them, you can actually have it all. However, the desire to load up too much sometimes overburdens the vessel, compromising its performance.
On vessels larger than 40 feet, headroom is sufficient, although individuals 6 feet and taller might have to make compromises in the forward part of the saloon or in the extremities of the hulls. Designers try to balance the need for ample bridgedeck clearance and place the cabin sole high enough to avoid underwing pounding created by waves. Low, good-looking silhouettes can be found on larger catamarans, although some manufacturers have the "no holds barred" approach and make their boats look like a toolbox. Although this maximizes space, the chunky appearance is detrimental to the performance of the boat as it increases air drag. Finally, square coachhouses make catamarans look rather unattractive.
Some builders elect to pull the solid bridge deck all the way from bow to stern.
above This recently launched Yapluka 72' catamaran is seen here in full cruising trim and serves her owner-couple as a liveaboard world voyager and mobile office.
Bridgedeck pounding caused by waves is one of the drawbacks of low underwing catamarans. Moderate displacement, full-volume bow and stern sections, and a high and long bridgedeck will minimize, if not eliminate, annoying wave slap under the saloon sole. Although bridgedeck height is a very important parameter, it is a misconception that it is the only design feature to look for. One has to consider weight as well as its distribution and support by the hulls, especially in the extremities. Heavy, low bridgedeck multihulls might make great liveaboard vessels, but they should only be taken to sea by masochists.
below A partial bridgedeck cat, such as the older Outremer 43, was a swift boat but had the disadvantage of separate saloon and hull access.
Parameters Contributing to Bridgedeck Pounding

This book would not be complete without the mention of the new breed of luxury yacht: the Multihull Supercat. These magnificent vessels usually measure in

This is beneficial for stiffening the structure and making the most out of the available deck space. The Gemini catamaran is a very successful design which employs this layout. Yet designers who try to put too much weight into the ends must be careful. These types frequently suffer from excessive pitching in a seaway and display mediocre performance under sail.
Superyacht Catamaran
This book would not be complete without the mention of the new breed of luxury yacht: the Multihull Supercat. These magnificent vessels usually measure in excess of 100' and can sail on free wind energy at more than 30 knots without any heel. They feature living rooms the size as found on monohull superyachts twice their size, and require neither a dozen crew to run them nor large diesel engines. Very few builders in the world specialize in these types of vessels, yet their ideal application as large eco-expedition vessels, corporate entertainment platforms, or ultimate private yachts is unquestionable. Blubay Yachts of France seems to be on the forefront of this group as they have gained invaluable experience by being the only builder that has built a succession of composite superyacht multihulls upwards of 100'.
The world market for extravagant pleasure boats has been steadily growing, yet the catamaran platform for luxury sailing vessels has only recently been recognized.
Modern composite materials and highlevel engineering utilizing Finite Element Analysis now permit the construction of large structures such as multihulls, which was not possible 10 or 20 years ago. The aeronautical and automobile racing industry have contributed considerably to the design and engineering of complex composite structures from which super-catamarans have greatly benefited. The use of aluminum has been the classic hull and superstructure material for large vessels around 60' and it is still a strong and economical build alternative. With the advance of composite technology experienced builders (usually French yards) are developing lighter, stronger and increasingly sophisticated super-yachts, providing clients alternatives that were unheard of just years ago.
Large catamarans, with their wide and stable platforms are becoming recognized as ideal structures for lavish, as well as exciting, pleasure boats. Their vast living accommodations and privacy layout make them ideal for people looking for an alternative to deep draft and heavy monohulls. In addition, their low-profile underbodies permit access to shallow harbors. The new generation of research vessels and oceanographic laboratory ships are frequently large catamarans. They project the image of eco-friendliness and efficiency as they are propelled by clean wind energy. Their shallow draft allows access to reefs and remote anchorages. Their wide aft platforms provide superior storage facilities for large dive tenders and even ideal helicopter landing pads. The demand for these types of superyacht catamarans worldwide is steadily growing.
below Large luxury yachts, such as this 100' catamaran, can easily accommodate several dozens of guests in ultimate comfort while, at the same time, they can sail at double-digit speeds. With world oil prices steadily rising, they very well might become the new breed of mega-yacht.

Continue reading here: Catamaran Design Guide
Was this article helpful?
Recommended Programs

Myboatplans 518 Boat Plans

Boat Alert Hull ID History Search

3D Boat Design Software Package
Related Posts
- How Much Payload Do A Cruizing Catamaran Need
- Bridge Clearance - Maintaining Boats
- How Are Catamaran Masts Fixed Down
- Configuration Types - Catamarans Guide
- Hull Hydrodynamics and Design
Readers' Questions
How to build a catamaran free plans?
There are a number of online sources that provide free plans for building a catamaran, such as: The Boat Plans Collection: <a href="http://www.theboatplanscollection.com/catamaran-plans/" >http://www.theboatplanscollection.com/catamaran-plans/</a> Boat Design Net: <a href="https://www.boatdesign.net/forums/multihulls/free-catamaran-plans-54219.html" >https://www.boatdesign.net/forums/multihulls/free-catamaran-plans-54219.html</a> DIYCatamaran: <a href="https://www.diylargecatamaran.com/category/plans/" >https://www.diylargecatamaran.com/category/plans/</a> Multihulls 4 U: <a href="https://www.multihulls4u.com/diy-catamaran-plans/" >https://www.multihulls4u.com/diy-catamaran-plans/</a> BoatBuilderCentral: <a href="https://boatbuildercentral.com/category/boat-plans/power-catamaran.html" >https://boatbuildercentral.com/category/boat-plans/power-catamaran.html</a> Before beginning the project, be sure to read and understand all instructions, diagrams, and safety guidelines that are included in the plans. Additionally, consider consulting with a professional boat builder in the case of any questions or doubts.
9 Types of Boat Hull Designs and Their Advantages
Imagine gliding through the crystal-clear waters, the gentle breeze kissing your face as your boat slices through the waves effortlessly. While the allure of the open sea is undeniable, what often goes unnoticed is the intricate dance between water and hull that makes this experience possible. Boat hull designs, the unsung heroes of maritime engineering, play a pivotal role in shaping a boat’s performance, handling, stability, and overall characteristics. Whether you’re an avid sailor, a leisurely cruiser, a competitive racer, or a dedicated angler, the type of hull beneath your vessel can make all the difference in your aquatic adventures.
Just as each sailor has their unique voyage, every body of water has its own temperament. The marriage between hull design and boating needs is a testament to the versatility of maritime engineering. From tranquil lakes and meandering rivers to tumultuous oceans and challenging bays, different conditions necessitate distinct hull designs. A flat-bottomed hull might offer stability and shallow-water access for a peaceful day on a calm lake, while a deep-V hull could provide the agility and seaworthiness required to navigate through unpredictable ocean swells. As the water varies, so do the demands on the boat’s performance, and it’s the hull’s responsibility to rise to the occasion.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey through the fascinating world of boat hull designs. We’ll navigate the intricate waters of hull anatomy, exploring the nuances of design that distinguish one type from another. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice boater, this guide aims to provide you with a deep understanding of the various types of boat hull designs and the unique advantages they offer. So, whether you’re seeking the thrill of high-speed racing, the tranquility of leisurely cruising, the art of angling, or the adventure of exploration, your choice of hull design can be your most steadfast companion on the water, shaping your experience in ways you might never have imagined.
The Role of Boat Hull Designs
At the heart of every boat’s performance and characteristics lies its hull design—an engineering masterpiece that defines how the vessel interacts with its aquatic environment. The hull is not merely the shell that holds the boat together; it is a dynamic and intricate component that significantly influences various aspects of boating. From stability to speed, maneuverability to efficiency, the hull design serves as the cornerstone upon which a boat’s capabilities are built.
Stability is perhaps one of the most fundamental attributes affected by hull design. The shape and dimensions of the hull determine how the boat sits in the water, its resistance to rolling, and its ability to maintain an even keel. A wider, flat-bottomed hull offers greater initial stability, making it well-suited for activities such as fishing or leisurely cruising. On the other hand, a narrower hull with a deep-V shape might sacrifice some initial stability in favor of better handling in rough waters and higher speeds.
Speed, a quintessential aspect of boating pleasure, is another realm where hull design takes center stage. The interaction between the hull and water directly impacts how efficiently the boat moves through its medium. A sleek, streamlined hull can reduce drag and enhance hydrodynamics, allowing the boat to achieve higher speeds with less effort. Racing vessels often feature hulls with minimal surface contact, optimizing for speed and agility. Conversely, a displacement hull, designed for displacement-style cruising, is engineered to glide efficiently through the water at lower speeds, making it perfect for long-distance journeys.
Maneuverability, closely intertwined with both stability and speed, hinges on the boat’s hull shape. A hull’s responsiveness to steering inputs, its ability to carve sharp turns or navigate confined spaces, and its resistance to skidding are all influenced by its design. A planing hull, characterized by a flatter shape, can rise up and skim the water’s surface at higher speeds, enhancing maneuverability and responsiveness. In contrast, a hull with a rounded shape might prioritize stability over nimbleness, making it a better fit for leisurely cruising.
Efficiency is a goal that transcends mere performance, impacting the boat owner’s wallet and environmental footprint. The right hull design can significantly affect fuel consumption and overall energy efficiency. A well-designed hull minimizes drag, reducing the amount of power needed to propel the boat forward. This translates to cost savings and a reduced impact on the environment.
Choosing the right hull design is not just an exercise in aesthetics or engineering prowess; it’s a critical decision that directly influences the quality of your boating experiences. Whether you’re seeking the thrill of high-speed runs, the peaceful tranquility of a calm lake, or the efficiency of long-haul cruising, understanding the intricacies of hull design is essential. By aligning your boating aspirations with the right hull design, you can unlock the full potential of your vessel and create memorable adventures on the water.
1. Flat Bottom Hull
A flat bottom hull design refers to a type of boat or watercraft hull that has a relatively flat, wide base with minimal curvature or V-shape. Unlike other hull shapes that have pronounced keels or V-shaped bottoms, a flat bottom hull is characterized by its even and level surface along the entire width of the boat’s bottom. This design is commonly used in various types of boats, ranging from small recreational boats to larger vessels used for specific activities.

Advantages of Flat Bottom Hulls:
- Shallow Water Navigation: One of the primary advantages of flat bottom hulls is their ability to navigate in shallow waters. The absence of a deep keel or pronounced V-shape allows these boats to travel in waters with low depths, such as marshes, lakes with fluctuating water levels, and coastal areas.
- Stability: Flat bottom hulls tend to offer enhanced stability compared to other hull designs. The broad base distributes the boat’s weight over a larger surface area, resulting in reduced rocking and swaying. This stability can be especially beneficial for passengers and crew, making the boat suitable for various activities, including leisure cruising and fishing.
- Calm Water Conditions: Flat bottom hulls are well-suited for calm water conditions, such as lakes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers. Their design minimizes resistance, making them efficient for leisurely cruises and relaxed outings. These hulls are not as well-suited for rough seas or choppy waters, as they lack the ability to cut through waves effectively.
- Maneuverability: The flat bottom design allows for improved maneuverability, particularly at lower speeds. This makes them suitable for activities like fishing, where precise positioning and control are essential. Additionally, their ability to turn in tight spaces can be advantageous for activities like navigating through narrow channels or docking in confined areas.
- Ease of Construction: Flat bottom hulls are generally simpler to construct compared to more complex hull designs. This can result in cost savings in terms of both materials and labor, which may contribute to more affordable boat options for consumers.
- Simplicity and Versatility: Due to their straightforward design, flat bottom hulls are versatile and can be adapted for various purposes. They can be used for fishing, pleasure cruising, transportation, and even as workboats in certain industries.
- Beaching: The flat bottom design enables boats to be easily beached or grounded in shallow waters without causing damage to the hull. This can be useful for activities like picnicking or making temporary stops in shallow areas.
Flat bottom hulls are known for their shallow water navigation capabilities, stability, and suitability for calm water conditions. They are particularly well-suited for activities like fishing due to their maneuverability and ease of use in various environments. However, their design limits their effectiveness in handling rough seas or high-speed applications. When choosing a boat with a flat bottom hull, it’s important to consider the intended use and the specific water conditions in which the boat will be operated.
2. V-Shaped Hull
A V-shaped hull design is a type of boat or watercraft hull characterized by a pronounced V-shape along the bottom of the hull. This design features two sloping sides that come together at a keel or centerline, forming a pointed V at the bow (front) of the boat. The degree of the V-shape can vary, with some hulls having a deeper V angle and others having a shallower angle. V-shaped hulls are commonly used in a variety of watercraft, from small recreational boats to larger vessels designed for specific purposes.
Advantages of V-Shaped Hulls:
- Smoother Ride in Rough Water: One of the primary advantages of V-shaped hulls is their ability to provide a smoother ride in rough water conditions. The V-shaped hull is designed to cut through waves and choppy waters, reducing the impact of waves on the boat and minimizing the discomfort experienced by passengers. This makes V-shaped hulls particularly well-suited for offshore or open water boating where rough conditions are common.
- Better Performance in Rough Water: V-shaped hulls excel in rough waters due to their design’s ability to efficiently displace water downward and outward as the boat moves forward. This reduces the amount of pounding and pitching that can occur in rough seas, resulting in improved stability and comfort for those on board.
- Efficiency in Cutting Through Waves: The V-shaped hull’s sharp bow and keel allow it to effectively cut through waves rather than riding over them. This design helps to reduce resistance and increase the boat’s speed and efficiency when moving through water.
- Versatility for Various Activities: V-shaped hulls are versatile and suitable for a wide range of boating activities. They can be used for offshore fishing, cruising, water sports, and even commercial applications like search and rescue operations. The ability to handle rough conditions makes them a preferred choice for boaters who venture into different water environments.
- Directional Stability: The V-shape of the hull, along with the keel, provides excellent directional stability. This stability is beneficial for maintaining a straight course and accurate steering, especially in challenging conditions where maintaining control is crucial.
- Reduced Roll and Sway: V-shaped hulls typically have a narrower beam (width) compared to flat bottom hulls. This narrower beam contributes to reduced rolling and swaying, providing a more stable platform even in moderate to rough seas.
- Enhanced Performance at Higher Speeds: V-shaped hulls are well-suited for higher speeds, as their design allows them to effectively cut through the water while maintaining stability. This can be advantageous for water sports enthusiasts and those who enjoy cruising at faster speeds.
-shaped hulls are designed to provide smoother rides in rough waters, better performance in challenging conditions, and efficient wave-cutting capabilities. Their versatility makes them suitable for various boating activities, especially in environments where rough seas and choppy waters are encountered. When choosing a boat with a V-shaped hull, it’s important to consider the intended use, as they may not perform as well in very shallow waters or calm conditions compared to flat bottom hulls.
3. Deep V-Shaped Hull

A deep V-shaped hull design is a specific variation of the V-shaped hull, characterized by a more pronounced and deeper V-angle along the bottom of the boat’s hull. This design features two sloping sides that meet at a keel, forming a sharp V-shape that extends from the bow (front) to the stern (rear) of the boat. Deep V-shaped hulls are commonly used in various types of watercraft, particularly those designed for offshore and high-performance applications.
Advantages of Deep V-Shaped Hulls:
- Enhanced Stability: Deep V-shaped hulls offer enhanced stability, especially when compared to shallower V-shaped hulls or flat bottom hulls. The deeper V-angle contributes to better lateral stability, reducing the boat’s tendency to roll from side to side. This stability is particularly advantageous in challenging water conditions where waves and chop can cause significant rocking.
- Improved Handling in Rough Seas: Deep V-shaped hulls excel in rough sea conditions. The design allows the boat to cut through waves and provide a smoother ride, minimizing the impact of waves on the hull and reducing the discomfort experienced by passengers. This makes deep V-shaped hulls ideal for offshore boating, where rough waters are common.
- Better Wave Resistance: The deep V-angle and sharp bow of the hull enable the boat to efficiently slice through waves rather than ride over them. This reduces the amount of water sprayed onto the deck and enhances the boat’s ability to maintain forward momentum, resulting in improved performance in challenging water conditions.
- Offshore Boating: Deep V-shaped hulls are particularly well-suited for offshore boating and long-distance cruising. Their ability to handle rough seas and challenging conditions makes them a popular choice among boaters who venture far from shore. The increased stability and wave-cutting capabilities are crucial for maintaining safety and comfort in open water.
- High-Speed Performance: The design of deep V-shaped hulls allows them to achieve high speeds with greater stability compared to other hull shapes. The ability to maintain control at high speeds is essential for water sports enthusiasts, racing, and other high-performance boating activities.
- Directional Control: The deep V-hull design enhances the boat’s directional control, making it easier to steer and maintain a straight course even in challenging conditions. This control is especially valuable when navigating through tight spaces or crowded waterways.
- Reduced Spray: The deep V-shape helps to direct water away from the boat’s deck, reducing the amount of spray and splash that can occur in rough waters. This feature contributes to a more comfortable and dry ride for passengers.
Deep V-shaped hulls are characterized by their pronounced and deeper V-angle, providing enhanced stability, excellent handling in rough seas, and suitability for offshore boating and high-speed performance. Their design allows them to cut through waves efficiently and maintain control even at high speeds, making them a preferred choice for boaters who prioritize safety, comfort, and performance in challenging water conditions.
4. Modified V-Shaped Hull
A modified V-shaped hull design, often referred to as a “modified V” or “modified deep V,” is a hybrid hull design that combines elements of both deep V-shaped hulls and other hull shapes, such as flat bottoms or planing hulls. This design aims to strike a balance between the stability and wave-cutting capabilities of deep V-shaped hulls and the maneuverability and efficiency of other hull types. Modified V-shaped hulls are commonly found in a wide range of watercraft, from recreational boats to performance-oriented vessels.
Characteristics of Modified V-Shaped Hulls:
- Hull Transition: A modified V-shaped hull typically features a deeper V-shape towards the bow, gradually transitioning to a flatter bottom towards the stern. This combination allows for improved stability in the forward sections and better planing and maneuverability towards the rear.
- Chine: Modified V-shaped hulls often have chines, which are pronounced edges or corners along the sides of the hull. Chines help in redirecting water away from the boat’s hull, enhancing stability and lift.
- Deadrise Angle: The angle of the V-shape is typically less steep than that of deep V-shaped hulls, offering a compromise between stability and maneuverability. This angle allows the hull to handle various water conditions while maintaining a smoother ride.
Advantages of Modified V-Shaped Hulls:
- Stability and Maneuverability Balance: The design of modified V-shaped hulls aims to provide a balanced combination of stability and maneuverability. This makes them versatile and suitable for a range of activities, from leisure cruising to water sports and light offshore boating.
- Smooth Ride: While not as specialized as deep V-shaped hulls, modified V-shaped hulls still offer a smoother ride compared to flat bottom hulls. This is beneficial for maintaining comfort on the water, even in moderate choppy conditions.
- Efficiency and Planing: The flatter sections towards the stern of the hull enable modified V-shaped boats to achieve planing quickly. This efficiency allows for better fuel economy and the ability to reach higher speeds with less effort.
- Versatility: Modified V-shaped hulls are versatile and well-suited for a variety of boating activities. They can handle calm waters for leisurely cruises, but they also have enough stability and control for activities like water skiing, wakeboarding, and tubing.
- Maneuverability: The design of modified V-shaped hulls often includes features like chines, which enhance the boat’s maneuverability. This is particularly advantageous when navigating tight spaces, docking, or performing water sports maneuvers.
- Comfortable Ride: The balance between stability and maneuverability in modified V-shaped hulls contributes to a comfortable and enjoyable boating experience for passengers, even when encountering varying water conditions.
- Adaptability: The design of modified V-shaped hulls can be adapted for various boat sizes and types, making them suitable for both smaller recreational boats and larger vessels with multiple purposes.
Modified V-shaped hulls offer a compromise between stability and maneuverability, making them versatile for a wide range of boating activities. Their design allows for a smoother ride, efficient planing, and the ability to handle different water conditions. This adaptability and balance make modified V-shaped hulls a popular choice for boaters seeking versatility and performance in their watercraft .
5. Round-Bottom Hull
A round-bottom hull design is characterized by a curved and continuous surface along the bottom of the boat’s hull. Unlike other hull shapes with flat or V-shaped bottoms, a round-bottom hull has a smooth and curved profile that extends from the bow to the stern of the boat. This design is often associated with traditional sailboats and historic boat designs.
Advantages of Round-Bottom Hulls:
- Smooth Sailing: One of the primary advantages of round-bottom hulls is their ability to provide a smooth and comfortable sailing experience. The curved shape allows the boat to gracefully glide through the water without abrupt changes in motion, leading to reduced rocking and pitching.
- Minimal Resistance: Round-bottom hulls are known for their minimal hydrodynamic resistance. The lack of sharp edges or flat surfaces reduces friction with the water, allowing the boat to move more efficiently and achieve higher speeds compared to hulls with more complex shapes.
- Efficient in Light Winds: Round-bottom hulls are particularly well-suited for light wind conditions. The smooth curvature of the hull allows the boat to maintain momentum even in gentle breezes, making them ideal for sailboats that rely on wind power.
- Historic and Aesthetic Appeal: Round-bottom hulls are often associated with traditional sailing vessels and historic boat designs. As a result, they hold a strong aesthetic appeal for those who appreciate the elegance and craftsmanship of classic boats.
- Balanced Heeling: The rounded shape of the hull contributes to a more balanced heeling (tilting) motion when sailing in wind. This can enhance the stability of the boat and provide a more comfortable experience for passengers.
- Sailing Performance: Round-bottom hulls can be optimized for sailing performance, allowing boats to respond quickly to changes in wind direction and speed. This responsiveness is crucial for competitive sailing and maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Graceful Appearance: The curvature of a round-bottom hull gives boats a graceful and elegant appearance both in and out of the water. This aesthetic quality is often favored by enthusiasts of traditional boat design.
- Heritage and Tradition: Round-bottom hulls have a rich heritage in boatbuilding and maritime history. Many classic sailboats and traditional vessels feature this hull design, contributing to a sense of tradition and cultural significance.
Round-bottom hulls offer advantages such as smooth sailing, minimal resistance, and a strong aesthetic appeal. They are particularly well-suited for sailing vessels, especially in light wind conditions, where their efficiency and responsiveness shine. These hulls are often associated with historic and classic boat designs, preserving the artistry and tradition of boatbuilding while providing an enjoyable and timeless boating experience.
6. Multi-Hull (Catamaran and Trimaran) Designs
Multi-hull designs refer to boat or watercraft designs that feature two or more hulls instead of a single hull. The two most common types of multi-hull designs are catamarans and trimarans.
Catamarans:
Catamarans have two parallel hulls connected by a deck structure. The hulls are typically symmetrical and provide a wide and stable platform. Catamarans can vary in size from small recreational boats to large luxury yachts and even commercial vessels. The space between the hulls can be used for various purposes, such as living quarters, storage, or amenities.
Trimarans:
Trimarans have three hulls—a central hull and two smaller outrigger hulls, or “amas,” on either side. The central hull is usually larger and provides most of the buoyancy and stability, while the outriggers help with stability and lift. Trimarans offer a balance between the stability of catamarans and the performance of single-hull boats. They are often used in racing and cruising.
Advantages of Multi-Hull Designs:
- Increased Stability: Multi-hull designs, whether catamarans or trimarans, offer enhanced stability compared to single-hull boats. The wide platform provided by multiple hulls reduces the rolling motion, making them more comfortable for passengers, especially in rough seas.
- Reduced Draft: Multi-hull boats typically have shallower drafts compared to single-hull boats of similar size. This allows them to navigate in shallower waters and access areas that might be off-limits to deeper-draft vessels.
- Spacious Interiors: The space between the hulls in catamarans and trimarans can be utilized for various purposes, including cabins, lounges, galleys, and storage. This design allows for more spacious and comfortable interiors, making them popular for liveaboard cruising and luxurious yachts.
- Efficient Sailing Performance: Multi-hull designs often offer better sailing performance than single-hull boats. Catamarans and trimarans have less wetted surface area, which reduces drag and allows for higher speeds, particularly when sailing close to the wind.
- Reduced Heeling: Catamarans and trimarans experience less heeling (tilting) compared to single-hull boats. This is advantageous for both comfort and safety, especially when sailing in windy conditions.
- Sailing Versatility: Multi-hull designs are versatile and can be optimized for different types of sailing, from leisure cruising to high-performance racing. Trimarans, in particular, are known for their speed and agility, making them a popular choice for racing enthusiasts.
- Luxury and Comfort: Large multi-hull designs, especially catamarans, are often used for luxury yachts and charter boats. Their spacious interiors, stability, and amenities make them well-suited for comfortable cruising and entertaining guests.
- Economical Fuel Consumption: Catamarans and trimarans are known for their fuel efficiency due to their reduced drag and efficient hull shapes. This can lead to lower fuel consumption compared to single-hull boats of similar size.
Multi-hull designs, such as catamarans and trimarans, offer numerous advantages, including increased stability, spacious interiors, reduced draft, and versatile sailing capabilities. They are suitable for a range of activities, from sailing and cruising to racing and luxury yachting. The unique characteristics of multi-hull designs make them an appealing choice for boaters seeking enhanced comfort, performance, and functionality on the water.
7. Pontoon Hull Design

A pontoon hull design features a flat, deck-like structure that is supported by two or more airtight cylindrical tubes, known as pontoons. These pontoons are typically located underneath the deck and run parallel to each other along the length of the boat. The deck can be used for various purposes, including seating, storage, and amenities. Pontoon boats come in various sizes, from small recreational vessels to larger party boats and luxury pontoons.
Characteristics of Pontoon Hulls:
- Pontoons: The defining characteristic of pontoon hulls is the use of pontoons, which provide buoyancy and support for the boat. These pontoons are often made from aluminum or other lightweight, buoyant materials and are sealed to trap air inside, ensuring the boat remains afloat.
- Flat Deck: The deck of a pontoon boat is typically flat and spacious, providing ample room for seating, lounging, and various recreational activities. The open deck layout allows for customization and versatility in terms of seating arrangements and onboard features.
- Multiple Pontoons: Most pontoon boats have two or three pontoons, arranged parallel to each other. Some larger models might have more pontoons for increased stability and weight distribution.
- Shallow Draft: Pontoon boats have a shallow draft due to their design, which allows them to navigate in shallow waters without getting stuck. This is particularly useful for exploring lakes, rivers, and calm coastal areas.
Advantages of Pontoon Hulls:
- Stability: Pontoon boats are known for their exceptional stability, thanks to the wide and buoyant pontoons that provide a stable platform. This stability makes them ideal for passengers of all ages, including those who might be prone to motion sickness.
- Versatility: The open deck design of pontoon boats makes them highly versatile. Owners can configure the deck to suit their preferences, whether it’s adding seating, dining areas, fishing amenities, or even watersports features like diving boards or water slides.
- Spacious Interior: Pontoon boats offer generous interior space, allowing for comfortable seating arrangements and the option to accommodate a larger number of passengers. This is particularly advantageous for social gatherings, parties, and family outings.
- Ease of Boarding: Pontoon boats typically have a relatively low profile, making it easier for passengers to board from docks or swim platforms. This can be especially helpful for those with mobility challenges.
- Smooth Ride: Pontoon boats tend to offer a smooth and gentle ride, which is appreciated by those seeking a leisurely boating experience. The buoyant pontoons help absorb waves and reduce the impact of choppy waters.
- Suitable for Fishing: Many pontoon boats are equipped with fishing amenities such as rod holders, livewells, and fish finders. Their stable platform also makes fishing more comfortable and accessible.
- Entertaining: The spacious deck and comfortable seating arrangements make pontoon boats ideal for entertaining guests, whether it’s a casual day out on the water or a festive party.
Pontoon hull designs are characterized by their buoyant pontoons and flat deck. They offer excellent stability, versatility, and spaciousness, making them well-suited for a variety of recreational activities, including cruising, fishing, and entertaining. The ease of customization and comfort they provide make pontoon boats a popular choice among boaters looking for a relaxed and enjoyable on-water experience.
8. Planning Hull Design
A planning hull design is characterized by its ability to lift out of the water onto the surface, or “plane,” at higher speeds. Unlike displacement hulls that move through the water, planning hulls use their speed to create lift, allowing the boat to ride on top of the water’s surface rather than pushing through it. This design is commonly used in powerboats, speedboats, and watercraft designed for activities that require high speeds.
Characteristics of Planning Hulls:
- Shape: Planning hulls often have a flatter, more streamlined shape compared to other hull designs. This shape reduces hydrodynamic drag and allows the boat to transition onto the plane more easily.
- Flatter Stern: The stern (rear) of a planning hull is often flatter and wider, providing stability and a better surface for the boat to lift onto the plane.
- Trim Tabs: Some planning hull boats are equipped with trim tabs, adjustable surfaces on the stern that can be raised or lowered. These tabs help control the boat’s attitude and optimize its planing performance.
Advantages of Planning Hulls:
- High Speeds: The primary advantage of planning hulls is their ability to achieve high speeds by lifting out of the water onto the plane. This reduces hydrodynamic drag and allows the boat to glide more efficiently across the water’s surface.
- Efficient Fuel Consumption: Once on the plane, planning hulls require less power to maintain higher speeds compared to displacement hulls. This results in better fuel efficiency and longer range.
- Quick Acceleration: Planning hulls are known for their quick acceleration. The transition onto the plane allows the boat to rapidly gain speed, which can be advantageous for water sports and recreational boating.
- Responsive Handling: Planning hulls offer responsive and agile handling, making them well-suited for activities that involve quick turns, maneuvers, and changes in direction.
- Reduced Bow Rise: As a planning hull accelerates, the bow tends to rise, which can reduce the operator’s visibility and affect handling. However, many planning hulls are designed with features like stepped hulls or lifting strakes to counteract this effect.
- Versatility: Planning hulls are versatile and can be adapted for various water activities, including water skiing, wakeboarding, tubing, racing, and cruising.
- Agility in Calm Waters: Planning hulls perform best in calm or slightly choppy waters, where they can achieve their maximum speed and efficiency. They are less suitable for rough or turbulent seas.
- Adaptability: Planning hulls can be designed for a wide range of boat sizes and styles, from small runabouts to high-performance offshore racing boats.
Planning hull designs are characterized by their ability to lift out of the water and plane on the surface at high speeds. They offer advantages such as efficient fuel consumption, quick acceleration, and responsive handling. These hulls are commonly used in powerboats and watercraft that prioritize speed, agility, and dynamic water sports experiences.
9. Displacement Hull Design

A displacement hull design is characterized by its ability to move through the water by displacing the water around it, rather than riding on top of the water’s surface like a planning hull. Displacement hulls are commonly found in sailboats, trawlers, and other vessels designed for cruising and long-distance voyages.
Characteristics of Displacement Hulls:
- Shape: Displacement hulls typically have a more rounded and full shape compared to planning hulls. The bow is often more bulbous and less streamlined, which helps to displace water smoothly and efficiently.
- Narrow Stern: The stern (rear) of a displacement hull is often narrower compared to planning hulls. This design reduces turbulence and drag as the boat moves through the water.
- Deep Draft: Displacement hulls generally have deeper drafts, which can be advantageous for stability and reducing the effects of rolling in rough seas.
Advantages of Displacement Hulls:
- Fuel Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of displacement hulls is their fuel efficiency. Because they move through the water rather than plane on its surface, they require less power to maintain cruising speeds. This translates to better fuel economy and longer range.
- Smooth Ride: Displacement hulls offer a smooth and comfortable ride. They glide through the water, reducing the impact of waves and chop, and resulting in a more stable and less jarring experience for passengers.
- Stability: The rounded shape and deeper draft of displacement hulls contribute to their stability, especially in rough seas. This stability is particularly important for cruising and long-distance voyages, where comfort and safety are priorities.
- Less Noise and Vibration: Displacement hulls generate less noise and vibration compared to planning hulls at cruising speeds. This quieter experience enhances the overall comfort of passengers and allows for more enjoyable conversations and activities on board.
- Seaworthiness: Displacement hulls are well-suited for long-distance ocean voyages due to their stability and ability to handle various sea conditions. They are less affected by waves and wind, making them reliable choices for extended cruising.
- Safety: The stability and predictable behavior of displacement hulls contribute to their safety, particularly during rough weather or when navigating through challenging waters.
- Classic Aesthetics: Many classic sailboats and trawlers feature displacement hulls. Their rounded, traditional designs hold a timeless aesthetic appeal that resonates with boating enthusiasts.
- Efficient at Low Speeds: Displacement hulls perform well at lower speeds, making them ideal for leisurely cruising and exploring coastal areas or inland waterways.
Displacement hull designs are characterized by their ability to move through the water efficiently and smoothly. They offer advantages such as fuel efficiency, stability, comfort, and safety, making them suitable choices for cruising, long-distance voyages, and ocean crossings. The design of displacement hulls prioritizes a relaxed and enjoyable boating experience, particularly for those who value comfort and exploration on the water.
Watch Boat hull types explained for beginners | Video
Top 4 FAQs and answers related to What are the different types of boat hull designs and their advantages
What are the advantages of a planning hull design.
Planning hulls excel in speed and agility. They lift out of the water at high speeds, reducing drag and allowing for efficient movement. This design offers quick acceleration, responsive handling, and is suitable for water sports and activities that require rapid maneuvers.
How do V-shaped hulls differ from flat bottom hulls?
V-Shaped Hulls: Have a V-shape along the bottom, provide stability in rough waters, and efficiently cut through waves. Flat Bottom Hulls: Have a wide, flat base, are stable in calm waters, and are ideal for shallow water navigation.
What makes multi-hull designs like catamarans and trimarans unique?
Catamarans: Have two parallel hulls, offering stability, spacious interiors, and reduced draft. They’re versatile for cruising, fishing, and entertaining. Trimarans: Feature a central hull and two smaller outrigger hulls. They balance stability and performance, often used in racing and cruising.
What are the advantages of a displacement hull design?
Displacement hulls are known for fuel efficiency, providing a smooth ride, and excellent stability. They are suitable for long-distance voyages, cruising, and are less affected by waves. Their quietness and comfort make them great for leisurely exploration.
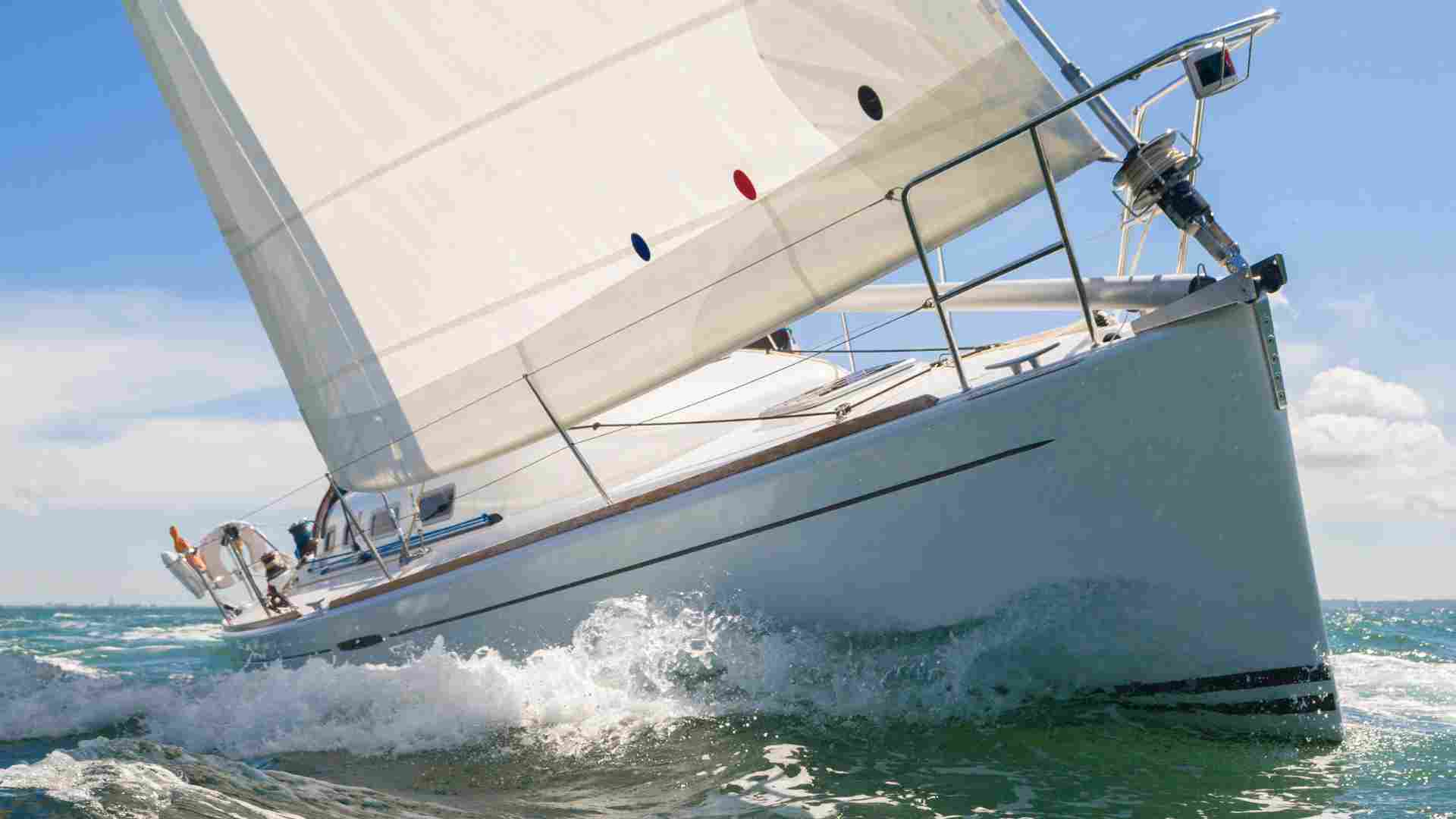

In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the diverse world of boat hull designs and their unique advantages. We’ve covered a range of designs, each tailored to specific purposes and water conditions. Whether you’re a recreational boater, an avid angler, a water sports enthusiast, or a seasoned cruiser, understanding these hull designs is crucial for optimizing your boating experience.
From the efficient fuel economy and gentle rides offered by displacement hulls, to the exhilarating speeds and agility of planning hulls, each design comes with its own set of benefits. V-shaped hulls conquer rough seas with stability, while flat bottom hulls navigate shallow waters with ease. Round-bottom hulls offer smooth sailing, and multi-hull designs like catamarans and trimarans balance stability and versatility.
Choosing the right hull design is paramount. Your intended activities, preferred water conditions, and desired experiences all play a role in this decision. Each design has its strengths, but understanding their characteristics empowers you to make an informed choice that aligns with your needs and aspirations.
As you embark on your journey into the world of boating, explore the nuances of different hull designs and their advantages. Whether you’re purchasing a new vessel or customizing an existing one, this knowledge will be your compass. With the insights gained from this guide, you’re equipped to navigate the waters with a deeper understanding, confidently selecting the perfect hull design to elevate your boating adventures. May your sails be steady, your rides be smooth, and your experiences be enriched as you set sail with newfound appreciation and expertise.
Share 9 Different Types of Boat Hull Designs and Their Advantages on a Budget with your friends and Leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read 8 DIY Modifications to Increase Boat Performance on a Budget until we meet in the next article.
Similar Posts

Essential Lights for Kayaking at Night: Navigating at Night
There’s a certain magic that comes with kayaking under the moon’s gentle glow or witnessing the stars’ twinkle reflected on the water’s surface. Nighttime kayaking offers an entirely different perspective, blending adventure and serenity in a unique way. However, to fully embrace this nocturnal escapade, safety and visibility should remain paramount. This is where proper…

How to Troubleshoot Common Issues with Boat Trailer Brakes?
Safe towing hinges on the reliability of boat trailer brakes—a critical factor often underestimated until trouble strikes. Navigating the open road with a boat in tow demands well-functioning brakes to ensure smooth and secure travel. The jarring reality of encountering brake issues mid-journey can turn a leisurely drive into a nerve-wracking experience. However, armed with…
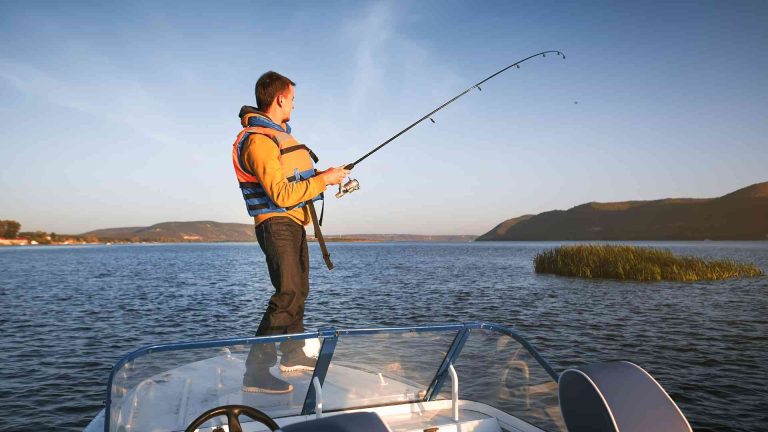

What Is the Importance of Fishing with a License? Reasons
Imagine spending a serene day on a tranquil lake, casting your line and patiently waiting for the perfect catch. Fishing, a beloved pastime enjoyed by millions worldwide, provides a peaceful escape and a chance to connect with nature. However, hidden beneath the beauty of this hobby lies a critical responsibility that every angler must uphold:…

How Much Does a Boat Weigh? A Guide with Factors to Measure
Boats have always captivated human imagination, from ancient voyages of discovery to leisurely cruises on serene waters. Their elegance, versatility, and ability to take us to new horizons make them objects of fascination. But have you ever wondered how much a boat weighs? Delving into a boat’s weight can unveil a world of insights, from…

How Much Is a New Pontoon Boat Cost?
There’s an undeniable allure to pontoon boating, a captivating blend of leisure and adventure that beckons water enthusiasts. The thought of cruising tranquil lakes, hosting memorable gatherings, or simply escaping into nature on a brand-new pontoon boat is a dream shared by many. However, as with any significant investment, the burning question often arises: How…

Buying a Boat in Europe After Brexit: Things You Should Know
Introduction to the topic Attention, boating enthusiasts! Have you ever dreamed of cruising the pristine waters of Europe, feeling the cool breeze on your face and the thrill of adventure in your veins? If so, you’re not alone. The allure of boating in Europe has captivated the hearts of countless enthusiasts like yourself, and today,…
11 Types Of Boat Hulls – Boat Hull Shapes & Designs

In many ways, the hull is the most important part of the boat because it’s what helps it float, pun intended. It’s the waterproof ‘base’ of the boat, with part of it submerged under the waterline. And these hulls come in lots of different styles and designs. Let’s check out a few.
Table of Contents
Overview of Boat Hull Types
A comprehensive list of boat hull types, bonus: jet ski hulls, quick clues about boat hull types.
First off, let’s look at the broad hull divisions . They can be categorized by:
- Form e.g. hard chine, soft chine, smooth chine
- Displacement e.g. full displacement, planing, semi
- Shape e.g. s-bottom, v-bottom, rounded, flat
These categories overlap a lot. For example, a v-bottom hull is sometimes described as a (hard) chined hull. And s-bottoms are sometimes labeled as rounded bilge hulls or smooth curve hulls. You can also classify hull types based on the number of hulls under the boat.
Just to make sure we’ve covered all the boat hull types, we’ve compiled them into a single list that cuts across the categories. This list will expand on any overlaps between the hull classes. Let’s start with the word chine, the angle at the bottom of the hull. It can be flat, curved, etc.
Hard chined hulls are sometimes called chined (without the word ‘hard’). And soft chined hulls are sometimes described as molded, curved, rounded, or smooth hulls. Finally, displacement hulls have a wider, heavier base designed to push water aside at lower speeds.
Conversely, planing hulls are streamlined to slice through the water at faster speeds. They ride high above the waves and seem to skim the water. Semi-planing / semi-displacement hulls fall in-between. Let’s look at the specific boat hull types, noting how they intermingle.
1. Flat-Bottom Hull (Chined)
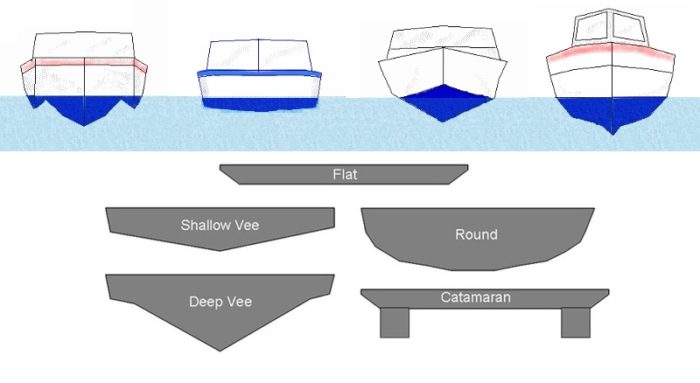
Just to refresh your memory, the chine described the angle at the outer bottom of the boat. This can be flat, slightly curved, fully rounded, or sharp and acute (e.g. a distinct v-shape, which is the harshest angle and is therefore called a hard chine. Flat-bottoms have no angle.
This means they’re sturdy and stable, sitting low and moving slow. That flat surface does drag the boat though, so flat-bottom hulls often have a pointed bow and stern to push the water more effectively. Or they may have an angular front and a reversed bell-shape back.
Flat-bottom hulls are categorized as displacement hulls. They work well on calm waters, so flat-bottom hulls are mostly used inland on large lakes and secure bays. They don’t do as well in wavy water. Small rowboats, rafts, kayaks, and paddle boats often have flat-bottom hulls.
2. V-Bottom Hull (Chined)
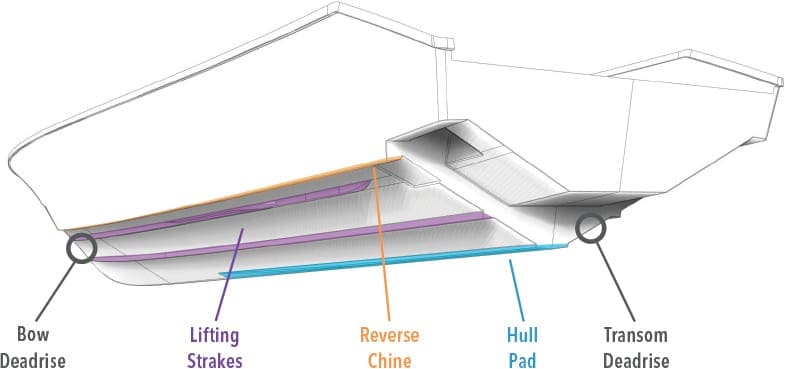
While flat-bottom boats are often displacers, v-bottom boats are better at planing. That triangular base is where the hard-chine name comes from because it’s a sharp or ‘hard’ angle of 6° to 23°. This hard chine is good at cutting through currents and riding over the waves.
V-bottom hulls are routinely combined with a powerful motor , which makes it even easier to zip above the waves. While sailing, the nose of the boat stays visible above the waterline. These boats aren’t as stable at slow speeds because the rolling waves can topple the boat.
Think of it this way – the V provides a wider surface for strong waves to push against, so the boat has to be fast and powerful enough to counter that roiling motion. A V-bottom hull can have a single V or several smaller ones strategically arranged for maximized boat balance.
3. Multi-Chine Hull (Hard)
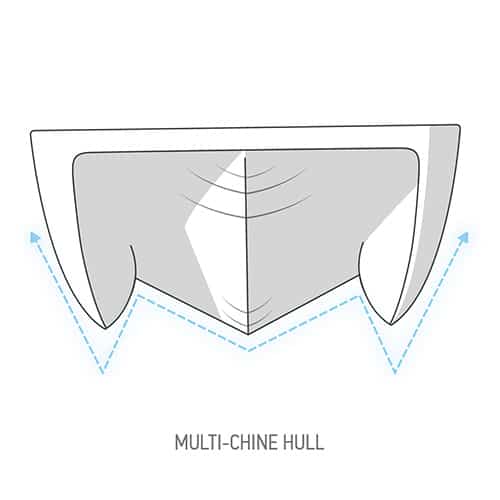
Multi-chined hulls can have twin or triplet chines. These chines can be parallel, identical, or have mixed sizes, and are ideal for speed sailing. The acute angles beneath the waterline help the boat soar over the water, while the multiple chines counter the effect of rolling waves.
But because there’s more than one hull, multi-chines are classed as displacement hulls. The hard chines push water into the valleys and ridges formed by the frames. Multi-chine hulls can be cathedral hulls or tunnel hulls, meaning the hull creates an M-shape under the water.
Multi-chine hulls will sometimes have a separate engine for each chine, so they can move quite fast. The platforms between the chines keep the boat stable while the alignment of the chines helps them battle the conflicting directions of circular waves and clashing currents.
4. Round Bilge Hull (Moulded)
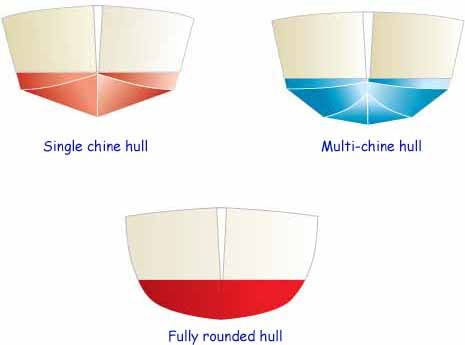
This is the most popular boat hull type because it combines the stability of a flat hull with the maneuverability of a curved one. The rounded bottom of the boat lets it handle waves more effectively than a flat hull. The soft-chine lets the boat glide and bob over larger, faster waves.
The reason molded hulls are so common is their middle-ground status. The curved bottom offers more speed and less drag than flat-bottom hulls. But because rounded bilge hulls are broader than v-bottoms, these boats can handle rougher, deeper waters than flat-bottoms.
Cargo boats, cruise ships, and ferries tend to have rounded hulls, especially if they sail deep waters. They can gain speed but are intended for slow gliding. But they tend to be large so you need plenty of room to turn, and extra care when you’re loading the boat at the docks .
5. Semi-Round Hull (Moulded)
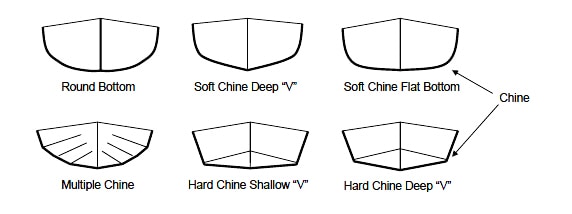
Semi-round bilge hulls are halfway between round hulls and S-hulls. They have a slightly gentler curve than S-bottoms, and they have a pointed keel down their middle. Small boats like dinghies and laser boats often have a semi-round hull, combining stability and speed.
Dinghies are generally used as non-inflatable lifeboats while lasers are for competitive solo sailing. They’re functional boats that can withstand deep, rough waters but are only intended for targeted spurts – like escaping a sinking ship or sprint sailing. They’re not distance boats.
You can also use semi-round hulls for buoy-sailing, where you race around designated ‘landmarks’ in the water. Semi-bilge boats do well here because they can work with flapping sails, go deeper with less drag, and retain stability during sharp turns and tricky maneuvers.
6. S-Bottom Hull (Moulded)
Sometimes called the arc-bottom hull, these boats have a smooth, curved bottom that meets at a pointed keel. The ‘s’ is the bulbous curve that forms from the waterline to the apex, and every boat has two. Think of it like a stereotypical temple dome roof that hangs upside-down.
This arch makes the boat an ideal hybrid. Its bulbous curves offer additional storage space and stability, while the pointy bit is great for planning since it lifts the boat as it slices through the waves. The curves also help to counter the push of rocking waves and currents.
Curiously, DIY boats routinely have that S-shape. These include the kinds of fishing boats that indigenous communities use. The arch creates space for your fishing haul while allowing you to sail swift rivers and deep lakes. Unfortunately, that arched keel is prone to capsizing.
7. Displacement Hull (Low-Speed)
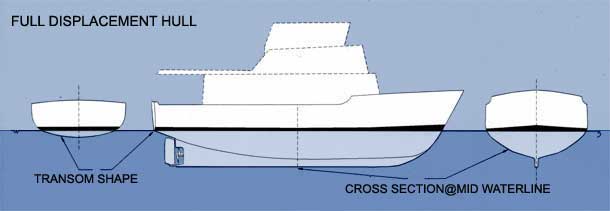
Any boat that moves by pushing water out of the way is defined as a displacement boat. They mostly have flat or round hulls , but they can also have a multi-chine design if the hull has grooves between the chines. This crucial difference distinguishes how the boat operates.
Think of it this way – a V-bottom boat, even one with several chines, needs flatter sections to join the separate hulls. If the platforms are 180, they glide above the waterline with stronger drag. But if those underwater sections are angular, the boat displaces the water down there.
And yes, displacement boats can still zoom along. But when they do, the flatter sections slam onto the water as every wave dips. That makes for a rather uncomfortable ride, which is why displacement hulls are best for boats that intend to carry heavy cargo across calm, slow seas.
8. Planing Hull (High-Speed)
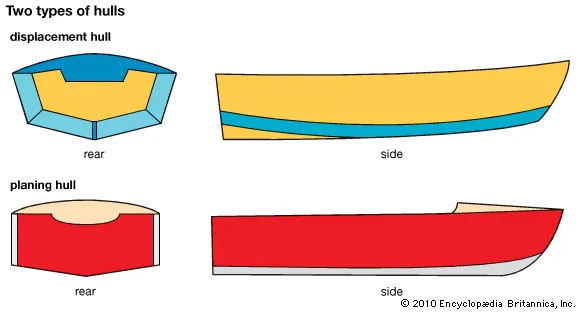
The opposite boat hull type is the planing hull, built for speed. You know that typical sailing shot where a suave spy seems to be bouncing on the waves in a pointed boat that’s apparently flying through the sea? That’s a planing boat, and the emphasis is on the boat’s lift or plane.
This means the hull is designed to carry more weight at the back, allowing the front to rise out of the water at high speeds . These boats are often equipped with high-powered motors , and if you drive too slowly, the angular hull will have a hard time idling in the water.
In such cases, the boat is likely to pitch. Here’s a shortcut you could use to remember the different boat hull types. Flat, rounded, and multi-hull boats are displacers. Arched, v-hull, and angular boats are planing boats. These features are combined for inflated hollow hulls.
9. Semi-Planing / Semi-Displacement Hull
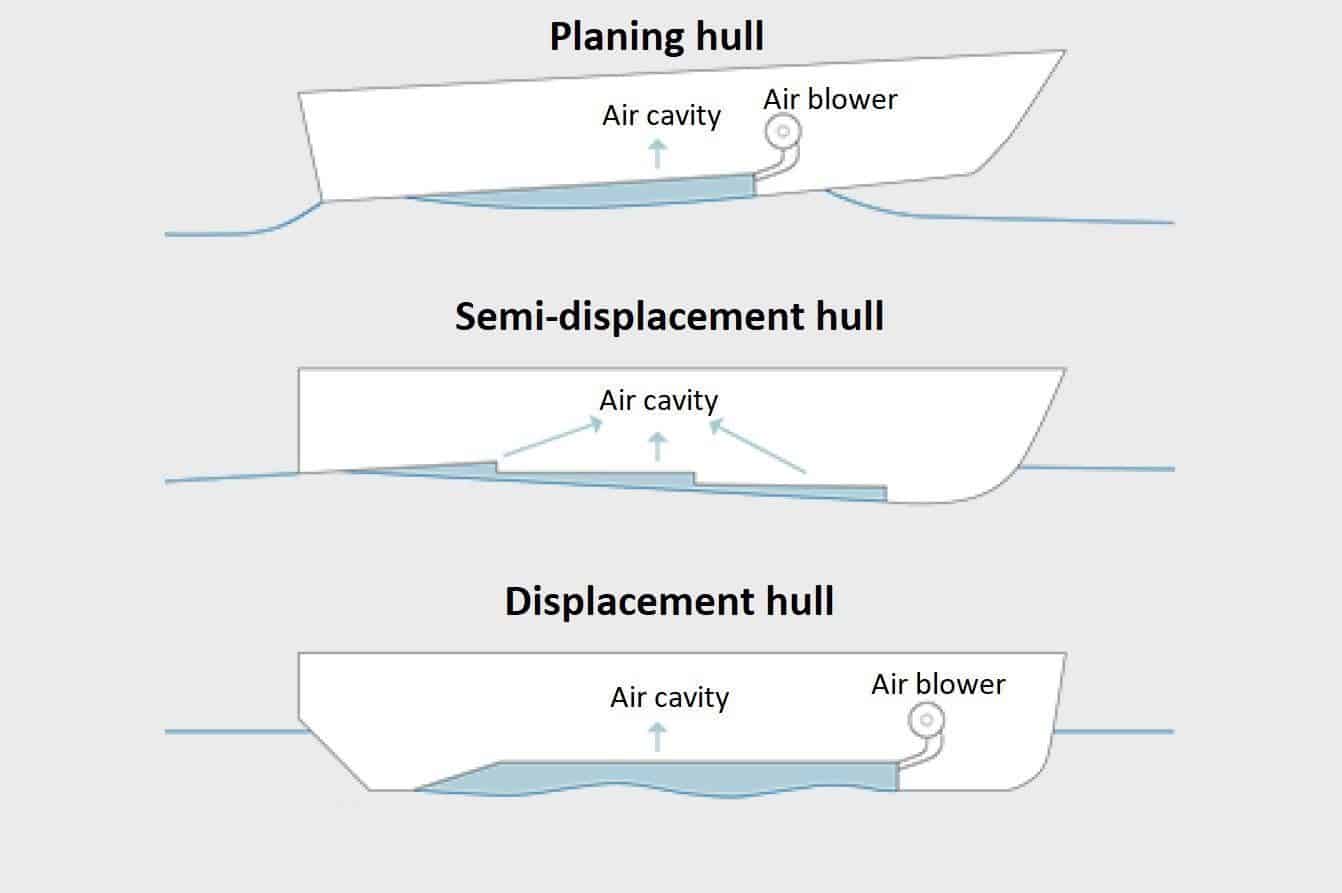
Cruise ships and luxury yachts are the best examples of semi-planing or semi-displacement boats. The design range is quite diverse, so the specs will depend on your particular needs. But the idea is that the hull has a composite surface to facilitate the various sailing features.
For example, you need speed between destinations, and maneuverability as you dock at every port. Massive storage space is essential for the passengers, their gear, and their … by-products. You also want a boat that stays stable as it faces deep-sea currents and creatures.
The draft (that’s the section of the hull that stays submerged) has straight bits, angular bits, and curved bits to allow for all this. Ocean trawlers and container ships can also have a semi-planing hull. These semi boats have Vs and wedges at the front and get rounder at the stern .
10. Pontoon Hull (Hollow)
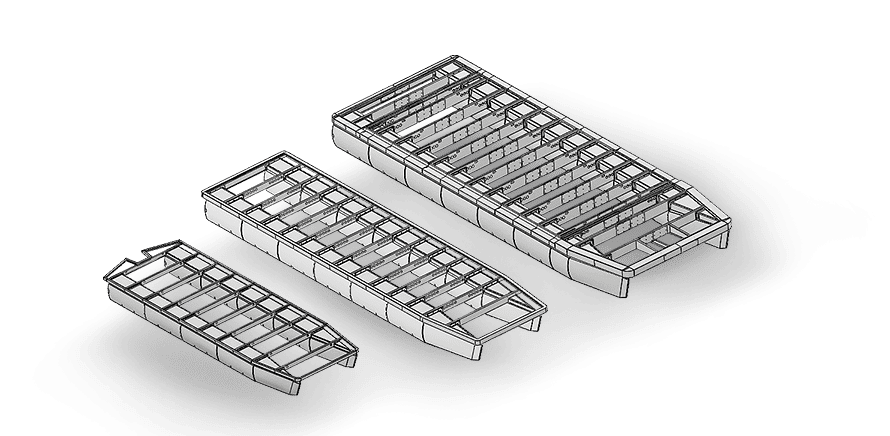
What happens when you want a ‘flat’ boat with a larger capacity? Well, aluminum fishing boats are flat-bottomed but tiny. So if you want to carry a larger crew (or even passengers in transit), opt for a pontoon hull. Its hull floats through the use of hollow cylindrical tubes.
These tubes are often made from aluminum, and your pontoon can have two or more tubes below its deck. The focus is on cargo space and balance. Passenger platoons have lots of padded seating space, and guests are carefully spread out to maintain the boat’s equilibrium.
Pontoon hulls are sometimes fitted on trawlers as well. Think of it as an industry-strength inflatable lifeboat, but with a solid, seaworthy frame. The seating area is centralized with raised sides and strategic guardrails. This helps the boat sit lower and safer inside the water.
11. Catamaran Hull (Multi-Chined)
While pontoons are built for slow freight, catamarans are built for speed. Both these boats have multi-chined hulls. But while the tubes on pontoons have a rounded bottom, the hard chines on catamarans are V-shaped and sometimes have sharper anglers for swifter sailing.
These boats have a massive footprint. But because of the shape and alignment of the hull, they don’t have as much storage space as pontoons. They also have to be carefully designed to ensure stability. This is why catamarans have large masts and sails to balance the boat.
The apparatus also helps you control the boat. Catamarans are preferred by seafarers who prize seamanship. Playing with those swirling ropes and heavy fabrics is both a science and an art, so catamarans are primarily used for competitive analog sailing on rough oceans.
Technically, jet skis or personal watercraft (PWCs) aren’t boats. But they use the same principles and are fitted with a V-bottom planing hull and a pressure jet engine. These jet ski hulls have extra parts to facilitate speed and stability as you ride the waves. They include:
- Chines – these angles can be soft or hard, but they’re always V-shaped.
- Strakes – smaller ridges that enhance the lift for smoother planing.
- Sponsons – side fins that help the jet ski balance better.
- Steps – ledges at the bottom of the hull to reduce drag.
PWCs rely on your balance and confidence. Their hulls are designed for maximum lift, sensational planing, dramatic turns, and extreme speed. The hull angle is sharper at the front than the back. It’s described as a modified V-hull, with all its extra edges and ledges.
With all these boat hull types available, it’s easy to get them mixed up! Here are some hints:
- Displacement hulls sit lower and move slower.
- Planing hulls sail faster and float higher.
- Flat, round, and S-hulls can be manual.
- V-bottoms and multi-chine hulls need engines.
- Sharper hulls use sails for extra control and balance.
- Hybrid hulls have a narrow front and a wide back.
- Pontoons emphasize buoyancy and floating power.
- Hard chines have acute angles while regular chines slop gently.
What type of hull do you have on your latest boat? Show us some photos in the comments!
Related posts:
- Do You Wear Socks With Boat Shoes?
- Wake Boat Vs. Ski Boat: What’s the Difference?
- 6 Simple Steps to Tie A Boat To a Dock Cleat
- Hydraulic Vs. Mechanical Boat Steering: Which Is Better?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More.
Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
- Catamaran Interviews
- Catamaran Reviews
- Buying Advice
- Selling Advice
- Woods Design Advice
- Americat 3014
- Balance 526
- Bali 40 Catspace
- Beneteau Blue II
- Broadblue 346
- Broadblue 38 Prestige
- Broadblue 385
- Broadblue 435
- Broadblue 46
- Catalac 10M
- Catalac 11M
- Catalac 12M
- Catalac 900
- Catana 42 S
- Chris White 48 Voyager
- Chris White 55
- Corsair F28 R
- De Villiers
- Dolphin 460
- Endeavour 30
- Endeavour 35 Victory
- Endeavour 36
- Endeavour 44
- Endeavour 44 TrawlerCat
- Fortuna 36 Island Spirit
- Fortuna 401 Island Spirit
- FP 32 Maldives
- FP 35 Tobago
- FP 37 Antigua
- FP 38 Athena
- FP 39 Fidji
- FP 40 Lavezzi
- FP 40 Lucia
- FP 40 Summerland MY
- FP 41 Lipari
- FP 42 Astrea
- FP 42 Venezia
- FP 43 Belize
- FP 44 Helia
- FP 44 Orana
- FP 46 Bahia
- FP 46 Casamance
- FP 48 Salina
- FP 56 Marquises
- FP 57 Sanya
- FP 60 Eleuthera
- FP Saona 47
- Gemini 3000
- Gemini 3200
- Gemini 3400
- Grainger 420 Mystery Cove
- Hirondelle 7M
- Lagoon 37 TPI
- Lagoon 42 TPI
- Lagoon 43 PC
- Leopard 39 PowerCat
- Leopard 45 Classic
- Leopard 47 PowerCat
- Leopard 51 PowerCat
- Leopard 53 PowerCat
- Maine Cat 30
- Maine Cat 41
- Matrix 450 Vision
- Matrix 760 Silhouette
- Maverick 400
- Maverick 420
- Maverick 440
- Nautitech 40
- Nautitech 442
- Nautitech 46 Open
- Nautitech 47
- Outremer 40
- Outremer 45
- Outremer 50 Standard
- Outremer 55
- Privilege 37
- Privilege 39
- Privilege 42
- Privilege 43
- Privilege 435
- Privilege 45
- Privilege 465
- Privilege 48 Transcat
- Privilege 482
- Privilege Serie 5
- Prout 31 Quest
- Prout 33 Quest
- Prout 34 Event
- Prout 35 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose Elite
- Prout 38 Manta
- Prout 39 Escale
- Royal Cape 45
- Royal Cape 530 Majestic
- Royal Cape Majestic 500
- Sailcraft 30 Iroquois
- Sailcraft 32 Comanche
- Sailcraft 35 Cherokee
- Sailcraft 41 Apache
- Sailcraft 44 Apache
- Wildcat 350
- Seawind 1000
- Seawind 1160
- Seawind 1200
- Seawind 1260
- Seawind 1600
- Solaris 36 Sunrise
- Solaris 36 Sunstar
- St Francis 44
- St Francis 48
- St Francis 50
- Stealth 11.8
- Heavenly Twins 26
- Ocean Twins 38
- Voyage 380 Maxim
- Voyage 400 Norseman
- Voyage 430 Norseman
- Voyage 450 Cabriolet
- Voyage 47 Mayotte
- Wharram 38 Tiki
- AMI 320 Renaissance
- Woods 22 Wizard
- Woods 35 Banshee
- Woods 35 Flica
- Woods 36 Scylla
- Woods 36 Vardo
- Woods 38 Transit
- Woods 40 Meander
- Xquisite X5
- Xquisite X5+
Catamaran Design Formulas
- Post author By Rick
- Post date June 29, 2010
- 10 Comments on Catamaran Design Formulas

Part 2: W ith permission from Terho Halme – Naval Architect
While Part 1 showcased design comments from Richard Woods , this second webpage on catamaran design is from a paper on “How to dimension a sailing catamaran”, written by the Finnish boat designer, Terho Halme. I found his paper easy to follow and all the Catamaran hull design equations were in one place. Terho was kind enough to grant permission to reproduce his work here.
Below are basic equations and parameters of catamaran design, courtesy of Terho Halme. There are also a few references from ISO boat standards. The first step of catamaran design is to decide the length of the boat and her purpose. Then we’ll try to optimize other dimensions, to give her decent performance. All dimensions on this page are metric, linear dimensions are in meters (m), areas are in square meters (m2), displacement volumes in cubic meters (m3), masses (displacement, weight) are in kilograms (kg), forces in Newton’s (N), powers in kilowatts (kW) and speeds in knots.
Please see our catamarans for sale by owner page if you are looking for great deals on affordable catamarans sold directly by their owners.
Length, Draft and Beam
There are two major dimensions of a boat hull: The length of the hull L H and length of waterline L WL . The following consist of arbitrary values to illustrate a calculated example.
L H = 12.20 L WL = 12.00

After deciding how big a boat we want we next enter the length/beam ratio of each hull, L BR . Heavy boats have low value and light racers high value. L BR below “8” leads to increased wave making and this should be avoided. Lower values increase loading capacity. Normal L BR for a cruiser is somewhere between 9 and 12. L BR has a definitive effect on boat displacement estimate.
- Tags Buying Advice , Catamaran Designers

Owner of a Catalac 8M and Catamaransite webmaster.
10 replies on “Catamaran Design Formulas”
Im working though these formuals to help in the conversion of a cat from diesel to electric. Range, Speed, effect of extra weight on the boat….. Im having a bit of trouble with the B_TR. First off what is it? You don’t call it out as to what it is anywhere that i could find. Second its listed as B TR = B WL / T c but then directly after that you have T c = B WL / B TR. these two equasion are circular….
Yes, I noted the same thing. I guess that TR means resistance.
I am new here and very intetested to continue the discussion! I believe that TR had to be looked at as in Btr (small letter = underscore). B = beam, t= draft and r (I believe) = ratio! As in Lbr, here it is Btr = Beam to draft ratio! This goes along with the further elaboration on the subject! Let me know if I am wrong! Regards PETER
I posted the author’s contact info. You have to contact him as he’s not going to answer here. – Rick
Thank you these formulas as I am planning a catamaran hull/ house boat. The planned length will be about thirty six ft. In length. This will help me in this new venture.
You have to ask the author. His link was above. https://www.facebook.com/terho.halme
I understood everything, accept nothing makes sense from Cm=Am/Tc*Bwl. Almost all equations from here on after is basically the answer to the dividend being divided into itself, which gives a constant answer of “1”. What am I missing? I contacted the original author on Facebook, but due to Facebook regulations, he’s bound never to receive it.
Hi Brian, B WL is the maximum hull breadth at the waterline and Tc is the maximum draft.
The equation B TW = B WL/Tc can be rearranged by multiplying both sides of the equation by Tc:
B TW * Tc = Tc * B WL / Tc
On the right hand side the Tc on the top is divided by the Tc on the bottom so the equal 1 and can both be crossed out.
Then divide both sides by B TW:
Cross out that B TW when it is on the top and the bottom and you get the new equation:
Tc = B WL/ B TW
Thank you all for this very useful article
Parfait j aimerais participer à une formation en ligne (perfect I would like to participate in an online training)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Parts of Catamaran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Components
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 2, 2023 | Sailboat Racing

Short answer: The key parts of a catamaran include the hulls, bridgedeck, mast(s), rigging, sails, rudders, and daggerboards. These components work together to provide stability, propulsion, and control for this type of multi-hulled watercraft.
Exploring the Essential Parts of a Catamaran: A Comprehensive Guide
From cruising the open seas to enjoying lazy afternoons by the shore, catamarans have become a popular choice for water enthusiasts. With their unique design and exceptional stability, these vessels offer an unmatched sailing experience . But have you ever wondered what makes up a catamaran and how each part contributes to its overall functionality? In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the essential parts of a catamaran, uncovering their purpose and shedding light on why they are instrumental in making these boats such fantastic options for adventure seekers.
1. Hulls: The hulls are the twin structures that form the main body of a catamaran. These structures play a pivotal role in providing stability and buoyancy while at sea. Catamarans boast wider hulls compared to traditional monohull sailboats, resulting in increased surface area and enhanced stability. The design allows for smoother sailing even in rough waters, as each hull slices through waves independently.
2. Keels: Unlike monohull sailboats that rely solely on a single keel positioned beneath the waterline for both lift and resistance against sideways drift (known as leeway), catamarans often feature two separate skegs or keels attached to each hull. These auxiliary structures enhance directional control and offer excellent stability while reducing drag.
3. Deck: The deck is where all the action takes place! It serves as the primary horizontal surface on which passengers can relax, sunbathe or engage in various activities while aboard the vessel. Catamaran decks usually come with ample space due to their wider design compared to monohull sailboats .
4. Trampoline: One of the standout features of a catamaran is its trampoline – a mesh-like netting stretched between the two hulls just above sea level. While it may seem like an unconventional addition, trampolines provide multiple benefits including giving passengers an exhilarating sensation as they sit or lay above the water. This ample recreational area additionally offers an unobstructed view of the sea, making it an ideal spot for stargazing or simply enjoying the soothing sound of the waves.
5. Cockpit: The catamaran’s cockpit is strategically positioned closer to the waterline, ensuring a thrilling and immersive sailing experience. It acts as the primary control center where the helm is located, allowing sailors to expertly navigate their vessel through various seascapes. Additionally, some catamarans offer spacious cockpits that provide sufficient seating capacity for socializing with fellow passengers or hosting intimate gatherings while at anchor.
6. Rigging: The rigging refers to all lines, cables, and hardware necessary for controlling and adjusting the sails . Catamarans typically employ a simple yet effective rigging system that ensures easy maneuverability and efficient sailing performance. By skillfully managing these components, sailors can harness wind power optimally and maintain smooth cruising speeds in any weather conditions.
7. Sails: Sails are central to a catamaran’s propulsion system, enabling it to move gracefully across bodies of water without relying on fuel-based engines alone. Modern catamarans often embrace a sail plan consisting of multiple sails designed to maximize efficiency and adapt seamlessly to varying wind strengths and directions. With innovative designs such as fully battened mainsails and lightweight genoas, these boats have become incredibly agile even when faced with challenging wind patterns.
8. Engines: While a catamaran’s sails provide a significant portion of its power source, auxiliary engines are still crucial for many aspects of sailing life – be it docking in tight spaces or maneuvering during low-wind situations. These engines are usually mounted within each hull beneath deck level as part of an integrated propulsion system comprising shafts, propellers, and operational controls.
9. Navigation Instruments: In today’s era of advanced technological aids, catamarans make use of a range of navigation instruments to enhance safety and efficiency. From GPS systems providing precise positional information to depth sounders measuring water depth, these sophisticated tools are essential for ensuring smooth journeys and avoiding potential hazards.
So there you have it – a detailed glimpse into the essential parts of a catamaran. Wherever your sailing adventures take you, now you can fully appreciate how each component contributes to the incredible performance and unrivaled experience offered by these magnificent vessels. So hop aboard a catamaran and embark on your next nautical journey with confidence!
How to Identify and Understand the Various Components of a Catamaran
Catamarans are fascinating vessels known for their unique design and exceptional performance on the water. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or just interested in learning more about these incredible boats, understanding their various components is essential . In this blog post, we will take a detailed, professional, witty, and clever dive into the world of catamarans and shed light on how to identify and understand their different parts .
1. Hulls: At the core of any catamaran are its hulls – the main supportive structures that keep the boat afloat. Unlike traditional single-hulled vessels, catamarans have two parallel hulls connected by a deck. These hulls play a vital role in providing stability and minimizing drag while sailing. Think of them as the sturdy legs that help the catamaran gracefully glide through the water .
2. Deck: The deck serves both as a platform for enjoying your time onboard and as an important structural element that connects various parts of the catamaran. It consists of multiple areas such as the helm station (where you control the boat), seating areas, dining spaces, trampoline nets for lounging, and storage compartments. Sunbathing or hosting friends for a sunset gathering? The deck has got you covered!
3. Rigging: If you’ve ever looked up at a sailboat’s mast with admiration, then you’ll love discovering how rigging contributes to a catamaran’s overall performance and elegance. The rigging includes all the supporting wires and ropes that hold up the mast(s) on your catamaran and control its position relative to wind direction (known as “trimming”). Understanding how to properly trim your sails can greatly enhance your sailing experience – from capturing optimal wind power to achieving picture-worthy maneuvers.
4. Sails: What could be more mesmerizing than watching billowing sails against an azure sky? Catamarans utilize various types of sails based on their purpose – mainsails, jibs, genoas, spinnakers – each designed to maximize performance under specific wind conditions. Learning about the different sails and their characteristics will help you navigate efficiently and make the most of your sailing adventures. Plus, understanding the art of sail trim is sure to impress your fellow sailors!
5. Rudders: Just as a captain relies on his or her compass for navigation, catamarans depend on rudders to steer through the water with precision. Mounted at the stern (rear) of each hull, these ingenious components allow you to control your course by diverting the flow of water passing beneath them. Rudders are essential for maintaining stability and maneuverability when tacking, jibing, or navigating challenging waters.
6. Engines: Catamarans aren’t solely reliant on wind power; they often incorporate engines as auxiliary means of propulsion. These mechanical marvels provide added security and flexibility during low-wind situations or when maneuvering in confined spaces like marinas or crowded anchorages. Understanding how to handle your catamaran’s engines confidently will ensure smooth sailing even when Mother Nature plays hard-to-get.
By expanding your knowledge about these various catamaran components – hulls, deck, rigging, sails, rudders, and engines – you’ll unlock a whole new level of appreciation for these magnificent vessels and gain confidence in navigating them.
Lastly, remember that wit and cleverness go hand-in-hand with professionalism when exploring any topic. So have fun while unraveling the mysteries of catamaran anatomy! Perhaps envision yourself as an expert sailor who can distinguish port from starboard blindfolded or sharpen your comedic skills by jokingly referring to hulls as “feline foundation” (though cats might not appreciate sharing their name with boats!).
Happy sailing!
Step-by-Step Breakdown: Unraveling the Mysteries behind Catamaran Anatomy
Catamarans have become increasingly popular in recent years, mainly due to their unmatched stability and impressive speed capabilities. But have you ever wondered what lies beneath the sleek exterior of these remarkable vessels? In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate details of catamaran anatomy, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how these boats are constructed and why they excel on the water.
1. The Hulls: The Foundation of Stability At the core of every catamaran lies its hulls – two parallel structures that run alongside each other. Unlike traditional monohull boats that feature a single hull, catamarans distribute their buoyancy across two hulls, offering superior stability even in rough waters. These hulls are typically made from fiberglass or aluminum and are designed to cut through waves effortlessly, minimizing resistance and maximizing speed.
2. Bridging the Gap: The Trampoline One striking feature present in many catamarans is the trampoline located between the two hulls. This sturdy mesh-like material serves various purposes. Firstly, it provides an additional platform for sunbathing or relaxing while underway. Secondly, it acts as a safety net by preventing crew members or passengers from falling into the ocean should any unexpected jolts occur during navigation .
3. Connecting Hulls: The Crossbeams In order to maintain structural integrity and connect both hulls securely, catamarans utilize crossbeams that stretch between them. These crossbeams play a vital role in sharing weight distribution evenly across both sides, ensuring stability and balance at all times.
4. Above Deck: Central Cockpit and Living Space Moving upwards onto the deck area, you’ll discover a central cockpit where most controls and steering mechanisms are located. This strategic placement allows for optimum visibility and easy maneuverability while sailing. Additionally, catamarans often feature large living spaces, including saloons and cabins that provide ample room for socializing, dining, and sleeping. Their spaciousness is a significant factor contributing to their growing popularity among cruising enthusiasts.
5. The Power of Sails: Rigging and Sail Plan Catamarans rely on sails for propulsion, utilizing a complex system of rigging to hoist and control them effectively. A unique feature of catamarans is the absence of a single mast; instead, they employ multiple masts strategically positioned between the hulls. This configuration optimizes sail area while reducing heeling (when a boat tips sideways due to windy conditions), resulting in smoother sailing experiences even during stronger winds.
6. Additional Features: Daggerboards or Foils To enhance performance further, some catamarans are equipped with daggerboards or foils – retractable appendages located beneath each hull. These boards reduce lateral slippage by providing lift, improving upwind capability and enhancing overall speed. As technology advances, advanced hydrofoil systems have also been introduced in certain catamaran models, allowing these boats to glide above the water ‘s surface entirely.
By unraveling the mysteries behind catamaran anatomy step-by-step, it becomes evident why these vessels are highly sought after by both leisure sailors and competitive racers alike. From their stable hull design to innovative features such as trampolines and foils – every element plays its part in creating an exceptional sailing experience that combines comfort, speed, and versatility. Perhaps now you can fully appreciate these engineering marvels whenever you set sight on one gliding gracefully through the waves!
Frequently Asked Questions about the Different Parts of a Catamaran Answered
Have you ever looked at a catamaran and wondered what all those different parts are called? Or maybe you’re thinking about buying or renting a catamaran and want to be familiar with its components . Well, look no further! We’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions about the different parts of a catamaran and will provide detailed, professional, witty, and clever explanations just for you.
1. What is a Catamaran? A catamaran is a type of boat that consists of two parallel hulls connected by a deck. It offers increased stability compared to traditional monohull boats due to the wider beam. This unique design allows for smoother sailing experiences and more spacious interiors.
2. Hulls – What Are They? The hulls are the main structure of a catamaran, providing buoyancy and supporting the entire vessel. Typically made from fiberglass or aluminum, they have curved shapes that help reduce resistance in the water while providing stability. Think of them as the legs of the feline-inspired boat!
3. Trampoline – Isn’t That for Jumping? While it may sound similar to the equipment used for bouncing around at your local playground, in the world of catamarans, trampoline refers to an open area between the hulls where passengers can relax or even stretch their sea legs! Made from durable materials like nylon mesh or PVC canvas, trampolines provide excellent circulation and an unobstructed view below deck.
4. Rigging – Is it Related to Sailing Techniques? Indeed! Rigging refers to all the elements involved in controlling sails on a catamaran . This includes mast(s), boom(s), standing rigging (shrouds & stays), running rigging (halyards & sheets), winches, cleats – basically everything needed to manipulate wind power efficiently and safely navigate through various conditions.
5. The Mast – How Tall Should It Be? The mast, often made of aluminum or carbon fiber composite, is the tall vertical pole that holds up the sails. Its height depends on several factors, such as boat size, intended use, and the desired sail area. Think of it as the catamaran’s lighthouse – guiding you along your aquatic adventures with grace.
6. Boom – Not Just a Sound Effect! Nope, not just an imitation of an explosion! The boom is a horizontal spar attached to the bottom of the mast, helping support and control the lower edge (foot) of the mainsail. It swings back and forth with changes in wind direction – think of it as a catamaran’s wagging tail!
7. Daggerboards – Are They Catamaran Ninja Weapons? While they may sound dangerous and ninja-worthy, daggerboards are actually retractable foils that extend from each hull into the water. Their purpose? Providing lateral resistance against sideways motion caused by wind force while improving upwind performance by reducing leeway – no martial arts skills required!
8. Rudders – Steering Like a Pro Like most boats, catamarans have rudders for steering purposes. These underwater blades at the stern help control direction by redirecting water flow around them when turned. Whether you’re tacking or gybing through waves or researching rudder-related puns like this one—we’ve got you covered.
So there you have it – frequently asked questions about the different parts of a catamaran answered in detail! Now you can impress your fellow sailors with your newfound knowledge or confidently embark on your next seafaring adventure aboard one of these sleek double-hulled vessels ! Remember to keep exploring and enjoy every nautical mile!
The Key Elements That Make up a Catamaran: Everything You Need to Know
Title: The Key Elements That Make up a Catamaran: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction: Catamarans have long fascinated sailing enthusiasts with their unique design, efficient performance, and spacious interiors. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or a curious novice, understanding the key elements that make up a catamaran is essential. In this enlightening article, we will delve into the intricate details of these remarkable vessels, uncovering the secrets behind their success on the open seas .
1. Hull Design: Stability Meets Speed At the heart of every catamaran lies its dual-hull structure. Unlike traditional monohulls, catamarans feature two separate hulls connected by a spacious deck. This design offers enhanced stability and reduced heeling, making them less prone to capsizing compared to their single-hulled counterparts. The inherent buoyancy allows for faster speeds and smoother sailing experiences—enabling both exhilarating adventures and relaxed cruising.
2. Beam: Embracing Extra Space One of the most significant advantages of a catamaran is its beam—the width between its two hulls—which can be quite impressive. The ample beam creates an exceptionally generous living area that sets catamarans apart from other sailboats . More space means greater comfort for passengers and crew alike; accommodating larger groups, luxurious amenities, and even personalized additions such as Jacuzzis or sunbathing decks.
3. Stability & Balance: A Steady Journey In addition to their unique structural design, catamarans offer exceptional stability through weight distribution and physics principles. With twin hulls spread apart at a considerable distance, it becomes significantly easier to maintain balance during sailing motions—a significant advantage for those susceptible to seasickness or seeking effortless navigation under challenging conditions.
4. Sailor-Friendly Handling: Ease-of-Use at Sea Catamarans excel in terms of maneuverability due to several factors working harmoniously together. Their shallow drafts allow for exploration in shallower waters, and docking becomes a breeze with the ability to navigate narrower marinas. Furthermore, their twin engines operate independently, offering excellent control even in tight spots or challenging wind conditions—a maneuverability dream for sailors of all skill levels.
5. Sailing Performance: Effortless Speed When it comes to performance on the water, catamarans stand tall once again. The efficiency gained from their two hulls reduces drag and enables quicker acceleration, resulting in higher average speeds than traditional monohulls. Even when faced with light winds, their ample deck space allows for customized rigging options—such as efficient sails or high-tech foiling capabilities—that can unlock extraordinary speed potential.
6. Comfortable Living Spaces: An Unprecedented Haven Catamarans redefine on-board living by providing both ample space and superior comfort. The expansive interior saloon offers panoramic views of the surroundings while being versatile enough to cater to various activities—from hosting lively social gatherings to peacefully reading a book by the window. Additionally, private cabins are often located in each hull, creating secluded sanctuaries for relaxation and tranquility amidst enchanting seascapes.
Conclusion: As we conclude our exploration into the key elements that make up a catamaran, it becomes evident why these vessels have become revered in the sailing world . The revolutionary dual-hull design ensures stability and faster speeds while offering unparalleled comfort and spaciousness aboard. Whether you seek adventure or serenity on the seas, understanding these elements will help you appreciate catamarans’ remarkable qualities truly—an embodiment of innovation and maritime excellence brought together harmoniously by human ingenuity.
Mastering the Parts of a Catamaran: A Beginner’s Guide for Sailing Enthusiasts
Are you a sailing enthusiast who is fascinated by the sleek and efficient design of catamarans? If so, then you’ve come to the right place! In this comprehensive beginner’s guide, we will delve into the key components of a catamaran and unlock the secrets to mastering its various parts. So grab your sailor’s hat and get ready to embark on an exciting journey through the intricate world of catamaran sailing!
The first component that sets a catamaran apart from other sailboats is its dual-hulled structure. Unlike traditional monohull sailboats, which have only one hull, catamarans feature two parallel hulls connected by a deck or bridge. This unique design grants them exceptional stability, speed, and even more interior space for amenities such as cabins and lounging areas.
Now let’s move onto a crucial part of any sailboat – the rigging . The rigging system on a catamaran consists of numerous elements that work harmoniously to control and manipulate the sails . Firstly, there are the masts: tall vertical structures that support the sails. Catamarans typically have two masts placed towards each end of the boat , allowing for efficient distribution of power.
Attached to these masts are various types of sails, including mainsails, jibs or genoas (fore-sails), and spinnakers (used for downwind sailing). The main sail is the largest sail on a catamaran and is hoisted up the mast using halyards – ropes specifically designed for this purpose. Jibs or genoas assist in maneuverability by generating additional power when sailing upwind.
For those seeking exhilarating downwind adventures, spinnakers add an extra element of thrill to your journey! These expansive triangular or bulbous-shaped sails catch wind from behind and propel your catamaran with remarkable swiftness. Learning how to handle these different types of sails will be crucial to seamlessly controlling the boat and maximizing performance on the water.
Next in line are the helm and steering system, responsible for guiding your catamaran ‘s path as it gracefully glides through the waves. The helm, often referred to as the steering wheel , is used to control the rudders located at each hull’s stern. One unique characteristic of catamarans is their tilting tendency caused by wind pressure acting upon the exposed surface area of their broad decks. Therefore, mastering steering techniques, including adjusting sail configurations and keel positions, will help you navigate with finesse and maintain balance.
One particularly innovative feature found in some catamarans is a daggerboard or a centerboard system. Located between the two hulls beneath the waterline, these retractable fins can be individually raised or lowered to vary their depth while sailing. By adjusting these boards according to wind conditions and point of sail , you can minimize resistance, optimize speed, and even prevent lateral drift.
We cannot overlook catamarans’ anchoring systems when discussing their components . Anchors are vital for keeping your vessel secure when moored or stopping for a leisurely swim in crystal-clear waters. Most modern catamarans employ bow rollers integrated at the front end that facilitate effortless anchor deployment and retrieval. With an array of anchor types available — from plows to flukes — it’s essential to understand each one’s characteristics in various seabed environments.
Lastly, let’s not forget about safety equipment onboard! While mastering catamaran parts allows for glorious adventures on calm seas, unforeseen challenges may arise during your sailing odysseys. It’s important always to have safety essentials like life jackets, fire extinguishers, first-aid kits, emergency flares, and navigational tools like GPS systems.
So there you have it – a comprehensive overview of key components necessary for mastering the art of sailing a catamaran! Understanding how each piece of the puzzle fits together and harmonizes uniquely will set you on a path to becoming a skilled catamaran sailor . Whether you’re gliding across tranquil bays or tackling exhilarating rough seas, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on unforgettable nautical journeys!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
- Pontoon Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- nauticalknowhow
- Nautical Knots
- Tools and Calculators
Understanding The Different Types Of Boat Hulls
Just as there are many different types of boats, there are just as many different types of boat hulls. They come in different sizes, different shapes, and every single one of them is a feat of design and engineering. Despite having so many different types of boat hulls to choose from, they’re only designed to do one of two things: displace water or plane on top of it.
Hulls that displace water are usually reserved for sailing boats, cargo ships, and cruise ships. They’re mainly used to pull heavier loads at slower speeds, and moving lower and slower in the water. Their hulls need to push a lot of water out of the way.
Planing hulls are built for speed. They’re most commonly found on smaller boats that don’t have tricky weight demands. These planing hulls are designed to rise out of the water as they reach higher speeds. Power boats and smaller watercraft are often equipped with planing hulls for these reasons.
Now that you know the two main styles of boat hulls available, let’s look at some of the more specific designs that you might see around the marina.
Types Of Boat Hulls
Vee bottom boat – The vee bottom tends to have a sharper entry into the water which provides for a smoother ride in rough water. They do, however, require more power to achieve the same speed. Many runabouts use the vee-bottom design. Some have a deep v for better performance.
Round bottom boat – These move easily through the water, especially at slow speeds. They do, however, tend to roll unless they are outfitted with a deep keel or stabilizers. Many trawlers , canoes and sailboats have round bottoms.
Multi-hull boat – Catamarans , trimarans, pontoon boats , and some houseboats use a multi-hull design. The wide stance provides greater stability. Each of the hulls may carry any of the above bottom designs.
Here’s a closer look at the two most common kinds of multi-hull boats.
Catamarans: These boats feature two separate hulls with a deck or a stretched material suspended between them. Having two hulls gives them great stability, and a lot more living and storage space compared with other vessels. Having two hulls makes them very stable on the water, reducing seasickness for the passengers. They also come equipped with two engines which makes them very easy to pilot. However, having two hulls means they have a wide footprint and require a lot of room to maneuver. They are very popular for charter use.
Trimarans: A trimaran is like a catamaran but it has three hulls instead of two! A typical trimaran has a main hull in the middle that’s flanked by two side hulls that keep the whole thing stable. These boats can be quite wide, though some have foldable arms that can make them smaller and easy to transport out of water. Most trimarans are sailboats, and they only require small engines for propulsion thanks to their smaller profile.
What About Those Funny Shapes On The Hull?
These funny shapes are strakes and chines. The strakes are the strips that stretch across a boat’s hull from the front to the back. They’re almost always found on planing boats. The reason for this is that these little strips can help lift the front of a boat out of the water, reducing drag, and increasing speed. Most modern boats with a planing hull will have them
What’s interesting is that they are also beneficial to a boat’s stability and passenger comfort. These strakes can help to soften the impacts made when a boat charges through a choppy wave. They also help deflect any spray from the water back towards the sea rather than up into the cockpit. Finally, they also act like little flat bottom hulls in places to boost stability.
The bigger folds that you see in a boat’s hull are chines.
Chines are the folds you see where a boat’s hull meets the sidewall. Kind of. Under normal circumstances, they don’t do much. However, some boat designers have exaggerated the fold to further assist a boat from lifting out of the water. Some chines are quite large, and these help a boat remain stable when at rest. The chines act like flat-bottom hulls, which can help fishing boats stay stable when an angler walks from one side to another. They can also reduce rolling motions and improve maneuverability in some cases.
Which Boat Hull Design Is Best For You?
Different hull shapes will suit different boaters . Here’s a quick rundown of which hull types work best for different pursuits.
Speed Enthusiasts
For real speed enthusiasts, there are two ways you can go. Flat-bottom boats can work very well on flat, calm water such as a lake or river. Unfortunately, flat-bottoms aren’t so great at speed if the water is a little choppy. That’s when a deep v hull design will help. Out on the ocean, a deep v is the best way to go faster without getting thrown around by rough waves.
For fishing, the best choice of boat hull will largely depend on what conditions you’re fishing in…and what you’re fishing for. An angler casting for perch will have different needs to an Ahab harpooning a whale! Freshwater fishermen can get away with a shallow hull bass boat, while deep-v or catamaran vessels will work better on the coast. Even better, some anglers might prefer a pontoon fishing boat , or even an inflatable kayak instead.
Sports Junkies
Wakeboarders and waterski enthusiasts will need a special modified-V boat shape to get the best performance for their sport of choice. There are plenty of different modified shapes to choose from, specially crafted for different sports, different waters, and different equipment needs.
Casual Boaters
For casual boaters looking for leisurely family outings, then a v-shaped hull will offer the best level of versatility and practicality. You’ll be able to enjoy a gentle put around a lake or explore your nearest coastline without having to worry whether your boat is capable enough. Then again, if you’re only after a casual boat that you only use now and again, a sturdy inflatable boat might be a better option , and more cost-efficient too.
About Chris
Outdoors, I’m in my element, especially in the water. I know the importance of being geared up for anything. I do the deep digital dive, researching gear, boats and knowhow and love keeping my readership at the helm of their passions.
Categories : Boats
Lilly Margolis on December 16, 2019
We are doing the Multi-hull boat
Luka Nash on August 13, 2020
Thanks I am making a reciyled boat and it is powered by a Sphero Thanks so much again
Harri on November 5, 2022
Is that fixing fishing boat with trimaran effect its required speed
carter on November 9, 2022
can you do more about flat bottom and start doing wide bottom boats and what ones can carry heavy cargo please?
Mark DeChambeau on November 30, 2022
I want to design and perhaps build my own rowing/sailboat. I’ve always liked the whaleboat form as a good compromise between stability and maneuverability. Also, I’m simply enamoured of its form. Do you have any thoughts on how or even whether to proceed in this direction? I appreciate your time.
logan moore on September 8, 2023
Thanks i am going to make a flat boat and a multihull boat (alone): I am very excited to make the boat.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More in Boats

What Is A Gunwale?

131 of the Best Hawaiian Boat Names

167 Patriotic Boat Names

The 138 Best Boat Names for Dog Lovers

The People’s Poncho Review and Ratings

Oru Lake Kayak Review

About Boatsafe
Established in 1998, BoatSafe is your independent guide into the world of boating, fishing, and watersports. We provide expert insights and detailed guides to help you find products tailored to your needs and budget.
Contact Boatsafe
- Address: 4021 West Walnut Street. Rogers, AR 72756
- Phone: (479)339-4795
- Email: [email protected]
Site Navigation
- How We Test
- Corrections Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Editorial Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure
Our Reviews

All content is © Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.

Main Types of Catamarans Used in the Shipping World
A catamaran is a boat with two hulls instead of a monohull which the traditionally designed sailing boats have. They were designed to be fishing boats though their use has increased today. Generally, they have more interior space, saloons and cabins than a conventional sailing vessel.
The following points will enable us to understand the boat and its types clearly.
Origin of Catamarans/Cats
The fishing community ‘Paravas’ in Tamil Nadu first created the catamaran in the 17 th century. The main feature of these boats was that they had two hulls which offered a lot of stability and balance compared to the other fishing boats of that era. This concept of two-hulled boats was adopted by the British and then made famous across the world.
Present-Era Cats
In the present times, cats have evolved from being mere sailboats or fishing boats. There are two basic design types of catamarans: Pontoon and SWATH (Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull).
The former is relatively small, compact and uses floats (known as pontoons in marine slang) as a major technology to propel the water along with the dual hulls. In contrast, the latter is quite large and is designed primarily to maintain balance in sea areas with unpredictable currents and tides.
It has to be noted that in today’s times, all variations of catamarans are made of fiberglass or carbon fiber. They are motorised and engine-powered, making them even more reliable than they used to be before.
Physical Characteristics of Cats
Generally, charter catamarans have twin engines, one in each hull to manoeuvre. It also has a mast that supports the mainsail and another for the headsail. Power cats are an example of innovation, offering the best experience.
Power cats or multi-hull powerboats have large engines and no masts or sails. Their powerful motors give them high speeds, and their reinforced hull types handle their weight. Their demand is growing daily, and they are available in many stylish designs. Another feature of cats is that they can go into shallower waters, as they don’t have deep keels.
Catamaran sailboats have a minimum sail area of 470 square feet and a maximum of 2260 square feet. Some famous builders are Robertson and Caine, Lagoon, Seawind, Fountaine Pajot, Gemini and Leopard. They make catamarans with secondary inboard, outboard, electric and other propulsion systems in diesel, gas, and other fuel systems. Custom-made catamaran sailing vessels are a speciality of the Privilege Shipyard. Usually, the vessel’s average capacity depends on its size. Some can carry about 16 to 60 people.
These new vessels are sought for their rich legacy, greater draft and wide beam, which make them excellent for overnight cruising and day sailing.
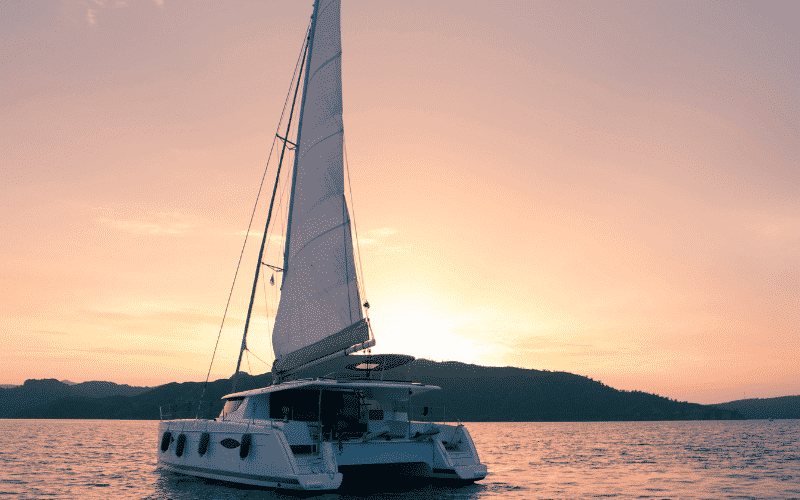

Some of the main types of catamarans can be elaborated as follows:
Cruise Catamarans
These catamarans are also known as luxury catamarans or ferry catamarans. This is because they offer the best possible luxury to the passengers who take a trip in such ferries. And the addition of engines has made such ferries even more attractive to the crowd.
Also, the space between the two hulls is filled by a cockpit, a main cabin and netting for relaxing in the sun. Their size and stability is the reason for their popularity. With two hulls, there is enormous space on a catamaran above and below the decks, which provides comfort on sailing vacation. Hence, they are preferred by vacationers for their unique characteristics.

They also offer great speed, which ensures that the passengers get the cruise trip of their choice without any lapse in time. It has to be noted that luxury catamarans operate not internationally between nations but internally within a country.
Some popular cruise catamarans worldwide are the Stena Voyager (operating in the Irish Sea) and Victoria Clipper IV (operating between Seattle and Victoria in the USA).
Sailing Catamarans
Catamaran sailing is another type and utility of a catamaran. Sailing catamarans are used for recreational purposes by people who want to experience the life of a sailor.
Catamaran sailing does not involve any place for residing in the boat. In other words, catamaran sailing can also be referred to as catamarans used as yachts .
The average speed achieved in a day in a sailing catamaran is up to 300 nautical miles. Such catamaran sailing was first introduced in Europe though it has started gaining popularity worldwide.
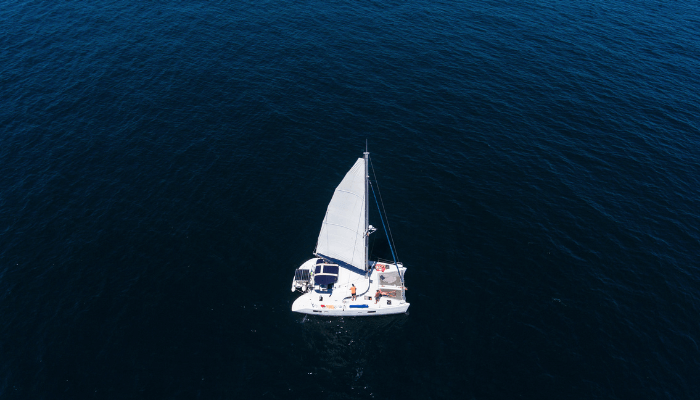

It has to be noted that catamarans are quite novel in their creation and development. Unlike other boats, they have not become inoperative or extinct.
Their name still commands unique respect, making a catamaran adapt more successfully to the changing era and times .
Frequently Asked Questions About Catamarans
1. what are catamarans used for.
Catamarans are a preferred option for day sailing, cruising, fishing etc. Many boat charter companies offer their customers yachts, motor yachts and catamarans. Though their design dates back 100 years, the updated and technologically updated catamarans have a massive demand in the sailing market.
2. What are the disadvantages of catamarans?
Catamarans are 150 to 200 per cent more expensive than yachts of the same length. Also, special marinas are built for these vessels due to their width. Also, they are costlier to maintain and repair than other similar vessels.
3. What is the speciality of catamarans?
Catamarans offer more stability as they have two hulls, which decrease the chances of people falling overboard. They are larger and more comfortable than normal sailing boats, not to forget their eye-catching designs.
4. Do they have washrooms?
Today, catamarans have all amenities, including saloons, seating areas, well-fitted washrooms and plenty of interior space. Also, during bad weather, they can be steered from inside.
5. What is the lifespan of a catamaran?
On average, a catamaran can last for 15 to 25 years and even 30 years if it is well-kept and maintained. Its lifespan also depends on the usage, type, quality of construction material etc.
You might also like to read
- L-Cat: A Multi-Purpose Supply Catamaran
- The Devil Cat: The Devilishly Fast Wave Piercing Catamaran
- Unique Catamarans: The Afai 08
- What is a SWATH Ship?
- Types of Sailboats – A Comprehensive Classification
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used in the article, have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction

Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories

About Author
Zahra is an alumna of Miranda House, University of Delhi. She is an avid writer, possessing immaculate research and editing skills. Author of several academic papers, she has also worked as a freelance writer, producing many technical, creative and marketing pieces. A true aesthete at heart, she loves books a little more than anything else.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Marine Insight Daily Newsletter
" * " indicates required fields
Marine Engineering
Marine Engine Air Compressor Marine Boiler Oily Water Separator Marine Electrical Ship Generator Ship Stabilizer
Nautical Science
Mooring Bridge Watchkeeping Ship Manoeuvring Nautical Charts Anchoring Nautical Equipment Shipboard Guidelines
Explore
Free Maritime eBooks Premium Maritime eBooks Marine Safety Financial Planning Marine Careers Maritime Law Ship Dry Dock
Shipping News Maritime Reports Videos Maritime Piracy Offshore Safety Of Life At Sea (SOLAS) MARPOL
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2023 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety

Six Amazing Boat Hull Designs
- By Dean Travis Clarke
- Updated: October 25, 2016

The American boating consumer bears a remarkable psychological profile when it comes to wants and needs.
A cursory glance at the lines of most boats proves that profiles haven’t changed dramatically over the past 60 or so years. Certainly, construction methods such as resin infusion and injection molding have altered business as usual, and ingredients have also changed to include all manner of space-age composites, epoxies, paints, computer mapping for engines that produces vastly greater horsepower from smaller blocks, and so on. Even propulsion has changed with the advent of pod drives and big outboards. But here’s the weird part: Any time a designer or builder introduces a model that looks significantly different, whether it is Euro-styled or functionally clunky, it fails. It doesn’t matter how well the boat performs, the typical boater rejects it because it doesn’t look like what he knows. We, as an enthusiast niche involving boats, are horribly set in our aesthetic ways.
Look at how well multihulls handle heavy seas. When it comes to seakeeping ability, efficiency and performance, the catamaran has a lot going for it, as anyone who happened to catch some of the most recent America’s Cup racing can attest. And yet, to date, production multihulls have enjoyed only moderate acceptance by boaters.
Here are six of the latest hull-design innovations and technologies being used elsewhere in the maritime world that we will likely never accept for our recreational boats — even though they all work well.

Wave-Piercing Hulls Most accounts cite wave-piercing technology as coming on the scene around the start of the 20th century. However, it has been employed as far back as the times of the Phoenicians and ancient Romans. The design concept consists of a bow with little buoyancy, a hull that slopes inward from the waterline and, ergo, a large reduction in wave-making resistance. While it works well in heavy seas, the drawbacks include reduced interior volume forward and a very wet ride because the waves come up and over the bow as a matter of course. Wave piercers fell out of favor for a period of time due to these same drawbacks but have recently enjoyed a resurgence of popularity because of their dramatic fuel-efficiency gains.

Stepped Hulls OK, this hull form has achieved a certain level of acceptance in our recreational boats, mostly in performance boats or offshore center consoles. But why isn’t it more popular? The stepped bottom has been around as a V-bottom refinement since at least 1912. Steps are grooves in the hull stretching outward from the keel to the chines. Most hulls sport one or two steps per side. And a vessel should really be capable of cruising in excess of about 30 knots for a stepped hull to be worthwhile. Steps work by allowing air to be “injected” against the running surface, breaking contact between part of the hull and the water, which in effect turns the running surface into numerous short, wide planes, rather than one long, narrow one.
How much the hull surface contacts the water directly determines the amount of drag a hull suffers. Steps (also called vents) decrease the amount of hull contacting the water (called the wetted surface), thereby decreasing drag, increasing speed for the same horsepower, and increasing fuel efficiency. It all sounds good. But steps also come with potential drawbacks. Though modern deep-V designs have enough deadrise to counteract the problem in most cases, stepped hulls have been known to suffer from transom slide in sharp turns at speed. They also require attention to loading and trim because the steps need the proper angle of attack to function correctly; they don’t offer an advantage in flat, calm water; and they require a special trailer.
Most owners of stepped-hull vessels are experienced and want to travel at high speeds in moderate to heavy seas, and/or achieve good economy and range. Yet to date, performance and center console builders aside, only Regal Boats, with its FasTrac hulls, and Formula have committed to using steps in production cruisers and sport boats.

Asymmetrical Twin Hulls This unique design concept comes from the drawing board of Larry Graf, the pioneer who put power catamarans on the map here in the U.S. when he founded Glacier Bay Boats in 1987. His new company, Aspen Powerboats, employs a cat design where one hull is narrower (35 percent) than the other. His patent calls it a Power Proa, and it relies on a single engine in only the wider of the two hulls. The hull shapes, alignment and placement compensate for the offset propulsion thrust, allowing the vessel to run straight and true. With only one set of running gear in the water, inherent appendage drag is reduced by 20 percent. Combined with the efficiency of the hull designs, overall fuel efficiency of the Aspen rises to an impressive 70 percent over monohulls of comparable size. Aspen won an award for the best 30- to 39-foot catamaran in the world in 2014.

SWATH A quick glance might lead you to believe that a SWATH (small waterplane area twin hull) vessel is a catamaran. And it is but only to the extent that it has two hulls in the water with a bridge across the top. But that’s where the hulls’ similarities end.
Consider a submarine. Once under the surface, it runs stable, with no roll or pitching from wave action. All that wave energy remains on the sea surface. That basically explains how a SWATH design functions.
If you’ve ever dived under a wave at the beach to avoid being smacked by it, you know that the water beneath the wave is calmer. SWATH minimizes a vessel’s volume where the water meets the air (which is where all the wave energy is at its peak). The bulk of the vessel’s displacement and buoyancy runs beneath the waves, affording amazing stability, even in big seas and at high speeds. Please think of high speeds as a relative term here, as this is not a planing hull. What SWATH does provide, however, are a wide, stable deck and unsurpassed ride quality, especially in rough seas.
Drawbacks to SWATH designs include the fact that each hull must be custom designed. Draft runs deeper than standard hulls (especially planing hulls). The underwater “torpedoes” providing buoyancy must run parallel to the water’s surface, which requires a fairly complex trim-control system. And the underside of the deck must be far enough above the sea surface to avoid waves slamming up into it. Finally, SWATH vessels cost more to design and build than conventional hulls.

Hydrofoils Once the strict province of commercial ferries and a few high-speed military vessels, the most recent America’s Cup has spurred hydrofoil acceptance to new heights. Will it catch on with powerboats?
The hydrofoil design acts exactly like an airplane wing, providing more lift than the drag coefficient the vessel produces, thereby lifting the entire hull out of the water. Only the hydrofoils remain in the water, unaffected by surface wave action. In fact, hydrofoils cut inherent resistance to zero while the hull is out of the water. In the case of power-driven boats, you still suffer drag from the propulsion system (prop, shaft or the like).
The most significant disadvantage to this system on recreational boats is definitely the deployment of the foils. Unless you want the added draft of these struts sticking down below your hull all the time, you must be able to extend and withdraw them — a complex engineering feat. There is at least one recreational powerboat employing hydrofoils: Twin Vee builds a catamaran with foils that don’t actually lift the hulls completely out of the water. It does improve fuel economy and ride stability nonetheless. Still, boats ride more smoothly in a sea and go much faster with hydrofoils. With the dramatic acceptance of this technology in sailing, is it only a matter of time before recreational powerboats incorporate foils into their designs?

Ulstein X-Bow The Norwegian Ulstein Group has been designing offshore vessels since 1917. Presently, it has the notoriety of creating the most advanced bow design in history. The Ulstein X-Bow looks like it might be upside down, but it’s proven itself in more than 100 offshore support vessels to date. The X-Bow allows higher speeds and smoother rides in even the worst seas. Gone are the slamming and vibration that occur when the bow of a ship drops off a wave. It functions better on all points of sea, and its lower hydrodynamic drag substantially decreases fuel consumption. The X-Bow has proven so successful that Ulstein is in the process of creating an X-Stern design now.
You won’t ever see this on small recreational boats, but you can nod knowingly when someone points one out on a mega-yacht in the near future.
- More: Boats

Boat Test: 2024 Tidewater 3100 Carolina Bay

Boating On Board: Boston Whaler 365 Conquest

Boat Test: 2024 Bayliner Trophy T23 Pilothouse

Boat Test: 2024 Nuova Jolly Prince 33 CC

What to Do if Your Boat’s Engine Dies

ProTournament Elite Gen 3 Chargers

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
- HELP ME TO CHOOSE THE PERFECT BOAT!
- +44 20 3769 3987
More results...
- Mediterranean
Indian-ocean
- Atlantic Europe
Pacific-ocean
- Catamaran charter
- Motor yacht charter
- Sailboat charter
- Gulet charter
- Luxury yacht charter
- 12 person boat rental
- 20 person boat rental
- 60 ft yacht charter
- Last-minute yacht charter
- Early booking yacht charter
- Bareboat yacht charter
- Crewed yacht charter
- Cabin yacht charter
- Flotilla sailing
- Easy sailing destinations
- Experienced sailing destinations
- Culture sailing destinations
- Family sailing holidays
- Honeymoon yacht charter
- Types of yachts
- Boat rental services
- Sailing routes, tours, trips, itineraries
"The best solution for your real time boat rental from experts you can trust!"
Types of catamarans
Destinations
- 7 14 21 28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 nights
Please select Sailing yacht Catamaran Motor yacht Motor boat Gulet Rubber boat (R.I.B.) Mini Cruiser Jet Ski
Home » Types of yachts » Types of catamarans

This article will introduce the following:
The origins of the catamaran
Why is a catamaran a good choice, types of catamarans: catamarans may be categorized as follows, before you start…, how to rent a catamaran.
Catamarans were first built-in the 17th century by a fishing society called the Paravas in Tamil Nadu on the Northern shores of India. At first, the idea of two hulls was objected to by yacht manufacturers who had been used to models that have a single hull. Still, catamarans proved to have the best design amongst rapid vessels. This was due to their great stability and capacity. The main feature of these boats was the two-hulled design, which provided for more effective balance compared to other vessels of the era. The idea was first adopted by the British, and later it became widespread in the whole world. Evolution not only resulted in a change in relation to use but influenced and developed the designing and construction of boats to a great extent.
Types of catamarans: Design of catamarans
We distinguish between two types of catamarans in terms of design: the so-called Pontoon and the SWATH (Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull). The former is a small and compact boat that applies a floating technique in order to drive the two hulls. The latter is a large vessel which uses a method based on preserving the balance of the boat. They are ideal for areas where erratic waves are common. These larger types may be categorized as yachts. Today, a wide selection of catamarans are available, for instance, the motorized types, which are even more reliable.

Catamarans are available in several designs and sizes. Their size may vary, from 14 ft (4.5 m) to 100 ft (30.5 m) long models. Catamarans include sea cruisers with a weather deck, boats with cabins, etc. Besides the two hulls, they have a mast and, depending on the size, one or two sails. It may be a surprising fact that catamarans are considered standard yachts rather than sailboats.
Cruise catamarans
These boats are referred to as luxury catamarans or catamaran ferries. They provide the best service and luxury for passengers. The additional motors make these boats even more attractive for people. Having a shorter journey time, these ferries are ideal for passengers who want to spend more time in a city’s port. It must be noted, however, that luxurious catamarans only function within the country and not internationally. Catamaran cruisers offer all the best features of motor yachts. The Stena Voyager on the Irish Sea and the American Victoria Clipper IV are two of the most popular cruisers.
Sailing catamarans

Choose a route and get to know the destination better before leaving the port! Read the guides, search for information about a route or contact the charter agency which will provide you with recommended routes in a graphical form. When choosing a route, take into consideration the duration of your rental, and plan your programs accordingly! We recommend cruising for 3–6 hours a day while taking into account the fuel consumption that depends on the weather, and the size and type of the boat.
Boat rental is not as complicated as it first seems, especially if you have a good agent. There are always some basic questions arising during the rental process. The service provider can help you plan your cruising adventure. We have collected all the necessary information to make the process easier for you.
- First, you have to decide what type of boat you would like to rent. Certain models of catamarans are ideal for the whole family. This kind of journey can be a real adventure for the kids; a great example of active recreation.
- The number of people and the requirements for their comfort, the services provided on the deck and the need for a staff should all be considered.
- Make sure that you understood all the conditions and have received all the necessary information, including the duration, type and price of your rental.

Safety first!
Sibenik - Croatia
wir durften vom 19.06. bis zum 26.06.2021 zum zweiten Mal einen wunderschönen Urlaub auf einer BoatTheGlobe-Yacht genießen.Mit dem wunderschönen Bali...
Anna und Günter (Austria)
Caorle - Italy
Amazing Luigi was a fantastic host, accessing all areas of the yacht. The deck was comfortable with lots of space to relax and sunbathe and drink in the amazing...
Sebastian (Belgium)
Ibiza - Spain
Very Impressed with the quality of service. We had a small malfunction of one of the yachts that we had on our charter and they repaired it right away. They truly went...
Mike (South Africa)
HELP ME TO CHOOSE THE PERFECT BOAT
Need to find the right boat with the help of an expert send us your needs and we will find the most suitable yacht for you we offer only boat rentals, 1-day cruises not.
- press the right mouse button on the e-mail received from us
- select the following from the options: Add sender to list of safe senders.
More information on our privacy policy and personal data protection .
BoatTheGlobe
"The best solution for your real time boat rental from experts you can trust!"
- Indian Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Sailing in … Sailing intineraries, ports, coasts & islands
Not to be missed!
Subscribe to our newsletter to be the first to know about discounted boat rental options!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Catamaran Hulls Performance . Thanks to the catamaran hulls, the boat offers many advantages over other boat types. Stability. Because its dual-hull design provides a broader base, it offers more water stability than monohull boats. It makes the cat (catamaran) a popular choice for fishing expeditions and cruises.
If you have fine hulls you can use a lower Cp. Most monohulls have a Cp of 0.55- 0.57. And that is about right for displacement speeds. However the key to Catamaran design is you need a higher Cp if you want to sail fast. So a multihull should be at least 0.61 and a heavy displacement multihull a bit higher still.
All modern production catamarans are made with "FRP" construction (for Fiber Reinforced Polymer). Composites aren't new-it's just using materials together to strengthen the whole assembly. Straw was added to bricks centuries ago, and steel reinforced concrete is a staple of construction over the last century.
There are five common boat hull types: Round-bottomed hulls - handle well in rough water: sailboats. Flat-bottomed hulls - very stable for calm inland waters: fishing boats. Multihulls - very stable and buoyant: catamarans. V-Shaped Hulls - fast and comfortable in chop: powerboats.
To determine which type of catamaran boat is right for you, we've simplified the most popular choices into four basic categories that encompass the most popular types of catamarans. ... Due to their two-hull design they offer increased stability in terms of side-to-side motion, or rolling, which is common in large swells. Most modern high ...
Perhaps the most popular multi-hulled boat is the catamaran. This type of boat has two separate hulls that run parallel to each other. These hulls sit on either side of the boat and the deck connects them. This type of design allows forecast amounts of space onboard. Many catamarans are luxury boats that can have the space to hold swimming ...
Typically modern catamaran designs have sharp bows to drive the vessel through the seas with as little wave making as possible. High freeboard assures a dry ride. ... Similarly, the narrow asymmetrical type hull, such as found in the Hobie 16 beach catamaran, is hardly used in today's cruising multihull. The idea was to keep the underwater ...
A 16-passenger catamaran is a type of boat or vessel specifically designed to carry 16 people comfortably. Catamarans are multihull boats with two parallel hulls, which are connected by a deck or a structure. ... No, the hull floor of a catamaran is not always on the waterline. The design of a catamaran allows for the hulls to be elevated above ...
This twin-hull design often results in a wider beam, creating an inherently stable platform. While they boast a shallower draft compared to monohulls, ... Types of Catamarans. If we list out the types of catamarans, you'd encounter various classes tailored to different sailing needs. You have your cruising catamarans, spacious and comfortable ...
Design Dynamics. Amultihull, just as any other type of boat, presents a series of compromises, and this applies to overall hull, deck and configuration as well. Concessions often have to be made because of space, performance or construction costs. In addition, the intended usage will be a significant factor in determining the shape and size of ...
6. Multi-Hull (Catamaran and Trimaran) Designs. Multi-hull designs refer to boat or watercraft designs that feature two or more hulls instead of a single hull. The two most common types of multi-hull designs are catamarans and trimarans. Catamarans: Catamarans have two parallel hulls connected by a deck structure.
Overview of Boat Hull Types. First off, let's look at the broad hull divisions. They can be categorized by: Form e.g. hard chine, soft chine, smooth chine. Displacement e.g. full displacement, planing, semi. Shape e.g. s-bottom, v-bottom, rounded, flat. These categories overlap a lot. For example, a v-bottom hull is sometimes described as a ...
T c = 0.57. Here we put B TR = 1.9 to minimize boat resistance (for her size) and get the draft calculation for a canoe body T c (Figure 1). Midship coefficient - C m. C m = A m / T c (x) B WL. We need to estimate a few coefficients of the canoe body. where A m is the maximum cross section area of the hull (Figure 3).
1. Hull Design: Stability Meets Speed At the heart of every catamaran lies its dual-hull structure. Unlike traditional monohulls, catamarans feature two separate hulls connected by a spacious deck. This design offers enhanced stability and reduced heeling, making them less prone to capsizing compared to their single-hulled counterparts.
Dual Hull Design. A catamaran is a type of boat that features a dual hull design. Unlike traditional boats that have a single hull, a catamaran consists of two parallel hulls that are connected by a deck or platform. This unique design offers several advantages over monohull boats, including increased stability, speed, and spaciousness.
Hull Types. When it comes to how a yacht performs, handles, and takes on the seas, it's what lays beneath the waterline that really counts. Most modern yachts utilize one of these five basic hull designs: Deep-V; Displacement; Flat Bottom Boats; Power Catamarans; Semi-V; Deep-V Hulls
They do, however, tend to roll unless they are outfitted with a deep keel or stabilizers. Many trawlers, canoes and sailboats have round bottoms. Multi-hull boat - Catamarans, trimarans, pontoon boats, and some houseboats use a multi-hull design. The wide stance provides greater stability.
There are two basic design types of catamarans: Pontoon and SWATH (Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull). The former is relatively small, compact and uses floats (known as pontoons in marine slang) as a major technology to propel the water along with the dual hulls. In contrast, the latter is quite large and is designed primarily to maintain balance ...
Hull designs for boats typically serve one of two purposes: displacement or planing. Explore the variety of boats hull shapes in this article. ... Each of the hulls in a multi-hull design may be any of the above types. Catamarans are boats with two hulls that are linked in the center by a deck or other stretched material. They're inherently ...
When it comes to boat hull types, design is crucial. Whether your boat has a large or small engine, one berth or a dozen cabins, a gourmet galley or a one-burner stove, there is nothing that will enhance your boating experience more than the design of your hull. ... Catamarans: two hulls bridged by a deck. Chines and strakes: moulded strips ...
Asymmetrical Twin Hulls Aspen Power Catamarans. Asymmetrical Twin Hulls This unique design concept comes from the drawing board of Larry Graf, the pioneer who put power catamarans on the map here in the U.S. when he founded Glacier Bay Boats in 1987. His new company, Aspen Powerboats, employs a cat design where one hull is narrower (35 percent ...
Types of catamarans: Catamarans may be categorized as follows. Catamarans are available in several designs and sizes. Their size may vary, from 14 ft (4.5 m) to 100 ft (30.5 m) long models. Catamarans include sea cruisers with a weather deck, boats with cabins, etc. Besides the two hulls, they have a mast and, depending on the size, one or two ...
This type of hull is often also called a "double hull kayak," "tunnel hull," "dual hull design" or "catamaran hull kayak.". This kayak hull type prioritizes stability, at the expense of speed and maneuverability. Like a pontoon boat, a pontoon hull kayak is designed to sit flat on the water and resist rocking from side to side.