Yachting World
- Digital Edition


Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 7: should the worst happen – with Nigel Irens
- Belinda Bird
- October 1, 2015
Capsize is very unlikely in most modern catamarans, but should the worst happen it is as well to be prepared, says Nigel Irens
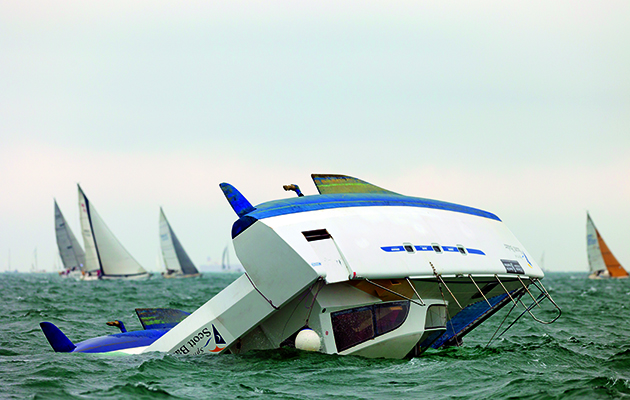

Photo: David Harding

The first thing to say is that as a general rule floating home-type catamarans are, in principle, less likely to be at risk than those designed with performance in mind.
That said, before making such a sweeping statement it’s important to mention that the level of risk involved is much more about the skill and experience of the skipper than about the qualities of the boat on which he or she goes to sea.
Over the years buyers of catamarans have tended to go more and more for the model with enhanced accommodation space (and de facto diminished performance). The bottom line is that in sailing on most ‘charter spec’ catamarans you’d have to be trying hard to win a bet to bring about a capsize.
Building catamarans down to a budget often seems to result in under-sizing of deck gear so that powering up the rig is not really possible. This really is not intended as a criticism – just a reflection on the real-life economics of this market.
If these factors combine make such a catamaran very hard to capsize then this could surely be perceived as a positive result.
Once the discussion turns from the prevention of capsize to the reality of it information and advice is not readily available. There are two different areas that need to be addressed.
The first is about actually surviving the incident in the short term. The second assumes you have managed to do that and is about surviving life on an upturned boat while summoning some help as soon as possible.
Rule one is that if you are on the inside of the boat you should immediately get away from the bridgedeck and head for one or other of the hulls as fast as possible. That’s easier said than done because you’ll be disorientated – especially if it’s dark outside and any lights inside won’t last long.
At the very least if sailing in challenging conditions (especially on a performance boat) it makes sense to bed down between watches in a hull rather than in the central saloon.

Not likely in a cruising cat!
The reasoning is that the boat is unlikely to be supported by the roof for very long when inverted and as she settles down in the water the bridgedeck will soon be close to the water, making an exit attempt risky – especially if there are warps washing around the cockpit.
Stay below if possible
As the hulls themselves are by definition watertight the boat will be buoyant enough to float with (at worst) the threshold of the companionways into the hulls at the surface.
It’s important not to rush for the escape hatch (fitted to the inboard side of each hull) because, although it provides a useful source of light, opening it will let some of the air that’s supporting the boat out of the hull, causing it to float lower in the water.
It is probably best to wait and take stock of the situation – together with anyone else who is in the same hull – and maybe wait for daylight if the capsize has happened at night. Try to find out if others are outside – or perhaps in the other hull.
If, on balance, the decision is taken to leave the hull then it is important to make a plan that results in the hatch being open for as short a time as possible.

Catamaran escape hatch
Clearly if the level of seawater inside the hull is high it is not going to provide a suitable environment for survival while waiting for assistance, so exit is the only option. If on the other hand it is only knee deep then the hull may be the place to stay.
Once again good planning for the worst before going to sea is the way to go and there is plenty of information available about that.
Discussion and planning
As part of the preparation for these dire circumstances it is important to have had a frank discussion about this whole scenario with the supplier of the boat. Has anyone ever capsized this particular design before, and what was learned from that?
Comparing the relative dangers of being at sea in a catamaran that could capsize with those of being in a monohull that could sink has always been a source of lively debate.
The truth is that there are now (and there have always been) risks in going to sea in any vessel. Our best hope in minimising that risk is to face the subject full-on and become as well informed as possible.
Man overboard
While discussing safety issues in the context of catamaran sailing we should take a brief look at that other seafarer’s nightmare – losing a man overboard.
All the normal recovery procedures apply to a catamaran with regard to the all-important location of the casualty, but there are some important differences in the way the approach is made for the recovery.
Because of the high windage of a catamaran and relatively small amount of lateral resistance under the water you can assume that, as you slow the boat down to attempt the pick-up, you’ll make a huge amount of leeway. As a result if you approach to windward of the casualty there is a real danger that the casualty’s legs will be carried under the leeward hull – with a real risk of serious injury from the propeller.

Because of high windage it can be a problem approaching a casualty in the water
To be absolutely safe from this peril just keep to leeward of the casualty. Of course this means that, despite you best efforts, you could pass too far to leeward and won’t be able to get a line to them.
A good way to avoid this problem is to motor at maybe two to three knots across the wind trailing a long line behind the boat (from the leeward stern). You should aim to pass at least 10m to windward of the casualty – which should be easy to judge because you have enough speed to have good steerage way.
Because the casualty will need to hang onto this line it should be easy in the hands – a 14-16mm 8 plait nylon mooring line or similar would be ideal.
When the casualty is directly to leeward of you turn sharply downwind, making a 180° turn that leaves you passing safely to leeward. Slow down at this point, being careful not actually to go astern and risk getting the line around the leeward propeller.
If all goes well the bight of the rope will now be encircling the casualty and at some point he or she will be able to grab hold of it.
From now on you shouldn’t need to engage the drive to either propeller. Keep the helm to leeward and the boat should lie with the wind somewhere on the quarter. If you’re moving too fast – making things difficult for the casualty – you could transfer the line to the bow so that the drag of towing will tend to make the boat round up somewhat – you should be able to control the angle at which the boat lies to the wind by moving the attachment point of the rescue line to different points along the sheer.
If all goes according to plan you should be able to haul the casualty in to the windward quarter of the boat, where they can use the emergency boarding ladder.
If they are not up to that then it should be possible to pass them another rope with a bight in the end of it big enough for them to pass it over their shoulders and under their arms so that they can be hauled aboard.
Do’s and don’ts
- DO take positive action to wise up on the risk of capsize on the catamaran you sail. Asking difficult questions of boat suppliers and collecting opinions from other owners are all valid.
- DO develop some kind of basic plan for the worst case – such as impressing on crew that if below in high-risk conditions then being in the hulls is much safer than being on the bridgedeck. In the case of a man overboard do always make the pick-up from a position downwind of the casualty.
- DON’T take the word of some designer who’s never capsized as gospel – ferret around online and find out what conclusions people who have actually been there have drawn from their experience.
- DON’T risk sailing in bad weather until you have plenty of experience with the boat in more moderate conditions.
- DON’T even think of steering by autopilot when in potentially dangerous conditions. Many accounts of capsize reveal that there was no one on the helm at the critical moment.
- DON’T make a meal of all this. Capsize is very unlikely in most cruising catamarans, but it does happen occasionally so, as with most seamanship issues, the smart move is to be on top of the subject and prepared for the worst.
Our eight-part Catamaran Sailing Skills series by Nigel Irens, in association with Pantaenius , is essential reading for anyone considering a catamaran after being more familiar with handling a monohull.
Part 8: the future of catamaran cruising
Series author: Nigel Irens
One name stands out when you think of multihull design: the British designer Nigel Irens.
His career began when he studied Boatyard Management at what is now Solent University before opening a sailing school in Bristol and later moving to a multihull yard. He and a friend, Mark Pridie, won their class in the 1978 Round Britain race in a salvaged Dick Newick-designed 31-footer. Later, in 1985, he won the Round Britain Race with Tony Bullimore with whom he was jointly awarded Yachtsman of the Year.
His first major design success came in 1984 when his 80ft LOA catamaran Formule Tag set a new 24-hour run, clocking 518 miles. During the 1990s it was his designs that were dominant on the racecourse: Mike Birch’s Fujicolour , Philippe Poupon’s Fleury Michon VIII , Tony Bullimore’s Apricot . Most famous of all was Ellen MacArthur’s 75ft trimaran B&Q, which beat the solo round the world record in 2005.
His designs have included cruising and racing boats, powerboats and monohulls, but it is multis he is best known for.
See the full series here
A special thanks to The Moorings, which supplied a 4800 cat out of their base in Tortola, BVI. www.moorings.com
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the foremost international magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have practical features to help you plan and prepare to realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge month by month with a subscription delivered to your door – and at a discount to the cover price. S ee our latest offers now.

Why Catamarans Capsize, A Scientific Explanation (For Beginners)
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
When people see a catamaran, many think of capsizing, which has proven to be a way less common event than your average forum thread would lead you to believe. This article will use a scientific approach to look at the data available for stability incidents with catamarans.
This article is based on a study made by the UK government concerning recommendations for regulating catamarans. I have used that knowledge to discuss some of the common misunderstandings considering catamaran stability. Let’s get to the short answer!
A Catamaran will capsize when rotational forces overcome the stability of the boat. Capsizing can happen in two ways, either the ship overtakes a wave and sinks it bows into the next one, inducing something called pitch-poling. Or a breaking wave, with the same height as the boat’s length, hits the vessel’s side, making it roll over to its side(a.ka. flipping).
Are you like me and need to understand why? Read on!
What Does It Mean to Capsize?
In the context of boats, to capsize means to flip the boat upside down unintentionally.
On a small dingy, it is part of the sailing experience, and the boat can quickly be righted, but on a cruising cat, it can be the difference between life and death.
This can happen in numerous ways that will be discussed in great detail below. The most common is a combination of high seas, strong winds, and sailor error.
Not only is it dangerous to be in the middle of the sea stuck on what has now become a very expensive chunk of plastic, but the act of capsizing is also hazardous. Depending on where you are, inside, outside, or in one of the hulls, you may face the risk of getting thrown overboard, stuck in a hull upside down in the dark, or getting hurt by flying objects.
Much of the discussion around capsizing and what to do after it has happened is theoretical. In this article, I will show you the science behind catamaran stability and how that interacts with the power of the sea.
Why Does a Catamaran Capsize?
Catamaran stability can sometimes be a little tricky to understand. To get us off to a good start, here is some terminology that will be useful;
- Wind heeling moment is the effect wind has on the rotational(heeling) movement of the boat.
- Apparent wind angle is the angle of the wind when the boat is moving; this can differ from true wind, which is measured in a fixed position.
The study reaches a couple of conclusions, some of which are of interest to this discussion.

Heeling Is Greatly Dependent on Apparent Wind Angle and Sheeting of the Sails
This means that a catamaran (or any other sailboat, for that matter) will have a greater rotational force if the sails are sheeted in hard. This is because the wind gets “caught” in the sails, and the forces act directly on the sails, mast, standing rigging, and onto the hulls.
If, instead, the sails were loosened or “sloppy,” the amount of wind “caught” would be less, and therefore, more wind would be able to pass around the sails, thus decreasing the heel.
When it comes to apparent wind angle, the study shows that the forces are most significant when the wind is forward of the beam. This is primarily due to the aerodynamic effectiveness decreases aft of the beam.
Large Waves From the Side or Aft
Large waves are always a factor con safety at sea; they can be divided into breaking waves, waves whose amplitude (basically when waves get so big that they start coming apart(breaking) reach a threshold where the shape of the waves suddenly changes.
The other category is non-breaking waves or rolly waves. These are more gentle and cannot change shape in a violent and uncontrolled manner.
The study concludes that (1)catamarans have less roll response than monohulls during non-breaking waves, which means a catamaran will generally follow the motion and wave shape as it goes up and down it in a predictable manner, and that (2) this behavior shows no indications of being dangerous.
A monohull will instead rock from side to side and show a pendulum-like behavior.
On the other hand, breaking waves pose a real threat and are something to be aware of if traveling on a smaller catamaran. The test showed that a sufficient beam-to-wave ratio is needed to avoid capsizing.
A common beam-to-length ratio is 50%; that is, the length of the boat is at least double the size of its width.
Together with wind forces, breaking waves seem to be the most significant factor affecting the risk of capsizing.
Breaking waves with a height equivalent to the beam of a catamaran, half the beam of a trimaran may be sufficient to cause a capsize. Smaller or narrower yachts are, therefore, more vulnerable.
What makes breaking waves dangerous is their ability to bring the boat past its tipping point (or range of stability); much of this is due to the steepness of the wave. A 30ft non-breaking wave will act as a rolling hill in the English countryside, while a 15ft breaking wave is more of a black slope in a French ski resort.
The closer a boat comes to its tipping point, the less energy is needed to move past it. This is why the combination of factors is essential, large breaking waves, high apparent wind forward of the beam, and a minor error from the cockpit, and disaster is around the corner.
Effect of Keels (Daggerboards, Centerboards)
When a catamaran is hit with a breaking wave from its side, one factor that reduces rotational forces is the ability to move sideways with the wave, in other words, to slide sideways.
Usually, this is not wanted since it reduces the cat’s ability to go windward; this issue is sometimes addressed by adding mini keels, dagger, or centerboards.
The issue with keels is that the crew cannot withdraw them into the hull to reduce drag; this means that they can become a security issue when hit by large breaking waves to the side. It will hinder the sideways sliding actions and increase the risk of capsizing, as the study indicates.
Here’s an article I wrote comparing daggerboards to centerboards .
Placement of Weight (Vertical Center of Gravity, Vcg)
We have already discussed the importance of having a big enough beam to create sufficient stability. Moving the hulls wider apart will lower the center of gravity (or center of weight) and increase stability; this is true if all other factors are the same.
I f we move the hulls closer to each other, the catamaran becomes narrower, and the center of gravity will move upwards. What happens then? You guessed it, removing the wide base makes it less stable and more prone to heeling.
The same effect can be had by moving weight on the ship vertically (VGC); lower = more stable, and vice versa (a monohull moves it below the surface using a heavy keel).
Pitchpoling (Frontflip)
Pitchpoling is when a catamaran sails with the winds and waves, and the speed of the boat increases to levels above the wave speed. When this happens, there is a risk that the catamaran will semi-surf down the wave and hit the next one. This will slow the boat down, increase apparent wind, and create a rotational force that will make the boat invert if big enough.
Pitchpoling can happen in two ways, symmetrically or asymmetrically. According to the testing in the study, it is more common for one of the bows to dig down into the water and then diagonally flip.
Factors That Affect Pitchpoling
To increase the rotational forces needed for pitchpoling to happen, the center of weighing needs to be shifted aft. This means that a catamaran that is improperly balanced, for example, the bows filled with gear instead of empty, will increase the risk of burying the bows and potentially flipping over. More on weigh issues below!
Another way to offset your balance is to allow water inside the bows; this can happen after repeated slamming of waves onto the hatches. Once filled up, they can hold tons of water and be a severe threat due to buoyancy loss and shift in the center of weight.
Surfing a wave is cool, but it is much safer to lower the speed through reefing early; this reduction in speed makes it less likely to sail into the next wave or trough and risk pitchpoling.
If the boat speed is still too high, the next option is to deploy a drogue that will break the boat and add some directional stability. If this, for some reason is not possible, the study suggests that the vessel should hit the waves head-on.
What is a drogue?

Trampolines
We have already discussed the issue of burying the bows; the effect is massively increased with a solid deck that almost makes the boat into a spoon(a terrible thing if you do want thousands of kilos of water onboard). A better way to dissipate water is with trampolines that lets the water through in a much faster way, like eating soup with a fork.
The effect of having trampolines is twofold; firstly, it will reduce the time the bows are submerged. Secondly, it will decrease the weight of the water on top of the bows and, therefore, how deep the bows will dive.
What is a trampoline on a catamaran?

Hull Shape and Freeboard
There is a discussion that too narrow hulls can increase pitchpoling risk since the hulls might easier dive into the water. I understand the logic, but I am unavailable to find any data to support that claim.
You could also make the claim that wider hulls would increase the braking effect and therefore add to rotational forces. As said, we need more data on this!
Freeboard is the distance between the water and the deck; the bigger this is, the less chance of burying the bows, and vice versa. Same here, It makes sense logically, but there are little data to understand what is enough freeboard.
Real Cases of Catamarans Capsizing
Some news sites have reported on catamarans flipping in different parts of the world. Unfortunately, there is not much data, so drawing well-grounded conclusions is hard.
The previously named study mentions only one report of a catamaran capsizing due to waves hitting its side precisely at the moment of breaking. The cat was 9 m long, and the owner had modified the boat by adding keels.
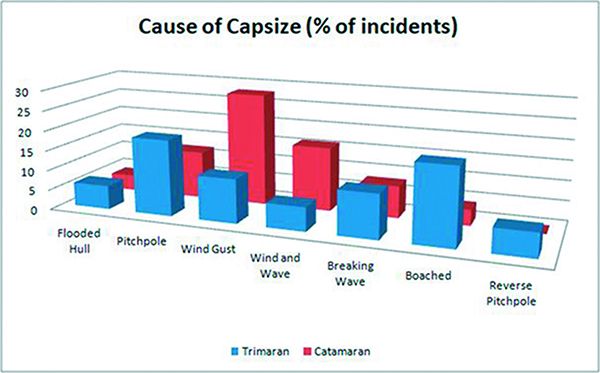
The study consists of a data set of over 120 incidents reported, of which only 33 are catamarans showing that catamaran capsizing is something very uncommon.
The reason for a catamaran sailboat capsizes;
- 28% Gust of wind
- 16% wave and wind
- 12% Pitchpoled
- 4% Braking Wave
It is also worth noting that most catamaran incidents happened in the range between 6-9 of wind force(Beaufort). Most incidents were on boats smaller than 11m.
News reporting and other articles
While researching this piece, I came across several relevant news articles regarding incidents and a few well-written case studies. I have incorporated these in this article as a point of discussion rather than factual claims. At the bottom of this page, you’ll find the links if you want to read the articles in full length.
2019 Australia, 39ft catamaran capsizes. The daggerboards can be seen and appear to be fully extended; considering the discussion above with keels, daggerboards will decrease the possibility of sideways movement even further. This is also indicated in the study.
There is a discussion on whether or not to leave one daggerboard deployed and one raised, but once again, the discussions of which one and when vary. And I have not been able to find any scientific support for these claims.
2010 Tonga, 57 ft Atlantic catamaran. The crew describes the situation to be very gusty, with winds up to 60kts! A full report on this incident would be very interesting and could really add to the knowledge database. 57ft is a huge ship, but a boat of this size also has a lot of sail area, and during this incident, the autopilot was steering the ship under reefed sails.
A ship of this size should be wide enough to be able to handle some very big waves, and it would be interesting to see whether the crew stuck to the wind charts. I think there is a lesson to be taught here on autopilot and being on the lookout for bad weather.
You should definitely be behind the helm if there is a squall coming so that you are ready to compensate for a change in wind pattern and quickly put in another reef if the initial assessment was wrong.
Chris White, the designer of Atlantic Catamarans shares his thought on this incident;
To summarize: 1) Neither captain thought capsize was even a possibility until way too late 2) Both boats were under autopilot, which had the helm all the way through the capsize 3) The main sheet was never eased or released Chris White of Chriswhitedesigns.com
Mythbusting!
The first part of this article takes its trustworthiness from a scientific study backed by the United Kingdom government; in this next section, I will use that knowledge to address some common myths and misconceptions.
A Charter Is Harder to Flip Than a Performance Cat.
As far as I understand, this argument is based on the following premises; the charter boat is heavier than the racing cat; therefore, it is more stable . As we have come to understand from above, it is a matter of total kilograms and where it is located.
A low and centered center of gravity means better stability. A cruising cat can easily be weighed in the wrong places due to all the extra gear that is usually brought along, such as generators or extra food for a long passage.
Moving the center of weight forward increases pitchpoling risk, and moving the weight up makes it vulnerable to breaching by breaking waves.
There is no need to believe a cruising cat is safer in that aspect inherently. Another common argument I hear is that the rigging would never be able to flip a fully loaded cruising cat since the standing rigging will break before lifting a hull.
What is standing and running rigging?
In theory, this might be true (I don’t have the data available), but in reality, this is certainly not the case; the data in the study clearly shows that catamarans can flip with their rigging intact.
Taking the combined factors of wind, waves, and the keels’ braking effect, there is not necessarily much force needed on the rigging for the boat to capsize. Yes (once again, in theory), a lighter catamaran will be easier to flip under some circumstances, but I would then argue that is more of a sailor error than due to the boat’s construction or weight.
Capsizing a Catamaran vs. Monohull
These two types of boats work in very different ways when it comes to stability; one significant factor is the ability of self-righting of a monohull due to its large and heavy keel.
On the other hand, the catamaran will stay bottom-up and mast down until intentionally righted by another ship.
Once the monohull starts leaning to its side, it will start to dissipate the pushing force that the wind acts upon the sails. This is an automatic way for a monohull not to become overpowered.
This lack of feedback (no or little heeling) on a catamaran means the sailor needs to rely on wind speed charts to tell him or her when to reef. If these charts are not followed, chances are the cat will get overpowered.
Another interesting aspect is that even though a catamaran is flipped upside down, it will still float due to the massive air compartments and low weight, something that a monohull will not. It will even stay afloat if there is a hole in one of the hulls.
What are the differences between monohulls and catamarans?
Catamarans Capsize More Often Than Monohulls
This is a wild debate in many online forums; some argue that it is less safe since it doesn’t have a keel, and some argue that I would rather be floating atop my inverted catamaran than alone in the middle of the ocean with a sunken monohull (while obviously totally missing the point of the discussion).
The truth is that there are no real data to back these claims, at least not that I am aware of. I have tried the insurance companies, but there doesn’t seem to be any big data available, only stories and myths.

The Skills of the Crew
When trying to avoid a catastrophe like a capsize, the most critical aspect is avoiding putting yourself in a bad spot, sailing above your skillset, and more winds and waves than the boat can handle.
This is evident, of course, but it is worth mentioning in detail what this actually means; planning to avoid bad weather and learning how to plan a sail safely and not rush is one of the best safety skills you can have. Once you’re out on the water, surprises will always come your way, so when that happens, use the radar to try to stay away and outrun the weather.
Outrun, you say, no boat is that fast. Well, the idea is to outrun it at an angle, not outrun it like Indiana Jones outruns a rolling stone. At least try to hit the part of the squall or bad weather with lower wind speeds.
Reef Often, Reef Early
Considering the data above, that most boats capsize during gusts of wind, there is a need to respect that data and make that old saying more accurate than ever. Reef early reef often. Make sure you turn off your autopilot; if there is a squall coming, you better be behind the helm to control your ship. Autopilot is stupid, your not!
Also, remember that reefing not automatically reduces speed!
As mentioned above, reducing sail area doesn’t necessarily reduce speed, but it reduces the area where the wind’s pushing can turn into rotational forces. Keep your speed so that you do not overtake the weaves and risk burying the bows.

Keels, Daggerboards, Centerboards
Before you decide on your standing operating procedures for heavy weather, make sure that you understand how your daggerboards will affect the boat handling. The research suggests that you might want to raise them, but make sure you understand why you do it and when.
Using fully deployed daggerboards while getting hit by a breaking wave to the side will increase the rotational force making a capsize more likely.
Heavy Weather Strategies
The boat’s performance is one thing; the crew’s skills are another; make sure you practice those skills and read up on the actual data that exists instead of reading too many forums and listening to know-it-alls. Ensure that your drills are based on science and not someone’s best guess! I encourage you to read the full article, it will be linked below, and go out there and look for more high-quality content.
- https://catamaranguru.com/top-6-characteristics-of-a-good-catamaran/
- http://www.wumtia.soton.ac.uk/sites/default/files/1441_merged.pdf
- https://shuttleworthdesign.com/NESTalk.html
- https://www.chriswhitedesigns.com/25-news/112-what-we-can-learn-from-anna-s-capsize
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250304001_Model_Tests_To_Study_Capsize_and_Stability_of_Sailing_Multihulls
News articles
- 2020 https://voilesetvoiliers.ouest-france.fr/securite-en-mer/disparition-en-mer/le-catamaran-hallucine-de-regis-guillemot-chavire-au-large-de-vigo-un-mort-trois-rescapes-491bc45c-237e-11eb-97e1-64af5fb563fa
- 2019 https://www.news.com.au/national/nsw-act/news/three-dead-two-rescued-after-catamaran-capsized-in-newcastle/news-story/8f94be3543c41368a4fd83b9b661033b
- 2010 https://www.chriswhitedesigns.com/25-news/112-what-we-can-learn-from-anna-s-capsize
- https://www.sailingtoday.co.uk/uncategorized/bullimores-33m-catamaran-capsized/
Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
2 thoughts on “ Why Catamarans Capsize, A Scientific Explanation (For Beginners) ”
Hi , Thanks for the advice, very good to know. Look forward to having a look at links. Best of luck on the trip, have fun. Mike
Thanks, Mike! Let me know if you have any other questions 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...

- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Hallberg-Rassy 42 Used Boat Review

Pearson 37 and 37-2 Used Boat Review

DIY Survey Checklist for Used-Boat Buying

Valiant 40: Reshaping the Cruising Hull

Best Crimpers and Strippers for Fixing Marine Electrical Connectors

Thinking Through a Solar Power Installation

How Does the Gulf Stream Influence our Weather?

Can You Run a Marine Air-Conditioner on Battery Power?

Practical Sailor Classic: The Load on Your Rode

Anchor Rodes for Smaller Sailboats

Ground Tackle Inspection Tips

Shoe Goo II Excels for Quick Sail Repairs

Dinghy Outboard Diagnostics

Spring Season Engine Start-Up for Winterized Engines

Solutions for a Stinky Holding Tank

Diesel Performance Additives

Vinyl Boat Lettering DIY Application and Repair

Those Extras you Don’t Need But Love to Have

Hidden Maintenance Problems: Part 3 – Gremlins in the Electrics

Three-Model BBQ Test

Alcohol Stoves— Swan Song or Rebirth?

Living Aboard with an Alcohol Stove

Preparing Yourself for Solo Sailing

How to Select Crew for a Passage or Delivery

Preparing A Boat to Sail Solo

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Chafe Protection for Dock Lines

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips
- Sailboat Reviews
Multihull Capsize Risk Check
Waves, squalls, and inattention to trim and helm contribute to instability..

In recent years we’ve seen a surge in interest in multihulls. Thirty years ago, when my experience with cruising multihulls began, nearly all of the skippers served an apprenticeship with beach cats, learning their quirks by the seat of their pants. They hiked out on trapezes and flew head-over-heels past their pitch-pole prone Hobie 16s, until they learned the importance of keeping weight way aft on a reach and bearing off when the lee bow began to porpoise.
By contrast, the new generation of big cat buyers skipped this learning process, learning on monohulls or even choosing a big stable cat as their first boat. Heck, nobody even builds real beach cats anymore, only pumped up racing machines and rotomolded resort toys. So we’re guessing there are a few things these first-time cruising multihull sailors don’t know, even if they have sailed cruising cats before.
It is extremely hard to capsize a modern cruising cat. Either a basic disregard for seamanship or extreme weather is required. But no matter what the salesman tells you (“none of our boats have ever …”), it can happen. A strong gust with sail up or a breaking wave in a survival storm can do it. And when a multihull goes over, they don’t come back.
Trimarans tend to be more performance oriented than catamarans. In part, this is because it’s easier to design a folding trimaran, and as a result Farrier, Corsair, and Dragonfly trimarans had a disproportionate share of the market.
In spite of this and in spite of the fact that many are raced aggressively in windy conditions, capsizes are few, certainly fewer than in equivalent performance catamaran classes. But when they do go over, they do so in different ways.
Trimarans have greater beam than catamarans, making them considerably more resistant to capsize by wind alone, whether gusts or sustained wind. They heel sooner and more than catamaran, giving more warning that they are over powered.
Waves are a different matter. The amas are generally much finer, designed for low resistance when sailing deeply immersed to windward. As a result, trimarans are more susceptible to broach and capsize when broad reaching at high speed or when caught on the beam by a large breaking wave.
In the first case, the boat is sailing fast and overtaking waves. You surf down a nice steep one, into the backside of the next one, the ama buries up to the beam and the boat slows down. The apparent wind increases, the following wave lifts the transom, and the boat slews into a broach. If all sail is instantly eased, the boat will generally come back down, even from scary levels of heel, but not always.
In the second case a large wave breaks under the boat, pulling the leeward ama down and rolling the boat. Catamarans, on the other hand, are more likely to slide sideways when hit by a breaking wave, particularly if the keels are shallow (or raised in the case of daggerboards), because the hulls are too big to be forced under. They simply get dragged to leeward, alerting the crew that it is time to start bearing off the wind.
Another place the numbers leave us short is ama design. In the 70s and 80s, most catamarans were designed with considerable flare in the bow, like other boats of the period. This will keep the bow from burying, right? Nope. When a hull is skinny it can always be driven through a wave, and wide flare causes a rapid increase in drag once submerged, causing the boat to slow and possibly pitchpole.
Hobie Cat sailors know this well. More modern designs either eliminate or minimize this flare, making for more predictable behavior in rough conditions. A classic case is the evolution of Ian Farrier’s designs from bows that flare above the waterline to a wave-piercing shape with little flare, no deck flange, increased forward volume, and reduced rocker (see photos page 18). After more than two decades of designing multihulls, Farrier saw clear advantages of the new bow form. The F-22 is a little faster, but more importantly, it is less prone to broach or pitchpole, allowing it to be driven harder.
Beam and Stability
The stability index goes up with beam. Why isn’t more beam always better? Because as beam increases, a pitchpole off the wind becomes more likely, both under sail and under bare poles. (The optimum length-to-beam ratios is 1.7:1 – 2.2:1 for cats and 1.2:1-1.8:1 for trimarans.) Again, hull shape and buoyancy also play critical roles in averting a pitchpole, so beam alone shouldn’t be regarded as a determining factor.
Drogues and Chutes
While monohull sailors circle the globe without ever needing their drogues and sea anchors, multihulls are more likely to use them. In part, this is because strategies such as heaving to and lying a hull don’t work for multihulls. Moderate beam seas cause an uncomfortable snap-roll, and sailing or laying ahull in a multihull is poor seamanship in beam seas.
Fortunately, drogues work better with multihulls. The boats are lighter, reducing loads. They rise over the waves, like a raft. Dangerous surfing, and the risk of pitchpole and broach that comes with it, is eliminated. There’s no deep keel to trip over to the side and the broad beam increases the lever arm, reducing yawing to a bare minimum.
Speed-limiting drogues are often used by delivery skippers simply to ease the motion and take some work off the autopilot. By keeping her head down, a wind-only capsize becomes extremely unlikely, and rolling stops, making for an easy ride. A properly sized drogue will keep her moving at 4-6 knots, but will not allow surfing, and by extension, pitch poling.
For more information on speed limiting drogues, see “ How Much Drag is a Drogue? ” PS , September 2016.
Capsize Case Studies
Knock wood, we’ve never capsized a cruising multihull (beach cat—plenty of times), but we have pushed them to the edge of the envelope, watched bows bury, and flown multi-ton hulls to see just how the boat liked it and how fast she would go. We’re going to tell you about these experiences and what can be learned from them, so you don’t have to try it.
First, it helps to examine a few examples of some big multihull capsizes.
Techtronics 35 catamaran, John Shuttleworth design
This dramatic pitchpole occurred in a strong breeze some 30 years ago. In order to combine both great speed and reasonable accommodation, the designer incorporated considerable flare just above the waterline, resulting in hulls that were skinny and efficient in most conditions, but wide when driven under water in steep chop.
The boat was sailing fast near Nova Scotia, regularly overtaking waves. The bows plowed into a backside of a particularly steep wave, the submerged drag was huge, and the boat stopped on a dime. At the same time, the apparent wind went from about 15 knots into the high 20s, tripling the force on the sails and rapidly lifting the stern over the bow. Some crew were injured, but they all survived.
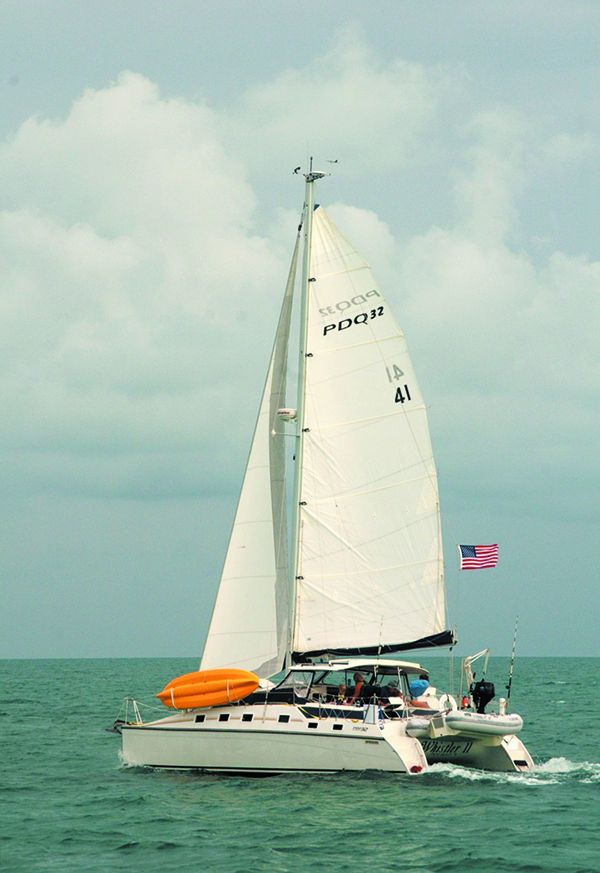
PDQ 32 Catamaran
On July 4, 2010, the boat’s new owners had scheduled time to deliver their new-to-them boat up the northern California coast. A strong gale was predicted, but against all advice, they left anyway. The boat turned sideways to the confused seas and a breaking wave on the beam capsized the boat. There were no injuries, and the boat was recovered with only moderate damage a few weeks later. Repaired, she is still sailing.
Another PDQ 32 was capsized in the Virgin Islands when a solo sailor went below to tend to something and sailed out of the lee of the island and into a reinforced trade wind.
Sustaining speed with wider tacking angles will help overcome leeway.
Cruising cats can’t go to windward. That’s the rumor, and there’s a kernel of truth to it. Most lack deep keels or dagger boards and ex-charter cats are tragically under canvassed for lighter wind areas, a nod to near universal lack of multihull experience among charter skippers. Gotta keep them safe. But there are a few tricks that make the worst pig passable and the better cats downright weatherly. Those of you that learned your craft racing Hobies and Prindles know most of this stuff, but for the rest of you cruising cat sailors, there’s some stuff the owner’s manual leaves out.
“Tune” the Mast
Having no backstay means that the forestay cannot be kept tight unless you want to turn your boat into a banana and over stress the cap shrouds. Although the spreaders are swept back, they are designed primarily for side force with just a bit of pull on the forestay. The real forestay tension comes from mainsheet tension.
Why is it so important to keep the forestay stay tight? Leeward sag forces cloth into the luff of the genoa, making it fuller and blunting the entry into the wind. The draft moves aft, the slot is pinched, and aerodynamic drag increases. Even worse, leeway (sideslip) increases, further increasing drag and sliding you away from your destination. Sailing a cruising cat to windward is about fine tuning the lift to drag ratio, not just finding more power.
How do you avoid easing the mainsheet in strong winds? First, ease the traveler instead. To avoid pinching the slot, keep the main outhaul tight to flatten the lower portion of the main. Use a smaller jib or roll up some genoa; overlap closes the slot. Reef if need be; it is better to keep a smaller mainsail tight than to drag a loose mainsail upwind, with the resultant loose forestay and clogged slot. You will see monos with the main twisted off in a blow. Ignore them, they are not cruising cats. It is also physically much easier to play the traveler than the main sheet. Be glad you have a wide one.
Check Sheeting Angles
Very likely you do not have enough keel area to support large headsails. As a result, you don’t want the tight genoa lead angles of a deep keeled monohull. All you’ll do is sail sideways. Too loose, on the other hand, and you can’t point. In general, 7-10 degrees is discussed for monos that want to pinch up to 40 degrees true, but 14-16 degrees makes more sense for cruising cats that will sail at no less than 50 degrees true. Rig up some temporary barber haulers and experiment. Then install a permanent Barber-hauler; see “ Try a Barber Hauler for Better Sail Trim ,” Practical Sailor , September 2019.
The result will be slightly wider tacking angles, perhaps 105 degrees including leeway, but this will be faster for you. You don’t have the same hull speed limit, so let that work for you. Just don’t get tempted off onto a reach; you need to steer with the jib not far from luffing.
Watch the fore/aft lead position as well. You want the jib to twist off to match the main. Typically it should be right on the spreaders, but that depends on the spreaders. If you have aft swept shrouds, you may need to roll up a little genoa, to 110% max.
Use your Tell-Tales
On the jib there can be tell-tale ribbons all over, but on the main the only ones that count are on the leech. Keep all but the top one streaming aft. Telltales on the body of sail are confused by either mast turbulence (windward side) or pasted down by jib flow (leeward side) and won’t tell you much. But if the leach telltales suck around to leeward you are over sheeted.
Keep Your Bottom Clean
It’s not just about speed, it’s also pointing angle. Anything that robs speed also makes you go sideways, since with less flow over the foil there will be less lift. Flow over the foils themselves will be turbulent. Nothing slows you down like a dirty bottom.
Reef Wisdom
Push hard, but reef when you need to. You will have the greatest lift vs. windage ratio when you are driving hard. That said, it’s smart to reef most cruising cats well before they lift a hull to avoid overloading the keels. If you are feathering in the lulls or allowing sails to twist off, it’s time to reef.

Don’t Pinch
Pinching (pointing to high) doesn’t work for cats. Get them moving, let the helm get a little lighter (the result of good flow over the rudder and keel), and then head up until the feeling begins to falter. How do you know when it’s right? Experiment with tacking angles (GPS not compass, because you want to include leeway in your figuring) and speed until the pair feel optimized. With a genoa and full main trimmed in well, inside tracks and modified keels, and relatively smooth water, our test PDQ can tack through 100 degrees with the boat on autopilot. Hand steering can do a little better, though it’s not actually faster to windward. If we reef or use the self-tacking jib, that might open up to 110-115 degrees, depending on wave conditions. Reefing the main works better than rolling up jib.
Boats with daggerboards or centerboards. The comments about keeping a tight forestay and importance of a clean bottom are universal. But the reduction in leeway will allow you to point up a little higher, as high as monohulls if you want to. But if you point as high as you can, you won’t go any faster than similar monohulls, and quite probably slower. As a general rule, tacking through less than 90 degrees, even though possible, is not the best strategy. A slightly wider angle, such as 100 degrees, will give a big jump in boat speed with very little leeway.
Chris White Custom 57
In November 2016, winds had been blowing 25-30 knots in stormy conditions about 400 miles north of the Dominican Republic. The main had two reefs in, and the boat was reaching under control at moderate speed when a microburst hit, causing the boat to capsize on its beam. There were no serious injuries.
Another Chris White 57 capsized on July 31, 2010. It had been blowing 18-20 knots and the main had a single reef. The autopilot steered. The wind jumped to 62 knots in a squall and changed direction so quickly that no autopilot could be expected to correct in time.
Gemini 105mC
In 2018, the 34-foot catamaran was sailing in the Gulf of Mexico under full sail at about 6 knots in a 10-15 knot breeze. Squalls had been reported on the VHF. The crew could see a squall line, and decided to run for cover. Before they could get the sails down, the gust front hit, the wind shifted 180 degrees, and the boat quickly went over.
38-foot Roger Simpson Design
The catamaran Ramtha was hit head-on by the infamous Queen’s Birthday storm in 1994. The mainsail was blown out, and steering was lost. Lacking any control the crew was taken off the boat, and the boat was recovered basically unharmed 2 weeks later. A Catalac catamaran caught in the same storm trailed a drogue and came through unharmed. Of the eight vessels that called for help, two were multihulls. Twenty-one sailors were rescued, three aboard the monohull Quartermaster were lost at sea.
15 meter Marsaudon Ts
Hallucine capsized off Portugal on November 11 of this year. This is a high performance cat, in the same general category as the familiar Gunboat series. It was well reefed and the winds were only 16-20 knots. According to crew, it struck a submerged object, and the sudden deceleration caused the boat to capsize.
Multihulls We’ve Sailed
Clearly seamanship is a factor in all of our the previous examples. The watch needs to be vigilant and active. Keeping up any sail during squally weather can be risky. Even in the generally benign tropics, nature quickly can whip up a fury. But it is also true that design choices can impact risk of capsize. Let’s see what the numbers can tell us, and what requires a deeper look.
Stiletto Catamaran
We’ve experienced a number of capsizes both racing and while driving hard in these popular 23-foot catamarans. The combination of light displacement and full bow sections make pitchpoling unlikely, and the result is very high speed potential when broad reaching. Unfortunately, a narrow beam, light weight, and powerful rig result in a low stability factor. The potential for capsize is real when too much sail is up and apparent wind is directly on the beam. The boat can lift a hull in 12 knots true. This makes for exciting sailing when you bring your A-game, but limits the boat to coastal sailing.
Corsair F-24 MK I trimaran
Small and well canvased, these boats can capsize if driven hard (which they often are), but they are broad beamed, short-masted, and designed for windy sailing areas. F-24s are slower off wind than the Stiletto, in part because of greater weight and reduced sail area, but also because the main hull has more rocker and does not plane as well. They are faster to weather and point considerably higher than a Stiletto (90-degree tacking angle vs. 110 degrees). This is the result of greater beam, a more efficient centerboard design, and slender amas that are easily driven in displacement mode. The boat is quite forgiving if reefed.
Going purely by the numbers, this boat seems nearly identical to the F-24. In practice, they sail quite differently. The Dash uses a dagger board instead of centerboard, which is both more hydrodynamic and faster, but more vulnerable to damage if grounded at high speed.
The rotating mast adds power that is not reflected in the numbers. The bridgedeck clearance is higher above the waterline, reducing water drag from wave strikes. The wave-piercing amas create greater stability up wind and off the wind. The result is a boat that is slightly faster than the original F-24 and can be driven much harder off the wind without fear of pitchpole or broach.
Without proper testing, calculating stability yields only a rough picture.

Evaluating multihull performance based on design numbers is a bit more complicated than it is with ballasted, displacement monohulls, whose speed is generally limited by hull form. [Editor’s note: The formula for Performance Index, PI has been updated from the one that originally appeared in the February 2021 issue of Practical Sailor.
The following definitions of units apply to the adjacent table:
SA = sail area in square feet
D (displacement) = weight in pounds
LWL = length of waterline in feet
HCOE = height of sail center of effort above the waterline in feet
B = beam in feet
BCL = beam at the centerline of the hulls in feet.
Since a multihull pivots around the centerline beam, the overall beam is off the point and is not used in formulas. Calculate by subtracting the individual hull beam from the overall beam.
SD ratio = SA/(D/64)^0.66
This ratio gives a measure of relative speed potential on flat water for monohulls, but it doesn’t really work for multihulls.
Bruce number = (SA)^0.5/(D)^0.333
Basically this is the SD ratio for multihulls, it gives a better fit.
Performance index = (SA/HCOE)^0.5 x (D/1000)^0.166
By including the height of the COE and displacement, this ratio reflects the ability of the boat to use that power to sail fast, but it understates the importance of stability to the cruiser.
Stability factor = 9.8*((0.5*BCL*D)/(SA*HCOE))^0.5
This approximates the wind strength in knots required to lift a hull and includes a 40% gust factor. In the adjacent data sheet, we compare the formula’s predicted stability to observed behavior. Based on our experience on the boats represented, the results are roughly accurate.
Ama buoyancy = expressed as a % of total displacement.
Look for ama buoyancy greater than 150% of displacement, and 200 is better. Some early trimaran designs had less than 100 percent buoyancy and would capsize well before flying the center hull. They exhibited high submerged drag when pressed hard and were prone to capsize in breaking waves.
Modern tris have ama buoyancy between 150 and 200 percent of displacement and can fly the center hull, though even racing boats try to keep the center hull still touching. In addition, as a trimaran heels, the downward pressure of wind on the sail increases, increasing the risk of capsize. The initial heel on a trimaran is more than it is on catamarans, and all of that downward force pushes the ama even deeper in the water. Thus, like monohulls, it usually makes sense to keep heel moderate.
These numbers can only be used to predict the rough characteristics of a boat and must be supplemented by experience.
This is the first real cruising multihull in our lineup. A few have capsized. One was the result of the skipper pushing too hard in very gusty conditions with no one on watch. The other occurred when a crew unfamiliar with the boat ignored local wisdom and set sail into near gale conditions.
Although the speed potential of the PDQ 32 and the F-24 are very similar, and the stability index is not very different, the feel in rough conditions is more stable, the result of much greater weight and fuller hull sections.
Like most cruising cats, the PDQs hulls are relatively full in order to provide accommodation space, and as a result, driving them under is difficult. The increased weight slows the motion and damps the impact of gusts. Yes, you can fly a hull in about 25 knots apparent wind (we proved this during testing on flat water with steady winds), and she’ll go 8-9 knots to weather doing it, but this is not something you should ever do with a cruising cat.
Stability by the Numbers
The “stability factor” in the table above (row 14) is based on flatwater conditions, and ignores two additional factors. Unlike monohulls, the wind will press on the underside of the bridgedeck of a multihull once it passes about 25 degrees of heel, pushing it up and over. This can happen quite suddenly when the boat flies off a wave and the underside is suddenly exposed to wind blowing up the slope of the wave. A breaking wave also adds rotational momentum, pitching the windward hull upwards.
Multihulls by the Numbers
| BOAT | STILETTO 27 | CORSAIR F-24 MKI | PDQ 32/34 | TECKTRON 35 | LAGOON 42 | GUNBOAT 48 | EXTREME H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEAM | 13.8 | 18 | 16 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 28 |
| BEAM CENTERLINE | 11.3 | 15 | 12.8 | 16.8 | 17.4 | 20 | 23 |
| DISPLACEMENT | 1,100 lbs | 1,800 lbs | 7,200 lbs | 4,800 lbs | 16,550 lbs | 17,700 lbs | 34,400 lbs |
| SAIL AREA | 336. sq. ft. | 340 sq. ft | 540 sq. ft | 850 sq. ft | 1,150 sq. ft | 1,370 sq. ft | 2,850 sq. ft |
| MAST HEIGHT | 32 ft. | 31 ft. | 40 ft. | 55 ft. | 48 ft. | 72 ft. | 110 ft. |
| HEIGHT OF CENTER OF EFFORT (HCOE) | 14.7 ft. | 12.4 ft. | 18.4 ft. | 24 ft. | 22.1 ft. | 28.8 ft. | 50.6 ft. |
| LOA | 27 ft. | 24 ft. | 34 ft. | 35 ft. | 42 ft. | 48 ft. | 66 ft. |
| LWL | 25.2 ft. | 22 ft. | 33.4 ft. | 34.5 ft. | 39 ft. | 46 ft. | 62 ft. |
| SA/D | 51.4 | 37.6 | 23.9 | 49.2 | 29.4 | 33.5 | 45 |
| BRUCE | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| PERFORMANCE INDEX | 0.9 | 1.7 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 7.1 |
| STABILITY INDEX | 2.3 | 4.9 | 8.3 | 3.2 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 5.3 |
| STABILITY FACTOR | 11 | 17.5 | 21.1 | 13.8 | 23.3 | 20.8 | 16.2 |
| OBSERVED HULL LIFT (TRUE WIND SPEED) | 14 kts. | 19 kts. | 24 kts. | NA | NA | 23 kts. | 18 kts. |
| WINDWARD SPEEDAT HULL LIFT | 7 kts. | 8 kts. | 8 kts. | 9 kts. | 8 kts. | NA | NA |
| REACHING BOAT SPEED | 12 kts. | 10-12 kts. | 9-10 kts. | 14 kts. | 10-11 kts. | NA | NA |
| MAX SPEED | 22 kts. | 16-17 kts. | 14-16 kts. | 24 kts. | 16-18 kts. | 24 kts. | 29 kts. |
| SEA AREA | Coastal | Coastal | Coastal/Offshore | Coastal | Offshore | Offshore | Coastal/Offshore |
| CAPSIZE MODE | Capsized in wind | Capsized in wind | Capsized in gale | Pitchpoled | NA | NA | Capsized in Squall |
Autopilot is a common thread in many capsizes. The gust “came out of no place…” No it didn’t. A beach cat sailor never trusts gusty winds. The autopilot should be disengaged windspeeds and a constant sheet watch is mandatory when gusts reach 30-40 percent of those required to fly a hull, and even sooner if there are tall clouds in the neighborhood. Reef early if a helm watch is too much trouble.
“But surely the sails will blow first, before the boat can capsize?” That would be an expensive lesson, but more to the point, history tells us that well-built sails won’t blow.
“Surely the rig will fail before I can lift a hull?” Again, that could only be the result of appallingly poor design, since a rig that weak will not last offshore and could not be depended on in a storm. Furthermore, good seamanship requires that you be able to put the full power of the rig to work if beating off a lee shore becomes necessary.
Keeping both hulls in the water is up to you. Fortunately, under bare poles and on relatively flat water even smaller cruising cats can take 70 knots on the beam without lifting … but we don’t set out to test that theory, because once it blows for a while over even 40 knots, the real risk is waves.
Everything critical to safety in a blow we learned on beach cats. Like riding a bike, or—better yet—riding a bike off-road, there are lessons learned the hard way, and those lessons stay learned. If you’ve been launched into a pitchpole a few times, the feeling you get just before things go wrong becomes ingrained.
Perhaps you are of a mature age and believe you monohull skills are more than enough to see you through. If you never sail aggressively or get caught in serious weather, you’re probably right.
However, if there’s a cruising cat in your future, a season spent dialing in a beach cat will be time well spent. Certainly, such experience should be a prerequisite for anyone buying a performance multihull. The statement might be a little pointed, but it just makes sense.
Capsize by Wind Alone

Capsizing by wind alone is uncommon on cruising multihulls. Occasionally a performance boat will go over in squally weather. The crew could easily have reefed down or gone to bare poles, but they clung to the idea that they are a sail boat, and a big cat feels so stable under sail—right up until a hull lifts.
Because a multihull cannot risk a knockdown (since that is a capsize), if a squall line is tall and dark, the smart multihull sailors drops all sail. Yes, you could feather up wind, but if the wind shifts suddenly, as gusts often do, the boat may not turn fast enough. Off the wind, few multihulls that can take a violent microburst and not risk a pitchpole. When a squall threatens, why risk a torn sail for a few moments of fast sailing?
You can’t go by angle of heel alone because of wave action. Cat instability begins with the position of the windward hull. Is it flying off waves?
A trimaran’s telltale is submersion of leeward ama. Is the leeward ama more than 30-40 percent under water? The maximum righting angles is a 12-15 degrees for cats and 25-30 degrees for trimarans, but that is on flat water. Once the weather is up, observation of motion becomes far more important. Is the boat falling into a deep trough, or is at about to launch off a steep wave and fly?
Just as monohulls can surprise a new sailor by rounding up and broaching in a breeze, multihulls have a few odd habits that only present themselves just before things go wrong. Excuse the repetition, but the best way to learn to instinctively recognize these signs is by sailing small multihulls.
Sailing Windward
Because of the great beam, instead of developing weather helm as they begin to fly a hull, multihulls can suddenly develop lee helm, causing the boat to bear away and power up at the worst possible moment. This is because the center of drag moves to the lee hull, while the center of drive remains in the center, causing the boat to bear away.
If the boat is a trimaran, with only a center rudder, this rounding up occurs just as steering goes away. This video of a MOD 70 capsize shows how subtle the early warning signs can be ( www.youtube.com/watch?v=CI2iIY61Lc8 ).
Sailing Downwind
Off the wind, the effect can be the reverse. The lee hull begins to bury, and you decide it is time to bear off, but the submerged lee bow acts like a forward rudder. It moves the center of effort far forward and prevents any turn to leeward. Nearly all trimarans will do this, because the amas are so fine. The solution is to bear away early, before the ama buries—or better yet, to reef.
Conclusions
We’re not trying to scare you off multi-hulls. Far from it. As you can probably tell, I am truly addicted. Modern designs have well-established reputation seaworthiness.
But multihull seaworthiness and seamanship are different from monohulls, and some of those differences are only apparent when you press the boat very hard, harder than will ever experience in normal weather and outside of hard racing. These subtle differences have caught experienced sailors by surprise, especially if their prior experience involved only monohulls or cruising multihulls that were never pressed to the limit.
Although the numbers only tell part of the story, pay attention to a boat’s stability index. You really don’t want an offshore cruising boat that needs to be reefed below 22-25 knots apparent. Faster boats can be enjoyable, but they require earlier reefing and a more active sailing style.
When squalls threaten or the waves get big, take the appropriate actions and take them early, understanding that things happen faster. And don’t forget: knockdowns are not recoverable. It is satisfying to have a boat that has a liferaft-like stability, as long as you understand how to use it.
Technical Editor Drew Frye is the author of “Rigging Modern Anchors.” He blogs at www.blogspot/sail-delmarva.com
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
22 comments.
It’s interesting to read the report of the Multihull Symposium (Toronto, 1976) regarding the issues of multihull capsize in the formative years of commercial multihull design. There were so many theories based around hull shape, wing shape, submersible or non submersibe floats, sail area and maximum load carrying rules. My father, Nobby Clarke, of the very successful UK firm Cox Marine, fought many a battle in the early Sixties with the yachting establishment regarding the safety of trimarans, and I am glad that in this modern world technolgy answers the questions rather than the surmises of some establishment yachting magazines of the time.
Thank You Mr.Nicholson and Thank You to Practical Sailor for this great read superbly shared by Mr.Nicholson God bless you and our great Sailing Family.
Great read! Multi hulls are great party vessels which is why companies like Moorings and Sunsail have larger and larger numbers in their fleets. More and more multihulls are joining the offshore sailing fleets. Dismasting and capsizes do happen. Compared to mono hulls I know of no comparative statistics but off shore and bluewater, give me a mono hull. That is probably because I took one around with zero stability issues and only minor rig few issues. Slowly though; ten years.
Great read! Multi hulls are great party vessels which is why companies like Moorings and Sunsail have larger and larger numbers in their fleets. More and more multihulls are joining the offshore sailing fleets. Dismasting and capsizes do happen. Compared to mono hulls I know of no comparative statistics but off shore and bluewater, give me a mono hull. That is probably because I took one around with zero stability issues and only minor rig issues. Slowly though; ten years.
What’s an ama? Those who are new to sailing or even veteran sailors who have never been exposed to a lot of the terms simply get lost in an article with too many of those terms. I would suggest putting definitions in parentheses after an unfamiliar term to promote better understanding.
Vaka is the central, main hull, in a trimaran.
Ama is the “pontoon” hull at the end of the aka, or “crossbeam”, on each side of a trimaran.
I’m a geek, and therefore live in a dang *ocean* of the Jargonian & Acronese languages, and agree with you:
presuming 100% of audience is understanding each Jargonian term, and each Acronese term, is pushing credulity…
( and how in the hell “composition” means completely different things in object-oriented languages as compared with Haskell?? Bah. : )
As I understand it: Cats have an advantage in big beam seas because they will straddle a steep wave whereas a Tri can have its main hull on the wave crest with the windward ama’s bottom very high off the water and acting as another sail. Also, rig loads on a mono hull are calculated to be 2.5-3x the righting moment at a 45 deg heal; the reason being at 45 degrees the boat will still be making headway and feeling the dynamic loads in the seaway but beyond 45 degrees is a knockdown condition without seaway shock loads. A multihull rig on the other-hand can experience very high dynamic shock loads that are too short in duration to raise a hull.
Though I agree with much of the article content, the statement: “… this is because strategies such as heaving to and lying a hull don’t work for multihulls.” does not ring true in my experience. I have sailed about 70,000nm on cruising catamarans, a Canadian built Manta 38 (1992, 39ft x 21ft) with fixed keels and my present boat, a Walter Greene Evenkeel 38 (1997, 38ft x 19ft 6″) with daggerboards. I came from a monohull background, having circumnavigated the world and other international sailing (60,000nm) on a mono before purchasing the Manta cat. I owned that catamaran for 16 years and full time cruised for seven of those years, including crossing the Arctic Circle north of Iceland and rounding Cape Horn. I usually keep sailing until the wind is over 40knots, then the first tactic is to heave-to, and have lain hove-to for up to three days with the boat lying comfortably, pointing at about 50 to 60degrees from the wind and fore-reaching and side-slipping at about 1.5 to 2knots. Usually once hove-to I wait until the wind has reduced to 20knots or less before getting underway again. Lying ahull also works, though I have only used that in high winds without big breaking waves, as in the South Atlantic in the lee of South America with strong westerlies. I have lain to a parachute sea anchor and it is very comfortable, though lots of work handling all that gear and retrieving it and was glad to have deployed it when I did. I heave-to first, then deploy the sea anchor from the windward bow while in the hove-to position. The daggerboard cat will also heave-to well, though takes some adjusting of the boards to get her to lay just right, though I have not experience being at sea on this boat in as high of winds as with the Manta (over 60 knots). Catamaran bows have lots of windage and have little depth of hull forward. Thus you need mostly mainsail and little jib to keep her pointing into the wind. I aim for the wind to blow diagonally across the boat, with a line from the lee transom to the windward bow pointing into the wind as an optimum angle. As per taking the boat off autopilot when the wind gets near 20 knots is just not practical. The longest passage I have made on my catamarans has been from Fortaleza, Brazil, to Bermuda, nearly 3,000nm and across the squall prone doldrums and horse latitudes, taking 20 days. The autopilot steered the whole distance. I have never lifted a hull nor felt the boat was out of control despite having sailed in some of the most dangerous waters of the world.
I believe that your Techtronics 35 should be Tektron 35 (Shuttleworth) and as far as I know the capsize that occurred off Nova Scotia was, in fact, a Tektron 50 (Neptune’s Car I believe) sailed by the Canadian builder Eugene Tekatch and was reported as being off PEI. This capsize was well documented under a thread in “Steamradio” that I can no longer find. It appears that Steamradio is now, unfortunately, no longer operating. The report of the capsize was along the lines of the boat being sailed off wind with all sail in a gale. I think Shuttleworth indicated that they would have been doing about 30 knots. They then hit standing waves off PEI, the boat came to a standstill and with the change in apparent wind to the beam, over they went. Reading between the lines, Shuttleworth was pretty unhappy that one of his designs had been capsized in this manner, unhappier yet that some of the findings of I believe an american committee/ board were that the design was somehow at fault. Given Shuttleworth’s rep it seems unlikely. As I say these are recollections only.
Shortly afterwards Neptune’s Car was up for sale for a steal price.
I think Jim Brown (Trimaran Jim) when speaking of the Tektron 50 referred to it as weighing less than similarly sized blocks of Styrofoam. Admittedly, blocks of solid foam weigh more than one might imagine, but still a vivid point. Though Tektron 50 was light, we have far more options to build lighter boats today, than in the past.
Good that Practical Sailor is looking at this issue and I agree with much of it, so thanks PS for that. Also fun to see Nobby Clark’s son chip in …. I met Nobby at the ’76 World Symposium in Toronto, when I was just starting to get interested in Trimarans. I have since owned 4 and as a naval architect, builder and sailor, now specialize in their design and ‘all things related’, with a quasi-encyclopedic website at: http://www.smalltridesign.com . So as a trimaran guru, I’d like to add a few things here. In my experience (now 45 years with multis) there is really too much difference between catamarans and trimarans to compare them on the basis of the same formulas. For example, lifting a hull on a cat brings about a major reduction in reserve stability ….. lifting an ama on a trimaran, certainly does not. Using 30-40% immersion of an ama is hardly a guide to limit or prevent a capsize on a trimaran as that’s not even close to normal operating immersion . I would recommend a reduction of ama bow freeboard to about 1-2% of the boat length (depending on a few size factors) is a better guide as the ‘time to really ease up’. This visual indicator is great on my boats but is very hard to judge on hulls with reverse bows where there is no deck up forward. For a number of reasons, I am against this shape but as I’ve already made my case on line about this, I’ll not repeat it here. Over 80% of the capsizes we see on line, show that mainsails were never released .. and that includes the capsize of the MOD70 in the YouTube referenced in the PS article. As several trimaran owners I deal with have also capsized or near-capsized their boats (particularly those between 22 and 40ft that ‘feel’ more stable than they really are, I am developing a few models of EMRs to help solve their issue, (EMR=Emergency Mainsheet Release) and these will be operated wirelessly by punching a large button under the skippers vest, as I am not in favor of any fully automatic release. This HAS to be a skippers decision in my opinion for numerous reasons. The first two units of this EMR dubbed ‘Thump’R, will be installed this Spring … one in Europe and the other in Australia, but one day, perhaps Practical Sailor will get to see and test one for you 😉 In a few words, my advice to all multihull sailors is to be very aware of the way your stability works on your specific boat and sail accordingly. We learn this instinctively with small beach boats, but is harder to ‘sense’ as boats get heavier and larger. I have sailed cats from a 60ft Greene cat to a 12ft trimaran and although some basics apply they are of course very different. But you still need to ‘learn the early signs’ of your boat, as these must be your guide. IMHO a good multihull design will be fairly light and easily driven which means that it will still sail well with less sail. This means that the use of a storm mainsail in potentially high wind can add much reserve stability and safety to your voyage. To give an example from my small W17 design that sets a rotating wingmast, the boats top speed to date is 15kts with 200 sqft, but with the storm mainsail and a partly-furled jib I can get the area down under 100sqft without losing rig efficiency. In fact, the tall narrow storm main with a 5.5:1 aspect ratio is now even MORE efficient as the wingmast is now doing a higher percentage of the work. In 25-30t storm conditions, I have now sailed 8kts upwind and 14.4kts down, and feel very dry and comfortable doing so … even at 80+. So get the right sails, and change down to small more efficient ones when it pipes up. A multihull storm sail should look nothing like a mono’s trysail … with our narrow hulls, we are sailing in a very different way. Happy sailing Mike
In the old days, low displacement, short and narrowly spaced amas were the design of choice. One was supposed to back off when they started to submerge. It was a visual indicator. Modern amas are huge. If a 24 foot tri like the Tremolino could be designed to use Hobie 16 hulls in the 70s, today it would carry Tornado hulls. The slippery shape of designs catches the eye, and their supposed less grabby when submerged decks, but these amas also carry 1.5-2x main hull displacement. The chance of burying them is significantly reduced.
The original intent of these slippery ama designs was to shake off wind. Though low drag shapes for reducing pitch pole risk are a consideration, it should be balanced against maintaining ama deck walkability. This is important in allowing one to service the boat or rig drogues or anchors, not to mention to position live ballast. I am thinking here of the smaller club and light crusing tris. You aren’t going to be able to do a lot of these things on monster luxury boats that are a different scale entirely. But they mater on the kinds of boat most people are likely to own.
Poring over tri design books, one will notice that the silhouette of, say, a 40 foot tri, and the smaller 20 foot design are very similar This yields a doubling of the power to weight ratio on the smaller boat. This difference can even be greater as the smaller boats are often nothing more than empty shells, yet may carry higher performance rig features like rotating masts. Smaller tris are often handicapped by the requirements of being folded for trailering which both limits beam and ama displacement, though it may tend to increase weight. On top of that, mainsail efficiency is much higher, these days, with squared shapes, and less yielding frabrics. And, of course, much larger sail plans. All the better, just so long as people realize what they have by the tail.
Excellent article…thank you!!!!!!!!!
Good article. One thing that concerns me about modern cruising cat is how far above water level the boom is. I first noticed this looking at Catana 47’s for hire in New Caledonia and recently saw large Leopards 48 & 50 footers visiting Fremantle Sailing Club, here in Australia, and in all cases the boom seems to be at least 20 feet (6 metres) above the water. This seems to greatly increase the heeling moment and reduce the amount of wind required to capsize the vessel. Mind you at 20+ tons, the weight of the Leopards probably makes them a bit more resistant to capsize. But why does the rig need to be so far off the water?
Notice to Moderator After having read this article a couple or days back, I emailed naval architect mike waters, author of the specialist website SmallTriDesign to read the article and perhaps comment. Nearly a day ago, he emailed me back to say that he had, yet there’s been nothing posted from him and now I see a post with todays date. With his extensive knowledge and experience I would have thought his insight to be valuable to your readers and I was certainly looking forward to seeing his input. What happened?
Yes, PS .. what’s cookin ? Thought readers would be interested to know that capsize control help maybe on the way 😉
Yes PS, what’s cookin’ ? Thought your readers would like to know that some anti-capsize help maybe on the way 😉
Great article! I’ve read it twice so far. Recently in Tampa Bay I sailed my Dragonfly 28 in 25 knots breeze and found that speed was increased (drag reduced?) after I put in one reef in the main. I think I should have reefed the Genoa first?
Absolutely Tim. Slim hulls, as for most trimarans and the finer, lighter catamarans will often sail more efficiently with less sail .., especially if with a rotating mast, and you can indeed get proportionally better performance. The boat sails more upright for one thing, giving more sail drive from improved lift/drag and less hull resistance .. and its certainly safer and more comfortable and can also be drier, as an upright boat tends to keep wavetops passing underneath more effectively. Even my W17 design has been shown to achieve over 90% of its top speed with only 1/2 the sail area, by switching to a more efficient, high-aspect ratio ‘storm mainsail’ set behind its rotating wingmast …, a far cry from a monohulls storm trysail in terms of upwind efficiency. Yes, wind speed was higher, but the boat sailed far easier and its definitely something that slim hulled multihulls should explore more, as they will then also be less likely to capsize. More here if interested http://www.smalltridesign.com
Darrell, is there some reason for blocking replies that hold opinions contrary to those of PS ? I am still hoping to read the expertise of those who actually study design and sail multihulls. The written target of PS is to accurately present facts and that implies the input of experts. Over the last 10 years, I have come to appreciate a few experts in the field of multihulls and right now, I see at least one of them is not being given a voice here. Your article made a lot of fine points but there are some issues needing to be addressed if PS it to remain a trusted source for accurate information. First, I have been told by a reliable source, you need to separate trimarans from catamarans and use different criteria to compare their stability as they do not respond the same and neither can you judge their reserve stability in the same way. I would also like to know what NA Mike Waters was hinting at when he said “capsize control help may be on the way” .. would you know anything about that? If not, then please invite or allow him space or the promise of PS fact-finding accuracy is heading down the drain for me. thanks
As a new subscriber to PS, it is a little disquieting to see no response to the two comments above by Tom Hampton.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

Hanse 410: What You Should Know | Boat Tour

Sailboat vs Fishing Boat – Rules of the Road

Catalina 445: What You Should Know | Boat Review

How to Wax and Polish Your Boat
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager
Can a Catamaran Capsize? The Surprising Answer
Capsizing often happens with small boats like canoes, kayaks, and sailboats. But even for bigger boats like catamarans, which have an established reputation for stability and safety, it's still normal to wonder if they can capsize too. To give you peace of mind and prepare you for the worst, let's answer that question in this article.
A catamaran can capsize under extreme conditions, just like any other boat. Even the most stable catamaran can capsize if it's hit by a large wave, caught in a sudden gust of wind, or if the rotational force has overcome the stability of the boat. However, it's not something that happens frequently.
It can be a scary experience if a catamaran capsized, but you have to stay calm and know that most modern catamarans are designed to self-right. This means that they can turn themselves back over after capsizing. Let's continue reading to know what else can we do to recover from a catamaran capsize.
- A catamaran's stability is attributed to its center of gravity, its freeboard, and its pendulum-like behavior. However, despite its stability and speed, a catamaran can still capsize due to strong winds and capsizing waves.
- There are factors that can contribute to the likelihood of a capsize happening, such as wind speed, wave height, weather conditions, breaking waves, and the overall sailing conditions.
- The best thing to do to quickly recover from a capsize is to stay calm and position the boat to make it self-right quickly.

On this page:
A catamaran can capsize despite its stability, factors influencing catamaran capsizing, safety measures to prevent capsizing, recovering from a capsized catamaran.
A catamaran can capsize. However, it's not very common, and most catamarans are designed to be stable and safe in a variety of conditions.
Despite their stability and speed, catamarans can still capsize under certain conditions. Strong winds, large waves, and imbalance can all cause a catamaran to capsize. When a catamaran is caught in a gust of wind, the increased wind pressure on one side of the catamaran can cause it to lean to one side, which can lead to a capsize if not corrected.
Any boat can technically capsize , but there are specific factors that can contribute to a catamaran capsizing. One of the main reasons for catamaran capsizing is the effect of rotational forces. When these forces overcome the stability of the boat, it can lead to capsizing.
A catamaran is a type of multihull boat that has two parallel hulls connected by a deck or bridge. They are well known for their stability and speed, making them a popular choice for sailors and boaters.
One of the key advantages of their twin hulls is that it gives them a larger base and makes them less likely to tip over . It also helps to distribute the weight of the boat more evenly, providing greater stability. This is especially helpful in rough seas , where the catamaran's stability can help keep you safe and comfortable. Below are factors that contribute to the stability of catamarans:
Their center of gravity makes them stable
In a catamaran, the center of gravity is typically lower than in a monohull, which helps reduce the likelihood of capsizing. This is because the lower the center of gravity, the more stable the boat will be.
The freeboard also adds up to their stability
Their freeboard of a catamaran is typically lower than a monohull's, which helps to reduce the windage and the chances of the boat being pushed over by strong winds.
Their pendulum-like behavior helps them to be stabilized
When they encounter waves, the two hulls move independently of each other, which helps to reduce the rolling motion of the boat. This is because the weight of the boat is distributed between the two hulls, which act like pendulums, swinging in opposite directions to counterbalance the motion of the waves.
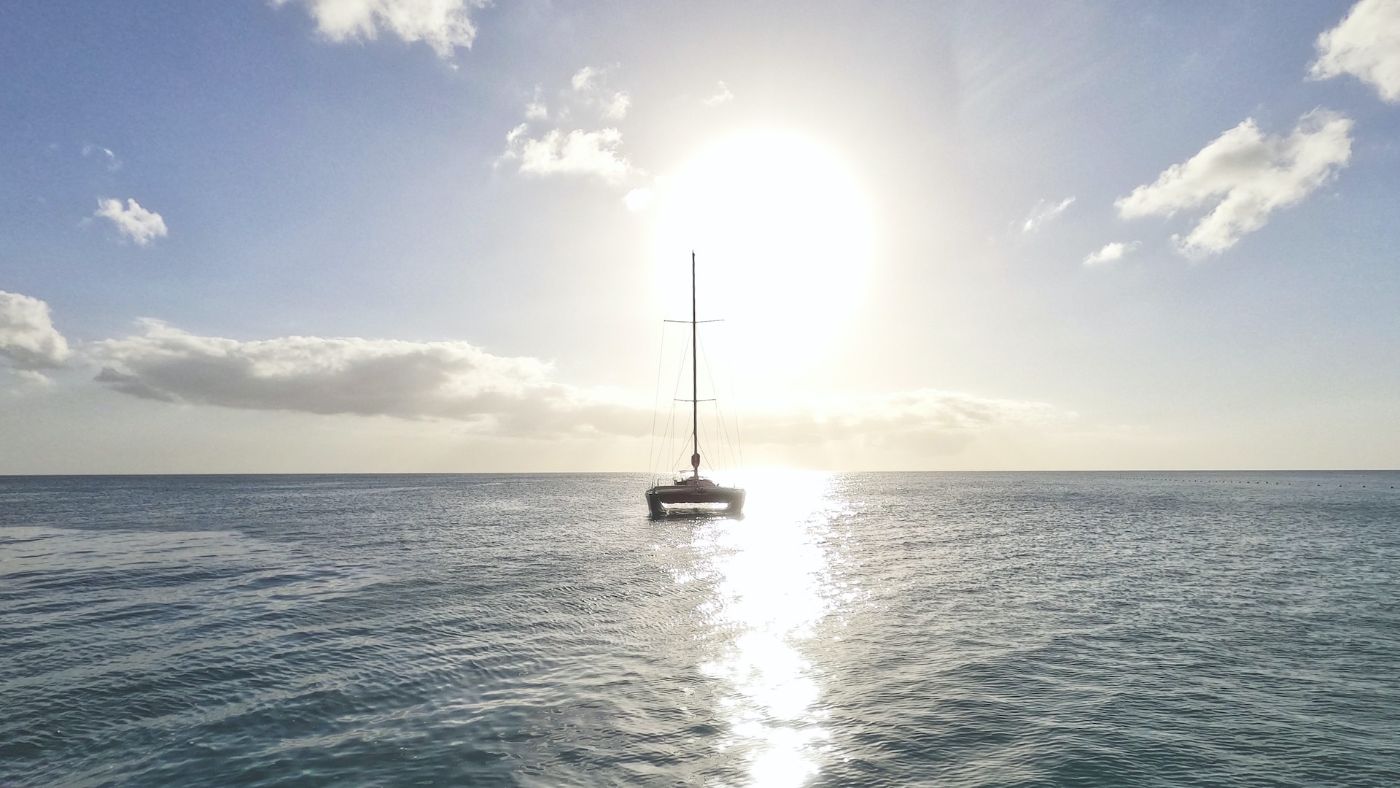

Aside from stability, another advantage of a catamaran is its speed. Because they have two hulls, they create less drag than a single hull and can move through the water more quickly and efficiently. This can be especially useful if you're trying to get somewhere quickly or if you're racing.
The height of the wave can affect the chance of capsizing
Wave height is a significant factor when it comes to catamaran capsizing. The higher the waves, the greater the risk of capsizing. This is because the waves can exert a significant amount of force on the boat, causing it to tip over.
Wave capsize occurs when a boat overtakes a wave and sinks its bow into the next one, causing it to capsize. However, this is also not very common and can usually be avoided by keeping an eye on the waves and adjusting your speed and course accordingly.
Wind speed is another important factor to consider
The stronger the wind, the more likely it is that a catamaran will capsize. The wind can create a lot of pressure on the sails, which can cause the boat to lean to one side and potentially capsize. To know more about the ideal wind speed in sailing, read this article.

Weather conditions can also play a role in catamaran capsizing
If there is a storm or other severe weather conditions, the risk of capsizing is much higher. Perhaps consider checking the weather forecast before setting out on a catamaran to ensure that conditions are safe. You may also try reading this article on the possible danger of sailing through thunderstorms.
Breaking waves can cause a catamaran to capsize
When waves break, they release a significant amount of energy, which can cause the boat to capsize. Try to keep an eye out for breaking waves and avoid them if possible.
The overall sailing condition can increase the likelihood of capsizing
You may need to be aware of the conditions and take appropriate precautions to ensure that you stay safe while on the water.
1. Ensure proper weight distribution
To prevent capsizing, you could check if the weight on your catamaran is evenly distributed, with heavier items stored low and towards the center of the boat. Try to avoid overloading your catamaran with too much weight.
2. Learn the right way of reefing
Reefing is the process of reducing the size of your sails to adjust to changing wind conditions. When the wind starts to pick up, you will need to reef your sails to prevent your catamaran from heeling over too much. You must learn how to reef your sails properly before you set out on your journey.
3. Know how to properly anchor and use the right anchor
An anchor can help keep your catamaran in place and prevent it from drifting in strong currents or winds. You need to know how to properly anchor your catamaran and always use an anchor that is appropriate for the size of your boat. Learn different anchoring techniques in tough conditions through this article: Boat Anchoring Techniques Explained (Illustrated Guide)

4. Utilize your catamaran's engine
Your engine can be a valuable tool for preventing capsizing. If you find yourself in a dangerous situation, such as strong winds or currents, you can use your engine to help keep your catamaran stable and prevent it from capsizing.
5. Use your boat tools to prevent it from capsizing
Keels, daggerboards, and centerboards all help stabilize your catamaran and prevent capsizing. You may need to check if these are properly installed and maintained.
6. Use the drogue to slow down the boat
A drogue is a device that can help slow down your catamaran and prevent it from capsizing in heavy seas. You can check if you have a drogue on board and learn how to properly use it in case you need to.
7. Make sure to have safety equipment onboard
Always make sure you have the proper safety equipment on board, including life jackets, flares, and a first aid kit. Everyone on board must also know where the safety equipment is located and how to use it.
8. Use an autopilot
Autopilot can help keep your catamaran stable and prevent it from heeling over too much. Consider learning how to properly use your autopilot before you set out on your journey.
Capsizing a catamaran can be a scary experience, but with proper preparation and practice, you can easily handle it. When the boat flips upside down, all the loose gear in the boat floats away (or sinks), and you are left with a capsized boat. Here are some steps that can help you recover from a catamaran capsize:
The first thing to do when your catamaran capsizes is to remain calm. Take a deep breath and assess the situation. Check if everyone on board is safe and accounted for.

Position the catamaran to self-right
Catamarans are designed to self-right, which means that they can turn themselves back over after capsizing. To self-right, the boat needs to be positioned in a certain way, usually with the mast pointing downwind.
Help the catamaran to self-right using the righting lines
If your catamaran doesn't self-right, you can help it by using the righting lines. These lines are attached to the bottom of the hulls, and they can be used to pull the boat back upright.
The buoyancy of the catamaran can help you recover
Catamarans are designed to be buoyant , which means that they can float even when they are upside down. This makes it easier to recover from a capsize.
Be prepared
The best way to prepare for a capsize is to practice recovering from one. Set aside some time to practice capsizing your catamaran in a controlled environment, like a calm lake. This will help you build confidence and prepare you for the real thing.
Leave a comment
You may also like, catamaran vs monohull in rough seas: which is better.
Catamarans and monohulls have different designs that affect how they handle rough sea conditions. In fact, they have an advantage over each other when sailing in …

Are Catamarans Safer than Monohulls? - Not Always

The Perfect Size Catamaran to Sail Around the World

What is the Ideal Wind Speed for Sailing?

The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)
Catamaran Capsize: What to Do When Your Boat Flips
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 10, 2023 | Sailing Adventures

Short answer catamaran capsize:
A catamaran capsize refers to the overturning or tipping over of a catamaran, a type of multihull boat with two parallel hulls. This can occur due to various factors such as strong winds, improper handling, or technical failures. Capsize prevention measures like proper training, ballasting systems, and stability considerations are crucial for safe navigation and reducing the risk of catamaran capsizing incidents.
Understanding Catamaran Capsizing: Causes, Risks, and Prevention
Catamarans are a popular choice among sailing enthusiasts due to their sleek design, stability, and impressive speed. However, even the most experienced sailors can fall victim to catamaran capsizing if they fail to understand the causes, risks involved, and how to prevent mishaps. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of understanding catamaran capsizing to ensure that you can enjoy your sailing adventures with peace of mind.
Causes of Catamaran Capsizing:
1. Overloading: One common cause of catamaran capsizing is overloading. Exceeding the weight limitations of your vessel can lead to instability and loss of control in rough waters. It is essential to understand your catamaran’s maximum carrying capacity and distribute weight evenly throughout the boat.
2. High Winds: Strong gusts can swiftly overpower a catamaran, making it prone to capsizing. Understanding weather patterns and keeping a close eye on wind forecasts becomes crucial before embarking on any sailing journey.
3. Wave Interference: Waves play an integral role in causing catamaran capsizing accidents. Large waves hitting the boat at unfavorable angles can destabilize it or even cause it to pitchpole (the front end dives into a wave while flipping). Studying wave behaviors and having knowledge of proper sailing techniques when encountering such conditions is vital for preventing mishaps.
Risks Involved in Catamaran Capsizing:
1. Injury or Loss of Life: The most significant risk associated with catamaran capsizing is potential injury or loss of life. Falling from a capsized vessel into rough waters poses serious dangers, especially if rescue or self-recovery measures are not promptly executed.
2. Damage to Property: Struggling against strong currents after a capsize can cause considerable damage to both your vessel and other boating equipment on board. Repairs can be costly, and the loss of personal belongings can be emotionally distressing.
3. Environmental Impact: Capsized catamarans may spill fuel, oil, or other hazardous substances into the environment, causing pollution and harm to marine life. Understanding the potential environmental impact of a capsizing event highlights the importance of responsible boating practices.
Preventing Catamaran Capsizing:
1. Proper Training and Education: Acquiring formal training courses in sailing, especially ones specifically focusing on operating a catamaran, is essential for preventing capsizing accidents. Learning about safety procedures, navigation techniques, and understanding your vessel’s capabilities will significantly reduce risks.
2. Maintenance and Inspection: Regularly inspecting your catamaran for any signs of wear or damage can help identify potential issues that could lead to a capsize. Maintaining sails, rigging, and hull integrity ensures that your vessel is in optimal condition for safe sailing .
3. Weather Monitoring: Stay updated with meteorological reports and observe weather patterns carefully before setting sail . Avoid venturing out during severe weather conditions such as high winds or thunderstorms to minimize the risk of capsizing incidents.
4. Weight Distribution: Pay close attention to how weight is distributed within your catamaran to maintain its stability . Ensuring an even distribution across both hulls reduces the risk of capsizing due to imbalance.
5. Safety Equipment: Always have suitable safety equipment readily available onboard your catamaran in case of emergencies. This includes personal flotation devices (PFDs), flares, whistles, safety lines, fire extinguishers, and distress signals – which are all vital tools for rescuers spotting you quickly during a capsize situation.
By thoroughly understanding the causes behind catamaran capsizing incidents along with their associated risks while implementing preventative measures explained above; you can minimize the likelihood of encountering such mishaps on your sailing adventures.”
Remember that maintaining vigilance at all times during your sailing trips is crucial , regardless of your experience level. Stay informed, respect the power of nature, and prioritize safety to ensure a memorable and enjoyable catamaran experience for yourself and everyone on board.
How to React When a Catamaran Capsizes: Step-by-Step Guide
Title: Successfully Navigating a Catamaran Capsizing: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction: Catamarans are undoubtedly marvelous vessels, designed to provide both stability and speed on the water . However, even the most experienced sailors may find themselves in a situation where their catamaran capsizes unexpectedly. To help you stay prepared and confident, we have crafted a detailed step-by-step guide on how to react when faced with such an unfortunate event. From staying calm to implementing effective techniques, this guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to swiftly recover from a catamaran capsizing.
Step 1: Maintain Composure In any crisis situation, keeping calm is key. Take a deep breath, clear your mind and remind yourself that panic only exacerbates the challenge at hand. Remaining composed allows you to think rationally and make wise decisions during each subsequent step.
Step 2: Assess the Situation Upon realizing that your catamaran has capsized, take a moment to evaluate the circumstances around you. Determine whether any crew members or passengers require immediate assistance or medical attention. Prioritizing safety should always be your primary concern.
Step 3: Activate Floatation Devices Ensure that everyone onboard has access to personal floatation devices (PFDs). Encourage everyone to put them on without delay – these will significantly enhance everyone’s chances of staying buoyant while awaiting rescue.
Step 4: Conserve Energy Capsizing can be physically demanding; therefore, it is crucial for everyone involved to conserve energy during this challenging time. Remind crew members and passengers not to exert themselves unnecessarily and advise them on using slow movements in order not to tip over or destabilize the boat further.
Step 5: Establish Communication Locate any communication devices available onboard, such as handheld radios or emergency flares . If possible, make contact with nearby vessels or coastguards immediately for assistance. Modern technologies like personal locator beacons (PLBs) can effectively alert authorities to your location, ensuring swift and targeted rescue efforts.
Step 6: Activate Self-Righting Mechanism Many catamarans are equipped with self-righting features. Determine whether your vessel possesses this capability and, if so, initiate the self-righting mechanism as per your specific manufacturer’s instructions. This will help upright the boat swiftly and minimize any further complications.
Step 7: Teamwork is Essential Maintain a collective mindset throughout the ordeal by fostering teamwork amongst crew members and passengers. Assign roles to individuals based on their abilities, such as staying close to less confident swimmers or assisting in communication efforts. Cooperation plays a vital role in maximizing everyone’s safety during a catamaran capsizing event.
Step 8: Abandon Ship If Necessary In extreme situations where the catamaran cannot be successfully righted or is taking on significant water , abandoning ship may become necessary. Ensure that everyone is aware of emergency escape routes and how to properly use life rafts or other flotation devices for evacuation. Stay together as a group to increase visibility for rescuers and minimize potential risks of separation.
Conclusion: No sailor desires to experience the unsettling event of a catamaran capsizing; however, being well-prepared significantly improves your chances of overcoming such an incident unscathed. By following this step-by-step guide with composure, careful assessment, effective communication, teamwork, and necessary equipment utilization, you will empower yourself and others with confidence when facing such circumstances at sea. Remember: Safety should always remain paramount on any sailing adventure !
Frequently Asked Questions about Catamaran Capsizing
Are you a catamaran enthusiast or someone interested in the world of sailing? If so, you may have heard about catamaran capsizing and the potential risks involved. In this blog post, we will delve into frequently asked questions about catamaran capsizing to provide you with a detailed professional explanation . So let’s dive right in!
1. What is catamaran capsizing? Catamaran capsizing refers to the situation where a catamaran boat overturns or flips onto its side or completely upside down due to various external factors such as strong winds, large waves, or improperly distributed weight on the vessel.
2. What are the common causes of catamaran capsizing? There are several factors that can contribute to a catamaran capsizing. Some of the most common causes include extreme weather conditions such as high winds and heavy waves, sudden shifts in wind direction, improper handling by sailors, insufficient crew experience or training, overloading of equipment or passengers, and structural issues with the boat itself.
3. How likely is it for a catamaran to capsize ? While catamarans are generally considered stable vessels, there is still a chance of capsizing under certain circumstances. The likelihood of capsizing depends on various factors including the size and design of the catamaran, prevailing weather conditions, crew skills and experience levels, and adherence to safety protocols.
4. Can you prevent catamarans from capsizing altogether? While it is impossible to completely eliminate all risks associated with sailing on a catamaran , there are measures that can be taken to minimize the chances of capsizing. These include proper weight distribution on board by evenly distributing passengers and equipment across both hulls, regular maintenance checks and repairs to ensure structural integrity of the vessel, acquiring adequate knowledge about weather patterns before setting sail , keeping an eye on changing wind conditions during trips, and investing in appropriate safety equipment such as life jackets and flotation devices.
5. What should I do if my catamaran capsizes? In the unfortunate event that your catamaran capsizes, it is crucial to remain calm and follow proper safety protocols. Firstly, make sure everyone on board is wearing a life jacket and accounted for. Attempt to right the boat by applying appropriate techniques learned through training or seek professional assistance if necessary. If unable to overturn the catamaran, seek refuge on top of the inverted hulls until rescue arrives or until you are able to safely swim to shore, depending on the proximity of land.
6. Are there any measures in place to enhance catamaran safety? Absolutely! In many sailing communities, there are regulatory bodies and organizations that promote safe sailing practices for catamarans. These can include mandatory safety inspections for vessels, standardized training programs for skippers and crew members, guidelines on weight distribution limits, and recommendations regarding suitable weather conditions for outings.
7. Is catamaran capsizing more dangerous than monohulls? Both catamarans and monohulls have their own unique characteristics when it comes to capsizing risks. While a monohull may be more prone to rolling over completely due to its single hull design, a catamaran is more likely to capsize onto its side or invert partially due to its dual-hull configuration. Both scenarios can present dangers depending on several factors such as sea state , weather conditions, crew experience level, and rescue accessibility.
8. Can I still enjoy sailing on a catamaran without worrying about capsizing? Absolutely! The joy of sailing on a well-maintained and properly operated catamaran far outweighs the potential risks associated with capsizing events. By taking appropriate precautions such as ensuring crew competency level matches prevailing conditions, adhering to weight distribution guidelines set by manufacturers or designers, using reliable weather forecasting services before embarking on trips, and practicing emergency drills with your crew, you can greatly minimize the chance of experiencing a capsizing event.
So there you have it – the frequently asked questions about catamaran capsizing. We hope this detailed professional, witty and clever explanation has shed some light on this topic and provided valuable insights for anyone considering sailing on a catamaran . Remember to always prioritize safety when enjoying your sailing adventures !
The Anatomy of a Catamaran Capsize: Key Factors to Consider
Catamarans are known for their outstanding stability and performance in the water. However, despite their impressive design, these amazing vessels are not immune to capsizing under certain conditions. Understanding the anatomy of a catamaran capsize is essential for sailors and boat enthusiasts alike, as it allows us to learn how to prevent such incidents and ensure our safety when navigating these remarkable watercraft.
One of the key factors that can lead to a catamaran capsize is excessive wind or gusts. While increased wind is generally advantageous for sailing, when coupled with strong currents or waves, it can create an unbalanced force on the boat, increasing the risk of tipping over. A sudden violent gust or wind shift can catch even seasoned sailors off guard, making it crucial to stay vigilant and react promptly by adjusting sails or heading into the wind to reduce pressure on them.
Another vital aspect contributing to a catamaran capsize is weight distribution. Catamarans rely heavily on their wide hulls for stability, which can sometimes lead novice sailors to overlook the significance of proper weight distribution within the vessel. If there is an excess load on one side due to unevenly distributed cargo or passengers congregating in one area of the boat, it can destabilize the catamaran and make it more prone to flipping over during challenging weather conditions .
In addition to excessive wind and poor weight distribution, wave action plays a significant role in catamaran disasters. When powerful waves crash against a catamaran’s hulls at certain angles or heights, they exert tremendous forces that can easily overcome its stability measures. For instance, if caught by an unexpected large wave while crossing a bar entrance or maneuvering through narrow channels where choppy seas prevail, there’s a higher possibility of encountering instability issues that may potentially result in capsize.
Furthermore, sail handling skills are critical when trying to prevent a catamaran from capsizing. A catamaran’s sail plan is designed to optimize performance, but this also means that sail forces can become excessive in challenging conditions. If the sails are not appropriately adjusted or if inexperienced sailors fail to anticipate gusts and adjust accordingly, the boat may be overwhelmed by the power of the wind, leading to an alarming loss of control and potential capsize.
Lastly, seaworthiness is a fundamental consideration when it comes to preventing catamaran capsizes. Regular maintenance and inspections should be conducted to ensure that all vital components such as rigging, rudders, and hull integrity are in impeccable condition. Proper communication equipment should also be onboard at all times to allow for quick distress calls or requests for assistance during unforeseen emergencies.
To conclude, understanding the various factors contributing to a catamaran capsize is essential for any sailor or boat enthusiast who wishes to embark on this exhilarating water adventure. By recognizing the crucial role of excessive wind, weight distribution, wave action, sail handling skills, and seaworthiness precautions, individuals can minimize their risk of encountering a catastrophic event while enjoying the pleasures of sailing on these beautiful vessels. So before setting out on your next catamaran voyage, make sure you’re well-prepared and equipped with safety knowledge that will keep you sailing smoothly !
Top Safety Tips for Avoiding and Surviving a Catamaran Capsize
Title: Navigating the High Seas: Top Safety Tips for Avoiding and Surviving a Catamaran Capsize
Introduction:
The allure of catamarans lies in their ability to skim across the water, effortlessly harnessing the wind’s power . However, as with any water-based activity, accidents can happen. Understanding the necessary precautions and knowing how to react in dire circumstances is paramount to ensure your safety while enjoying this thrilling experience . In this blog post, we present you with our comprehensive guide on top safety tips for avoiding and surviving a catamaran capsize. So buckle up; we’re about to set sail into the world of nautical preparedness!
1. Choose Your Vessel Wisely:
Your primary defense against a capsizing event starts with selecting a suitable catamaran . Ensure that it has appropriate stability features like outriggers or pontoons that offer additional buoyancy in case of rough waters or sudden gusts of wind. Additionally, always check the weather forecast before embarking on your journey to avoid unfavorable conditions.
2. Master Your Catamaran Handling Skills:
Knowledge and expertise are priceless while cruising aboard a catamaran. Familiarize yourself thoroughly with your vessel’s manual, understanding all systems and controls entirely—training courses and sailing schools can be excellent resources for acquiring essential skills such as docking maneuvers, navigation techniques, and emergency drills.
3. Keep an Eye on Weight Distribution:
A well-distributed weight load enhances stability significantly during transfers of power between hulls when riding waves or strong gusts. Ensure that weighty gear is evenly distributed between both hulls, taking care not to place excessive weight on one side which may lead to imbalance and potential tipping.
4. Rigorous Pre-sailing Checks:
Prior to setting sail , conduct thorough pre-departure checks focused on key safety areas such as rigging tension, mast integrity, hull conditions (including hatches), rudder alignment, and electronics functionality. Moreover, make it a habit to inspect the vessel’s keels, ensuring they are free from any debris or obstruction that might affect stability.
5. Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Never underestimate the importance of PPE for all onboard. Each crew member should be equipped with a well-fitting personal flotation device (PFD) suited for their weight and body type. Additionally, wearing non-slip footwear and donning protective clothing against sunburns will keep you comfortable throughout your journey.
6. Maintain Constant Vigilance:
While the joys of sailing can sometimes be entrancing, maintaining constant situational awareness is crucial aboard a catamaran. Always keep an eye out for sudden changes in wind direction or intensity, potential obstacles such as submerged rocks or reefs, and other moving vessels that may pose collision risks.
7. Execute Controlled Gybes:
Performing controlled gybes (turning the boat downwind) helps mitigate risks associated with strong gusts during maneuvers. By gradually turning instead of executing sharp turns, you reduce the chances of capsizing due to abrupt shifts in wind pressure on the sail .
8. React Swiftly During Capsizing:
Despite taking every possible precautionary measure, there may still be instances where your catamaran capsizes unexpectedly. If this happens, stay calm and remember these essential steps: hold on to something secure within the hull if accessible, prioritize assessing everyone’s safety first before attempting self-rescue; avoid panicking or swimming away from your vessel since it serves as a rescue platform until help arrives.
Conclusion:
Sailing aboard a catamaran provides an exhilarating experience loaded with adventure and serenity; however, being aware of potential risks associated with capsizing is vital to ensure a safe voyage. By following our top safety tips outlined above – choosing the right vessel, mastering handling skills, maintaining correct weight distribution, conducting rigorous pre-sail checks – you can vastly reduce the likelihood of a catamaran capsize. Remember, staying prepared and acting wisely during such an event is paramount to your survival at sea. So, bon voyage, fellow enthusiasts, and may the winds always be in your favor!
Exploring the Aftermath: Recovering from a Catamaran Capsize
Picture yourself sailing peacefully on a gorgeous sunny day, only to have your serene experience shattered by a sudden and unexpected event – a devastating catamaran capsize. It’s an unfortunate incident that can turn your joyful sailing adventure into a daunting and stressful situation . However, fear not! In this blog post, we will dive deep into the aftermath of a catamaran capsize and discuss the steps required to recover both physically and mentally from such an ordeal. So, grab your life jackets and let’s set sail into understanding the complexities of post-capsize recovery!
1. Assessing the Immediate Situation:
When faced with a catamaran capsize, it is crucial to remain calm and composed. Your immediate priority should be ensuring everyone’s safety onboard. Quickly conduct a headcount to account for all crew members while simultaneously checking for injuries or potential dangers in the surrounding environment such as debris or submerged objects.
2. Activating Emergency Signals and Communication Systems:
Once you have secured everyone’s safety, it is vital to activate emergency signals promptly. Utilize any available communication systems to notify nearby vessels or shore authorities about your predicament. This will enable them to dispatch rescue services swiftly, minimizing the time spent adrift.
3. Maneuvering Towards Stability:
With safety measures in place, it’s time to focus on stabilizing your catamaran after its terrifying roll-over incident. Depending on various factors such as water conditions and vessel type , there are multiple techniques you can employ for righting your capsized craft. Perhaps using auxiliary flotation devices or relying on collective crew effort, these methods may vary but share one common goal – restoring stability safely.
4.Controlling Water Intake:
Catamarans may suffer extensive damage during capsize incidents resulting in water flooding their hulls rapidly; thus controlling water intake becomes crucial for successful recovery efforts. Energetically employ bilge pumps or any other available means to eliminate excessive water ingress, as this allows your vessel to regain buoyancy and maneuverability.
5. Assessing the Extent of Damages:
Once stability is restored, it’s time to conduct a thorough inspection of your catamaran. Assess the extent of damages inflicted during the capsize incident carefully. Pay close attention to critical components such as rigging, sails, hull integrity, and safety equipment. Identifying potential structural issues upfront will aid in subsequent repair and recovery plans.
6. Towing or Sail-Assisted Recovery:
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of damage incurred, it’s time to plan your recovery strategy. Depending on the severity of damages and proximity to help, you may choose between towing your craft back to land or utilizing its remaining sailing capabilities for a sail -assisted return home. Remember, ensuring everyone’s safety remains paramount throughout this decision-making process.
7. Seeking Professional Assistance:
Involving an experienced maritime professional during post-capsize recovery can prove invaluable. They can offer expert advice regarding vessel repairs and assist in making critical decisions about whether immediate repairs are necessary or if repatriating via tow should take precedence.
8. Debriefing and Reflecting:
Finally, once your catamaran is safely repaired or taken for professional assistance; it is essential to reflect upon the tumultuous experience openly with your crew members and those involved in the rescue operation. A debriefing session will not only provide closure but also contribute towards bolstering future safety practices and enhancing preparedness for similar emergencies.
Facing a catamaran capsize might send waves of panic through even the most seasoned sailors; however, with proper preparation, quick thinking, and adherence to safety protocols outlined above – recovering from such an unpredictable event becomes feasible both physically and mentally.
Embrace every opportunity for learning from this experience while acknowledging the resilience displayed by yourself and your crew. Sail on, knowing that you now possess the knowledge to navigate through the aftermath of a catamaran capsize with confidence and grace. Bon voyage!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

Confident catamaran handling: how to master multihulls
- Katy Stickland
- July 3, 2020
Gavin Le Sueur shows Yachting Monthly how to step on board a catamaran for the first time with confidence

The Nautitech 40 Open, despite aimed at the cruising market, places an emphasis on performance and speed
It’s official: this year, for the first time ever, yacht charter holiday businesses ordered more catamarans for their fleets than monohulls, writes Gavin Le Sueur.
Capable of creeping into the shallowest of anchorages, sailing flat and fast, while being incomparably spacious, catamarans win the numbers game hands down and are the choice of many sailors looking for a perfect charter abroad.
Still, for even the most experienced monohull sailor, taking command of two hulls and two engines can seem a tall order.
No need for trepidation though. The wind and sea remain the same. The theory of sailing is unaltered.
What does change when sailing a multihull are the handling characteristics and some basic seamanship rules.
These changes are the result of using beam rather than ballast for stability.

Stepping ashore at the stern is the only option in this situation. This changes how coming alongside manoeuvres are conducted
Inherent in this is a lighter, more stable platform that accelerates quickly and has higher windage and different motion.
Seamanship is an evolving knowledge base.
Just when we think everything is as good as it can get and there’s no need for innovation, along comes a new idea that we eventually feel is essential.
From a design viewpoint, for instance, there are now production cruising cats being foil assisted to reduce wetted surface area and drag.
Materials tech also keeps changing the goalposts for multihulls.
As they get lighter and stronger, follow-on changes occur in beam and rig styles.
Multihulls come in all shapes and sizes.
Good seamanship requires knowledge of the theory behind sailing a multihull and understanding the characteristics of the specific design you are sailing.
Like all yachts, each multihull model has its own quirks.
This article provides an outline of some of the features you should be aware of when chartering a catamaran for the first time.
This knowledge base will also be of use to those sailing and anchoring in company with a multihull.
Manoeuvring a catamaran in a harbour
Twin-engined catamarans have wonderful manoeuvrability.
They can turn in their own length, which is good as they usually have twice the beam (or more) of an equivalent monohull and will slip sideways in crosswind due to reduced lateral resistance and higher hull and cabin tops.
Most of the boat is out of the water.
When docking, know the crosswind and current effects and allow for them, and how quickly you will come to a stop with engines in neutral or hard astern.
Because multihulls are lighter and have a higher wetted surface area than a monohull, they have reduced momentum and will generally pull up quicker.

Ensure the length of the yacht is well protected by fenders as each end will be used to exercise leverage
Twin-engine knowledge is needed to exit and enter berths.
There is little advantage in using the helm under 2 knots boat speed when you have two engines well spaced apart.
Learn to control your catamaran with engines alone at low speeds.
If both propellers rotate in the same direction, there will be an advantage docking in a specific way.
Counter-rotating engines lessen this effect.
You will be handling a much larger platform and, under you develop a feel for the size of the vessel, having crew on the bows help guide distance control.
If the multihull has daggerboards, lowering these while manoeuvring will reduce any sideways slip due to windage and increase it if your sideways movement is due to current.

Spend a little time getting used to the controls outside the marina and you’ll find that despite being big, modern cats are very responsive
Many multihulls have mini-keels and the effect on these of crosswinds and currents needs to be rehearsed before attempting a tight marina berth entry.
The stability of a multihull comes with a price: the platform is level, but the motion tends to be quicker.
There is reduced momentum and, as a result, they accelerate and stop much more quickly.
When manoeuvring, ensure the crew keeps ‘one hand for the boat’.
When sails are raised, be aware that the sheet lines are loaded immediately and wind gusts can cause rapid acceleration.
There is no heeling to spill the power.
Avoid sitting on or near loaded sheets.
Coming alongside leeward in a catamaran
1. position the boat parallel.

Position the boat parallel, with the bow angled slightly off the pontoon, aiming to bring the aft quarter alongside a cleat.
2. Let the wind bring you alongside

Control the boat’s angle while the wind pushes you on, then step ashore from the aft quarter with the sternline.
3. Use the outboard engine to hold steady

With the stemline secure, a few forward revs on the outboard engine will hold the boat in place while you secure the bow,
Coming alongside windward in a catamaran
1. line up the aft quarter with a cleat.

Instead of fighting the wind, simply aim to bring the aft quarter of the boat in line with a cleat.
Don’t worry about being parallel.
2. Secure a line and turn the boat with engine

With a short line to the pontoon, motor ahead with the outboard engine to bring the bows up into the wind.
3. Balance the power for a neat alongside

A few revs astern on the inboard engine will balance the boat to keep the aft line at 90° and the quarter clear of the pontoon.
Casting off a catamaran
1. cast off forward.

Remove the forward mooring line using the engines to hold position on the pontoon.
2. Make life easy with engines

If necessary, disengage the outboard engine to ease pressure on the remaining aft mooring line, then remove it.
3. Swing the stern out

Use the outboard engine to swing them stern out.
Stop the boat moving forward with the inboard, while the bow rests on a fender.
Taking control: Under sail
Under sail, multihulls respond to the wind quickly.
They accelerate with gusts and slow with lulls.
As a result, the apparent wind (the wind you feel) changes quickly also.
On many multihulls, it is easy to become complacent as to the true wind direction and strength.
You may appear to be pointing high and flying along when in reality, you have moved the apparent wind forward as you have accelerated and are actually laying off and losing ground to windward.
There is a sweet spot for each multihull where the sea state and wind strength combine to give you the optimum velocity made good (VMG) to windward.

Gauge how the wind is affecting you before making your final approach
This is not usually pinching hard to windward and it is also unlikely to be screaming away on a reach thinking you are tight on the breeze.
Downwind, a catamaran will outperform most similar-sized monohulls. Beware of the apparent wind in this situation.
It might be blowing 25 knots, your multihull running at 12 knots and you feel a gentle breeze.
Under spinnaker and full main, problems can quickly arise.
Although multihulls track well and tend not to broach, loss of concentration or autopilot failure can put you beam on and well overpowered.
Reef early. If you think you might need to reef, then reef.

Cruising speeds well into double figures require careful attention to the load on the rig
Better to be underpowered than overpowered, especially in unsettled or variable conditions.
A well-reefed multihull with sails well set will sail flatter and faster than one overpowered.
In downwind gusty conditions, the correct action when hit by a gust is to bear away and ease the sheets.
Never luff up as this increases the apparent wind.
By bearing away, you ease the pressure on the sails.
As soon as the gust passes, it’s time to reef .
When overpowered sailing to windward, immediately ease the traveller or mainsheet.
Be aware that the increased relative power in the headsail will want to drive the boat off the breeze.

Downwind under asymmetric, a catamaran will far outpace its monohull counterparts. Passage plan accordingly to utilise wind speeds
Round up slowly and keep control. Rapidly rounding up can stall the rudders and may worsen the capsize risk in big seas.
Spinnaker, headsail and main sheets should always be secured in a quick-release cleat.
A self-tailing winch or a cleat requiring tension to be taken to release is not quick release.
Never leave a winch handle in the winch as a released sheetline can easily foul on this.
Many multihull capsizes are a result of a series of issues – a squall, overpowered rig, inability to quick release, turning the wrong way to depower.
On a cruising catamaran these are reduced, but good seamanship dictates an awareness of what to do when the unexpected occurs.
Avoid getting caught ‘in irons’
Although not unique to multihulls, getting caught ‘in irons’ is a common problem.
‘In irons’ is the state of stalling when your multihull has pointed too high into the wind or lost momentum through a tack and all forward motion is lost.
It is possible to sail or drift backwards on a multihull with considerable skill.
To get out of irons, release the headsail and push the rudder over to the opposite side you would if going forward.
The multihull will drift backwards and around on to the tack required.
As soon as the bow falls away and the mainsail has wind on the windward side, sheet in the headsail, correct the helm and only sheet in the main once you are progressing forward.
Most cruising catamarans will generally have a conservative rig and minikeels.
Due to their higher windage, reduced momentum and increased hull surface area, sailing to windward requires a different skill set than on a monohull.
First of all, don’t try to point as high as the monohull you are used to sailing.

Modern catamarans rarely get stuck in irons. Maintaining power and speed through tacks, particularly in a seaway, will normally stop the boat from staling
Lay off and go for a bit of speed.
You have less weight so will generally go faster, albeit it further off the wind.
Doing this in practice, the velocity made good equation will work out in your favour.
Sailing to windward is about making the best speed toward your destination.
You might cover more ground but will generally arrive relaxed and at the same time (or earlier).
If the sea state is choppy and you are pounding into it, lay off a bit, power up the sails and punch forward.
The sea state can stall a cruising multihull quicker due to their reduced momentum.
Use the sails to maintain drive.
1. Get sailing

Putting the wind just off the bow and dropping the sail on to the coachroof makes for a trouble-free hoist clear of crew.
2. Aim for boat speed

Having raised the main and unfurled the job, bear away.
Aim for boat speed before getting closer to the wind.
3. Use beam to shape sails

The extra-wide traveller track can be used in place of a kicking strap to put more shape in the sail on a catamaran.
4. Use your instruments

Use the yacht’s instruments to track velocity made good, as well as true and apparent wind speeds.
Cats sailing flat sail faster. Avoid becoming overpowered and always reef early.
5. Avoid overpowering

Keep an eye on your leeward shroud if it’s very loose.
Consider whether you might be overpowered and if it’s putting too much strain on your rig.
Daggerboards and their effective use
Daggerboards increase the lateral resistance and assist in tracking and sailing to windward more effectively.
To adjust boards when sailing you may need to ‘unload’ them – jiggle the helm, partially round up and bear away quickly or adjust them when tacking.
On catamarans, when sailing to windward in light to moderate conditions have the centreboards fully down.
In very light winds have only one centreboard down to reduce the wetted surface area.
Continues below…

Get ready for your yacht charter holiday
Getting to grips with a few skills and checking your boat carefully will give you a more enjoyable yacht charter…

How to plan the perfect charter holiday
Whether you own your own boat or not, chartering offers the opportunity to sail somewhere different without complication. Will Bruton…

Multihull anchoring and mooring buoys
Handling a catamaran in manoeuvres can sometimes be easier than with a monohull, but there are a few surprising differences.…
To windward in heavy conditions, partially retract the boards, starting with the leeward board.
When sailing downwind the centreboards should be adjusted to balance the helm.
When broad reaching this usually means the windward board is half down and the leeward board nearly fully up.
A small amount of board down will improve downwind steering.
In storm conditions consider the tripping effect of increased lateral resistance and adjust the boards accordingly.
Remember to retract your boards when coming into shallow water!
Not all multihulls are the same.
A trimaran generally has a wider beam, single engine and rudder, and less internal space.
They heel a bit more and are usually better windward performers.

Trimarans generally have one engine. Credit: Emil Landry
Their wide hull windage is often less, and many have a central daggerboard which aids manoeuvrability and reduces lateral slide.
A trimaran will often be quicker to respond to the helm, and as they are proportionally lighter, will accelerate faster.
This is, of course, a generalisation as there are full bridge deck cruising trimarans with the internal volume and weight of a cruising catamaran.
Trimarans, like a single-engined yachts, require knowledge to the effect of the water flow over the rudder from the propeller when undertaking tight manoeuvring.

Further reading
Multihull Seamanship by Gavin Le Sueur (Fernhurst, £14.99)
After 22 years and five reprints, Multihull Seamanship has undergone a full rewrite to update the many changes that have come with further experience and design advances.
This book is an A-Z of skills for catamarans and trimarans, cruising and racing.
Dr Gavin Le Sueur is a lifelong multihull sailor with experience racing and cruising the seven multihulls he has owned.
He has survived cyclones and capsize, raced two-handed around Australia and cruised throughout the Pacific and Asia with his wife Catherine and their three children.
Accidents : How capsize-proof are cruising catamarans?
Johannes Erdmann
· 20.09.2023

When monohull yachts reach their stability limits, their crews can clearly feel it. The heeling increases sharply, often accompanied by a brilliant sun shot and loudly rattling sails. If there is too much cloth, the boat can overtake so far that it is difficult to hold on to the cockpit, let alone furl the genoa and tie in a reef. In other words: orange alert!
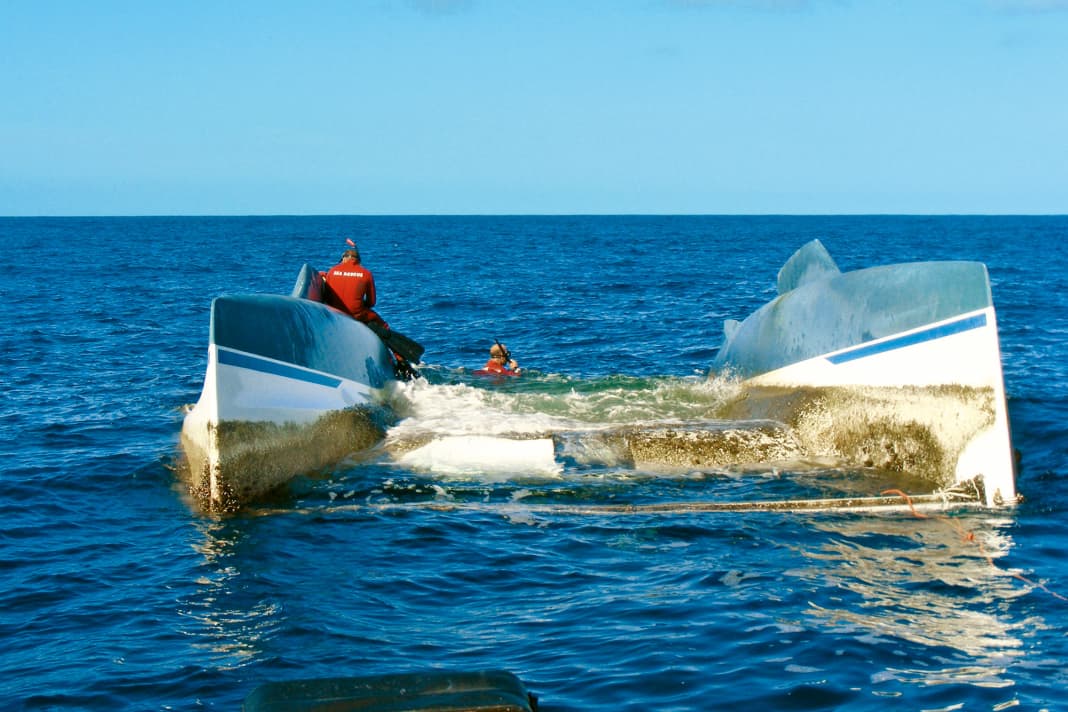

If you have already reduced the sail area with foresight, you will only be noticeably laid on your side in a gust. This reduces the wind pressure in the rig, and as soon as it eases, the ship rights itself again. This self-regulation and the ability to communicate at the limit makes keel yachts comparatively easy to handle. This is another reason why they are considered by many to be more seaworthy and safer.
Ride-on cats react differently to monohulls
A heavy, seven or even eight metre wide twin hull hardly heels. Thanks to its dimensional stability, its rig can withstand the force of the gust for much longer. This characteristic is particularly appreciated by beginners and occasional sailors, who often feel uneasy when sailing monohulls.
Static stability in comparison
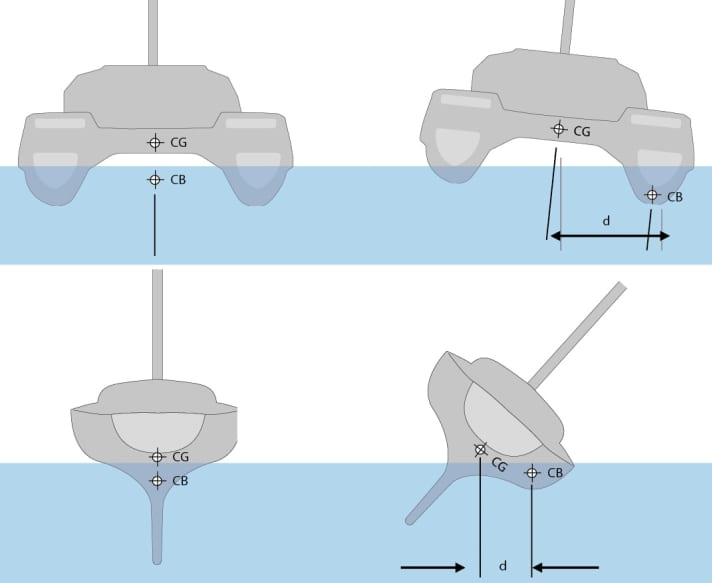
The righting moment (RM) defines how much resistance a yacht has to lateral forces. It is calculated from the product of the weight of the ship and the distance (d) between the centre of gravity (CG) and the centre of buoyancy (CB). In a monohull, both centres of gravity are close together even when heeled. Although the cat hardly heels when sailing, the empty hull is pushed slightly under water by the wind and the centre of buoyancy also moves to leeward. Due to the greater distance between the two centres of gravity, the righting moment of a catamaran is many times that of a monohull.
Most read articles

Stability curves
However, the advantage of greater initial stability does not override physics, nor does it replace the need for good seamanship. If the force applied is too great, even multihulls can tip over - not with long notice, but suddenly.
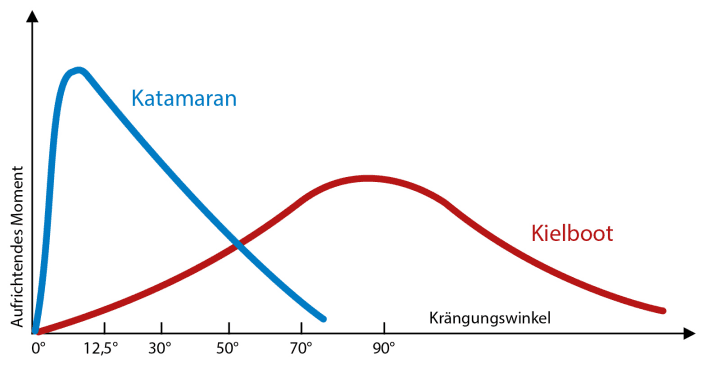
Even if the circumstances and the boats were very different and require a differentiated analysis, the overall picture nevertheless raises fundamental questions:
- Under what conditions can it become critical on catamarans?
- What safety reserves do they offer?
- And how has their design changed in recent years?
Firstly, it is important to categorise the accidents. The catamaran off Corsica, for example, was not an ordinary cruising catamaran, but an extremely lightweight construction from the 1990s. According to the shipyard, the Outremer 43 had an unladen weight of less than four tonnes. By comparison, a Lagoon 42 designed for cruising weighs a good three times as much today. Furthermore, the boat did not capsize while sailing, but at anchor after the wind had reached under the bridge deck with peaks of up to 90 knots.
The cat that capsized off Vlieland was also a lightweight construction, and an extremely compact one at that, with a hull length of just eight metres. The French-built Rackham 26, which was available in a basic and a regatta version until it was discontinued, is more of a sports catamaran than a touring catamaran and does not fulfil the CE requirements for offshore use. In the stormy conditions that were its undoing, it simply had no place in the choppy North Sea.
When does a catamaran capsize?
How much wind or wave does it take to exceed the stability limit? The physical background to stability is quite simple to outline: A boat that experiences a lateral force in the rig due to wind pressure always has a tendency to lean to one side. To prevent it from capsizing, it needs a righting moment (RM) that is stronger than the force applied. It can be understood as a kind of built-in static resistance to tipping and describes the product of the ship's weight and the distance (d) between the centre of gravity (CG ) and the centre of buoyancy (CB). Drift also plays a role, i.e. the tendency to counteract the wind pressure by pushing it away.
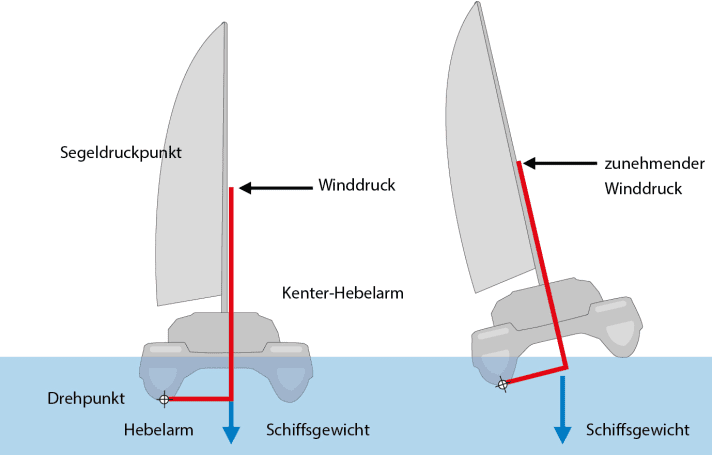
For those switching from a keelboat, this "sailing by the chart" is unfamiliar. But on a catamaran, there is no feedback for reefing by feel. Even more so than with a monohull: if in doubt, it is better to reduce the sail area too early than too late. A reefed cat sails better than an over-rigged one anyway.
The reaction to gusts also differs. If the wind suddenly picks up or there is more wind in a cloud than expected, there are two ways to temporarily compensate for the overclocking: When sailing courses from half to room wind, it helps to drop as far as possible without risking a gybe. Under no circumstances, however, should you jibe under pressure, otherwise the apparent wind will increase even more.
To quickly take pressure out of the sail, luff up on upwind courses, drop in half to full breeze
On an upwind course, on the other hand, it helps to lean a little, because usually only a few degrees are needed to reduce the pressure. The headsail and main may invert noticeably in the luff, i.e. show a counter-belly. On all courses, reef immediately after the gust has passed!

Bruno Belmont recommends always keeping an eye on the boat's speed in heavy weather and not surfing too fast into the valleys in big waves, otherwise capsizing over the bow is possible, especially with light trimarans.
Capsizing over the bow
With heavy cruising catamarans, there is hardly any risk of being undercut by the waves with the bows and going upside down when surfing. Today's boats have sufficient buoyancy in the bridge deck and in the area of the bows to quickly pull the bow tips back to the water surface when undercut. Capsizes over the bow happen more frequently on trimarans, such as the Dragonfly 28 on the Silverrudder 2015, on fast beach cats or extreme vessels such as the 72-foot America's Cupper from Oracle (see gallery above).
In a storm, Belmont advises setting a small storm jib when running off the waves and slowing the boat down with trailing lines, which he usually lays in long loops from stern cleat to stern cleat. If this is no longer sufficient, he recommends turning under a drift anchor.
He himself has only been scared once on a cruising catamaran, and that was decades ago. Back then, he was testing the prototype of the Lagoon 37 TPI in a severe winter storm. The problem: "The keels were still far too long back then, and we always had the feeling that we were about to capsize sideways." Keels that were too deep were a common problem with the cruising cats of the first generations because they had too much resistance leeward and caused the boats to stumble. For this reason, the windward centreboard is used at most on cats with centreboards in storms.
According to Belmont, capsizes are generally very rare. "We may have missed a few cases," he says, "but to my knowledge, only a handful of the 6,400 ships built have capsized."
So something must have gone wrong in Croatia when the Outremer 45 of a Berlin family capsized during a storm in mid-July. "In the storm, it only took a moment for the boat to capsize," the Croatian rescue team announced on its Facebook page. "But it took four long and labour-intensive days to turn the boat back around."
A well-built catamaran is extremely safe. Only a fire or a cargo ship can sink it
Once a cat is upside down, it is difficult to turn it back again. "One of the most fundamental laws of physics is that everything in nature seeks its most stable position," writes American blogger and catamaran fan David Crawford on his website. And admits: "Once a catamaran is upside down in the ocean, it has found its most stable position." As unfortunate as this is, Crawford also sees the good in it: "For a monohull, the most stable position is at the bottom of the ocean." In his opinion, there is no safer ship than a catamaran. "The most that can sink a well-built cat is a fire or a cargo ship."
Unsinkable life raft
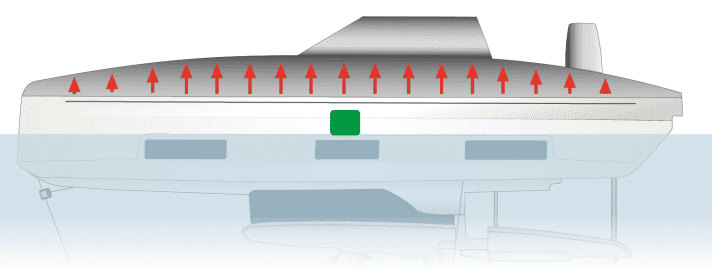
[{{{type}}}] {{{reason}}}
{{texts.summary}} {{#options.result.rssIcon}} RSS {{/options.result.rssIcon}}
{{{_source.title}}} {{#_source.showPrice}} {{{_source.displayPrice}}} {{/_source.showPrice}}
{{{_source.displayUrl}}}
{{{_source.displayDate}}}
{{{_source.description}}}
{{#_source.additionalFields}} {{#title}} {{{label}}}: {{{title}}} {{/title}} {{/_source.additionalFields}}
What we can learn from Anna's Capsize
August 15, 2010
On July 31, 2010 the Atlantic 57 Catamaran, Anna, with a crew of two, was capsized by a violent squall 125nm from Tonga in the South Pacific. This news came as a shock to me and most of the owners of Atlantic Catamarans, as well as sailors of other cruising catamarans. Fortunately neither the captain nor crew was injured beyond minor cuts and bruises.
Also fortunate was the fact that the EPIRB was located by the crew, switched on and a signal was immediately picked up by the satellite system. The owner had registered the EPIRB properly and the USCG was able to reach the owner's contact person to confirm details of the boat and crew before sending out an Orion search plane. The New Zealand Rescue Services plane located the catamaran quickly, and spoke to the captain by VHF radio. A ship that was less than 100 miles away was diverted and roughly 12 hours later picked up the two wet sailors.
As sailing calamities go, this could have been much worse. For decades I have dreaded the day when someone gets seriously hurt or killed sailing one of my designs. This accident certainly had the potential to do one or the other and I am very thankful that it did not.
In order to reduce the chances as much as possible of another capsize it is important to examine what happened and develop a methodology to avoid capsize. If capsize should occur it is also essential that some basic things are done beforehand to insure survival of the crew during as long a time as it might take to be picked up by another vessel.
Ten years ago I had the itch to learn to fly sailplanes and took the regular course of flight instruction. What was immediately apparent to me is how safety conscious the world of aviation is. In aircraft, accidents happen very fast and are often deadly. The major cause is pilot error, which is often due to either momentary confusion, lack of skill, or distraction. To combat this, many aspects of flying, such as takeoff, landing, and flying in turbulence are highly regimented. Each is performed with its own check list. You will not get a license to fly unless you can demonstrate that you know all of these check lists and have the skill to perform them properly.
Offshore sailing on the other hand is largely a free-form activity. Cruising sailors, me included, hate being told what to do at any level. Many of us are self taught and sail either alone or with small crews. We learn from each other- sometimes- but many sailors have not had the benefit of ever sailing long term with people of great experience. To complicate matters further, the boats are all so different that rules which may work for one size and type maybe useless for another. With that in mind I still think it will be wise to develop a protocol for multihull sailors to follow in squally or extremely gusty conditions.
Squalls come in all shapes and sizes. Most are benign, a little bit of rain, a few minutes of increased wind, then a stretch of near calm after it passes. They are often frustrating, but no big deal. Now and then a big one comes along, advertising itself long in advance with thunder and lightning, a black line of clouds and a froth of white on the sea surface as it approaches. These are the scary ones. You watch and wait, reef or drop sails ahead of time. The squall comes and does its thing, and in an Atlantic Cat, you stay nice and dry in the pilot house. Fine. No worry this time. The bark is often worse than the bite.
Then there is the dangerous squall. These are the ones that don't look that bad. There may be a large rain shield, it may not look too dark and or ominous, but within the squall, behind the first band of rain, lurk very strong winds. These are the squalls that can really bite. Only 2 weeks ago, as Kate and I sailed Javelin south along the Windward Islands in the Caribbean, a squall of this type hit us hard. There was a tropical wave passing through which was in the process of turning into a tropical storm, and atmospheric conditions were quite unstable with overcast skies and frequent squalls. It had been blowing 18-20 knots and we had a single reef in the main and the full self tacking staysail. We were sailing at a true wind angle of 50 degrees or so at about 9 knots. The squall looked like the others more or less, though I was concerned that its movement seemed different. In any case, a few minutes after the initial wind gust and rain, the wind really cranked up and headed us. Then it increased again and headed us more. There was way too much wind for the sail we carried, so I luffed up enough to depower Javelin, trying to walk the fine line between flogging the sails violently and keeping our boat speed down below 12 kts. It was exciting, too exciting, and when it did not let up after a few minutes we dropped the mainsail entirely. If truth be told, the whole event left me pretty rattled. We experienced an increase from 20 to 45 kts of wind in a fraction of a minute along with a 90 degree wind shift. I did not expect that at all. And that's the lesson. Sometimes a squall will dish out something that you don't expect and are not prepared for. It may only be one out of 50 or 100 squalls that are truly dangerous but you don't know and can never be sure which ones they are.
The report from Anna was the squall did not look any different than the others. But the last wind reading they noticed was 62 knots. That's a lot of wind. And they had the same sail up as Javelin did in the squall I just mentioned, a single reefed main and the full self tacking jib. Keep in mind that power in the wind increases as the square of the velocity. Doubling the velocity from 20 to 40 kts increases the pressure on the sails by FOUR times. Tripling the wind velocity from 20 to 60 kts increases the wind pressure by NINE times.
Reefing not only reduces the sail area but removes sail area from up high where the wind pressure exerts the most leverage trying to turn the boat over. The typical catamaran mainsail is large with a very rounded roach that increases the sail area near the top of the sail where it exerts the most heeling force. The combination of both reducing the sail area and reducing its height by reefing has a dramatic effect on stability, allowing the boat to stand up to much stronger gusts.
The autopilot is indispensable for short handed cruising. I love the autopilot on Javelin and use it almost all the time. It steers the boat very well, better than most helmsmen. But the autopilot is a dumb machine. It cannot see the black squall line coming nor the water being whipped white by the leading edge of a gust front. It does not deduce that since the wind velocity has increased from 20 to 30 knots in 6 seconds that it may shortly increase to 50 knots. The autopilot has no survival instinct. The autopilot cannot anticipate the future. It has severe limits and sometimes,
The Autopilot must be turned off!!
We sailors have to physically take control of the boat in a squall. Pilot off, hands on the wheel, ready to respond.
Putting it together:
On board distractions during moments of stress can overwhelm clear thinking. Discomfort from heat or cold, wet, fatigue, or motion sickness can and will diminish a sailor’s energy, mental acuity, responsiveness, and judgment when it is most needed. It is useful to remember the aircraft pilot’s invaluable, ever-ready, life saving tool in difficult situations. The pilot relies on familiar checklists and procedures to block out distractions, focus attention, and to make correct decisions quickly. The sailor can benefit from the same kind of help and preparation.
With the above in mind I offer the following procedure for sailing a cruising multihull in gusty or squally conditions:
STACS: it stacks the deck in your favor. S – sail area T - trim A- autopilot C- course S- sheets
S- Sail area . Sail area should be adjusted to deal with the expected increased velocity of gusts. If there are numerous squalls in the area it makes sense to reef deeper than normal. The same goes for sailing behind high capes and mountains where strong gusts are often present. Most Atlantic Cat sailors report how little a double reef slows the boat when there is a decent breeze blowing. The boat is able to deal with far more wind with a double reef than a single reef. That does not mean that no harm can come with shortened sail, but it does mean the velocity of a gust will have to be much greater to endanger the boat- and therefore far less likely.
T- Trim . When it is clear that a squall will overtake the boat, the sail trim should be adjusted to better cope with gusts. Typically this means moving the main traveler to leeward somewhat and easing the sheets if not reducing sail further.
A- Autopilot . When the squall is at least a couple minutes away turn off the autopilot and take control of the steering. This will enable rapid response should an overpowering gust occur.
C- Course . Adjust the heading to an appropriate and safe course. Keep in mind that large wind shifts are common in squalls. If the boat is sailing against the wind (true wind forward of the beam) and a dangerous gust occurs it is normal practice to turn into the wind enough to de-power the sails. Ideally the course can be held on the edge between flogging the sails and overpowering the boat until either the squall subsides or sail can be further reduced. Fully battened mainsails are usually well behaved but the jib may flutter violently for a short period. If sailing to windward it can also be very helpful to have the engines idling and ready because there may be need to drop the mainsail and that will be easier if the boat can be held head to wind. If the cat is sailing down wind (true wind aft of the beam) normal practice is to alter course away from the wind. This reduces the apparent wind velocity by your boat speed and in most cases is the least painful way to weather the squall. The main boom preventer should be made up to guard against an accidental jibe.
S- Sheets . In the case of an overpowering gust the first sheet to ease is the main sheet. In most catamarans the mainsail is likely to be larger than the jib and its area is concentrated higher up which contributes more toward turning the boat over than the jib.
There are so many variables – wind direction and strength, maneuvering room, vessel size and type, number of crew and their level of experience – that being too specific is likely to be counter productive. What is important is to recognize the potential danger in violent squalls and to develop an easy-to-remember protocol for dealing with dangerous wind gusts should they occur.
In the book titled The Cruising Multihull, I wrote extensively on the subject of capsize. At the time I drew a distinction between wind induced capsize and wave induced capsize. At the time, I judged capsize by wind to be the less likely of the two, because the risk could be controlled by the sailor by reducing or striking sail and altering course. On the other hand there is far less that the sailor can do to avoid wave capsize if the conditions are sufficiently bad to roll the boat over by wave action alone.
In retrospect, I did not adequately consider the risk from short duration violent wind gusts. There have been two capsizes of Atlantic catamarans in the 20 years since that book was published. Both capsizes were from strong winds. One was an Atlantic 42 on Lake Michigan in 2004, the other was Anna, which happened a couple weeks ago in the South Pacific. Even though the circumstances were different, there is a remarkable similarity in how the boats were capsized.
To summarize: 1) Neither captain thought capsize was even a possibility until way too late 2) Both boats were under autopilot, which had the helm all the way through the capsize 3) The main sheet was never eased or released
Anna was a very well built and extremely sea worthy catamaran. Her loss is a “wake up call” to all of us who sail catamarans. Accidents do happen, typically when you don't expect them. The cruising catamaran is normally so easy and so forgiving that we can be lulled into complacency.
Be aware, be alert. Have a plan.
Spectacular footage shows US catamaran flipping over and capsizing during pre-race in Bermuda
Sport Spectacular footage shows US catamaran flipping over and capsizing during pre-race in Bermuda
The crew of a catamaran that flipped during the pre-race at a Bermuda event escaped unharmed, as vision showed the US team being flung through the air.
The F50 capsized during the third and final practice race, and while the crew were unhurt in the spectacular moment, the team was forced to withdraw from the race due to the damage sustained to the catamaran.
Data from the vessel showed that wing trimmer Victor Diaz de Leon pressed a button by accident, which inverted the wing of the boat.
"While operating the wing, I chose the wrong function on my control panel, which caused our boat to flip. It was very scary and I'm thankful all my teammates are safe," Diaz de Leon said after the incident.
Team CEO and strategist Mike Buckley said mistakes can happen.
"We compete as a team and whatever the outcome is — whether it's what we want — we win and lose as a team and we learn from it," he said.
The ABC of SPORT
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Orlando Cepeda dies
Lindsey Vonn goes sailing with Team USA and joins grinder Anna Weis on the winches
Lindsey Vonn, second from right, Olympic skiing champion, rides a USA SailGP Team chase boat during racing practice ahead of the New York Sail Grand Prix, Friday, June 21, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Julia Nikhinson)
International SailGP teams practice racing ahead of the New York Sail Grand Prix, Friday, June 21, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Julia Nikhinson)
Members of the New Zealand SailGP Team man their catamaran ahead of the New York Sail Grand Prix, Friday, June 21, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Julia Nikhinson)
Members of the Canada SailGP Team practice racing ahead of the New York Sail Grand Prix, Friday, June 21, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Julia Nikhinson)
- Copy Link copied
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River on Friday aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team.
The retired skiing champion was the “sixth sailor” with Team USA for a jaunt off Manhattan before all 10 crews held practice races ahead of this weekend’s Mubadala New York Sail Grand Prix. It’s the penultimate regatta in Season 4 of tech billionaire Larry Ellison’s global league.
While there certainly will be some boardroom work involved for Vonn — she envisions helping with brand strategy and partnerships — being on the water was the place to be.
“For me, part of the excitement about being on the board is just being involved with another adrenaline sport,” Vonn said in a phone interview with The Associated Press.
The wind wasn’t strong enough to do much foiling, which is what makes the F50 catamarans among the world’s fastest boats.
The wind did pick up just after Vonn got off the boat.
“Just my luck,” she cracked. “It wasn’t what I hoped for. As someone that’s missing speed as a retired athlete, I was really hoping to go fast. But to be actually doing something, or at least they let me feel like I was doing something, was exciting. ... Downhill’s a little bit faster. But again, I’m retired so I’ll take what I can get.”
She was thrilled to work alongside grinder Anna Weis, turning the winches that help the wing trimmer do his job.
“It was fun,” Vonn said. “I was grinding with Anna and kind of following their lead. I was a little bit of a fish out of water, to some degree, but it was really fun. Grinding is so hard and what Anna does as a woman, I think, is really, really incredible. I don’t think many people know how difficult a role like that really is, so I just have a lot of respect for her and the team. To have a coed team like that, it’s amazing.”
As part of the Women’s Pathway program, every SailGP team must have a woman onboard. Weis, who competed in the Tokyo Olympics in the foiling Nacra 17 catamaran class, has done the most races as a grinder of any woman in SailGP, and she also trims the jib. Her job requires strength, cardiovascular endurance and finesse.
“She’s such an amazing young woman who’s incredibly strong,” Vonn said. “She’s a great example for the next generation.”
With women’s sports reaching a tipping point, Vonn mentioned the work Billie Jean King has done over the decades in championing women’s equality in sports, and how current women athletes, including in SailGP, “are showing people what is possible. And again, it’s a combination of the past paving the way for the present and the present really taking the opportunity and maximizing it.”
Vonn was outfitted in full protective gear, including a crash helmet. Team USA had a dramatic capsize in practice racing in Bermuda in early May that was caused by a crew error. While there were no serious injuries, the boat was damaged to the point the team missed the regatta.
“Since the capsize of a couple of weeks ago, I wanted to make sure I actually listened to the safety protocol this time,” said Vonn, who also sailed with an America’s Cup crew in 2016 off Manhattan before an exhibition regatta.
“I saw the video of it. It was pretty crazy,” she said. “Honestly, I think things like that are really exciting. Obviously, again, it was very expensive, but that’s what makes it exciting. Those are the type of things that make the sport really interesting.”
Vonn retired from skiing in 2019 after winning three Olympic medals, including one gold, and four overall World Cup titles. She was the first woman to win 82 World Cup races.
Team USA was purchased in November by a group of investors from the sports, technology and entertainment worlds. They include former Alabama linebacker Dallas Turner, who was drafted by the Minnesota Vikings at No. 17 overall; actress/producer Issa Rae; founding Uber engineer Ryan McKillen; and professional sailor Mike Buckley.
On Friday, Team USA announced a multiyear partnership with Tommy Hilfiger starting in 2025 that will include boat branding and crew uniforms.
The Americans are out of the running for the $2 million, winner-take-all season championship race July 14 in San Francisco. New Zealand sits atop the 10-boat fleet with an 11-point lead over Spain, with three-time defending champion Australia another point back in third.
Bernie Wilson has covered sailing for the AP since 1991.
AP sports: https://apnews.com/hub/sports
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access only $1 for 4 weeks.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition
Lindsey Vonn goes sailing with Team USA and joins grinder Anna Weis on the winches
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River on Friday aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team.
The retired skiing champion was the “sixth sailor” with Team USA for a jaunt off Manhattan before all 10 crews held practice races ahead of this weekend’s Mubadala New York Sail Grand Prix. It's the penultimate regatta in Season 4 of tech billionaire Larry Ellison's global league.
While there certainly will be some boardroom work involved for Vonn — she envisions helping with brand strategy and partnerships — being on the water was the place to be.
“For me, part of the excitement about being on the board is just being involved with another adrenaline sport,” Vonn said in a phone interview with The Associated Press.
The wind wasn't strong enough to do much foiling, which is what makes the F50 catamarans among the world's fastest boats.
The wind did pick up just after Vonn got off the boat.
“Just my luck,” she cracked. “It wasn’t what I hoped for. As someone that’s missing speed as a retired athlete, I was really hoping to go fast. But to be actually doing something, or at least they let me feel like I was doing something, was exciting. ... Downhill's a little bit faster. But again, I’m retired so I’ll take what I can get.”
She was thrilled to work alongside grinder Anna Weis, turning the winches that help the wing trimmer do his job.
“It was fun,” Vonn said. “I was grinding with Anna and kind of following their lead. I was a little bit of a fish out of water, to some degree, but it was really fun. Grinding is so hard and what Anna does as a woman, I think, is really, really incredible. I don't think many people know how difficult a role like that really is, so I just have a lot of respect for her and the team. To have a coed team like that, it’s amazing.”
As part of the Women's Pathway program, every SailGP team must have a woman onboard. Weis, who competed in the Tokyo Olympics in the foiling Nacra 17 catamaran class, has done the most races as a grinder of any woman in SailGP, and she also trims the jib. Her job requires strength, cardiovascular endurance and finesse.
“She's such an amazing young woman who's incredibly strong,” Vonn said. “She's a great example for the next generation.”
With women’s sports reaching a tipping point, Vonn mentioned the work Billie Jean King has done over the decades in championing women’s equality in sports, and how current women athletes, including in SailGP, “are showing people what is possible. And again, it’s a combination of the past paving the way for the present and the present really taking the opportunity and maximizing it.”
Vonn was outfitted in full protective gear, including a crash helmet. Team USA had a dramatic capsize in practice racing in Bermuda in early May that was caused by a crew error. While there were no serious injuries, the boat was damaged to the point the team missed the regatta.
“Since the capsize of a couple of weeks ago, I wanted to make sure I actually listened to the safety protocol this time,” said Vonn, who also sailed with an America's Cup crew in 2016 off Manhattan before an exhibition regatta.
“I saw the video of it. It was pretty crazy," she said. "Honestly, I think things like that are really exciting. Obviously, again, it was very expensive, but that’s what makes it exciting. Those are the type of things that make the sport really interesting.”
Vonn retired from skiing in 2019 after winning three Olympic medals, including one gold, and four overall World Cup titles. She was the first woman to win 82 World Cup races.
Team USA was purchased in November by a group of investors from the sports, technology and entertainment worlds. They include former Alabama linebacker Dallas Turner, who was drafted by the Minnesota Vikings at No. 17 overall; actress/producer Issa Rae; founding Uber engineer Ryan McKillen; and professional sailor Mike Buckley.
On Friday, Team USA announced a multiyear partnership with Tommy Hilfiger starting in 2025 that will include boat branding and crew uniforms.
The Americans are out of the running for the $2 million, winner-take-all season championship race July 14 in San Francisco. New Zealand sits atop the 10-boat fleet with an 11-point lead over Spain, with three-time defending champion Australia another point back in third.
Bernie Wilson has covered sailing for the AP since 1991.
AP sports: https://apnews.com/hub/sports
Trending Reader Picks

Biden addresses poor debate performance
- Jun 28, 2:09 PM

Biden's weakness displayed at debate: ANALYSIS
- Jun 27, 11:34 PM

5 takeaways from Biden-Trump presidential debate
- Jun 27, 11:56 PM

Shark attacks man while he's fishing in Florida
- Jun 28, 4:38 PM

Parents at beach with kids die in rip current
- Jun 21, 8:38 AM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
hh catamarans location

Where Are HH Catamarans Made? (Find Out Here)

Have you ever wondered where the renowned HH Catamarans are made? If youre considering purchasing one, youll want to know the details about the manufacturing process and the quality of materials used.
In this article, well take a look at the HH Catamarans overview, the manufacturing process, cutting-edge technology used, the quality materials and customization benefits, the experienced craftsmanship, and the customer testimonials.
Whether youre looking for a luxury yacht, a high-performance sports boat, or a family cruiser, youll find out what makes HH Catamarans special and why they are among the most sought-after vessels on the market.
Table of Contents
Short Answer
HH Catamarans are made in the United States, in Clearwater, Florida.
HH Catamarans has a state-of-the-art, climate-controlled facility, where the catamarans are constructed with the highest quality materials.
The company takes pride in their craftsmanship and attention to detail, and uses the latest in cutting edge technology to ensure the quality and performance of their catamarans.
HH Catamarans Overview
HH Catamarans is a leading manufacturer of luxury sailing catamarans based in Cape Town, South Africa.
For over 20 years, the company has been dedicated to providing the best sailing experiences possible by utilizing the latest technology and the best materials available in their state-of-the-art production facility.
At HH Catamarans, their commitment to excellence is evident in every catamaran they produce.
Every boat is custom-made to the exact specifications of the customer to ensure that their sailing experience is beyond compare.
The companys attention to detail and craftsmanship guarantee that each and every boat is of the highest quality.
The company prides itself on their commitment to innovation and excellence.
From their design and engineering processes to their production facility, HH Catamarans strives to stay ahead of the competition by constantly improving their processes.
They research the latest materials and technologies and use them to create the best sailing catamarans on the market.
HH Catamarans also puts a strong emphasis on customer service.
The company is committed to providing customers with the best possible experience and they go out of their way to ensure each and every customer is satisfied.
From the initial design process to delivery, the team at HH Catamarans is dedicated to providing the best level of service.
Whether youre an experienced sailor or a novice, the team at HH Catamarans can help you find the perfect catamaran for your needs.
With their commitment to quality, innovation, and customer service, HH Catamarans is the top choice for luxury sailing catamarans.
Manufacturing Process Overview

HH Catamarans are built in Cape Town, South Africa and the construction process is overseen by a team of experienced and highly-skilled professionals.
The facility utilizes the latest technology and best materials available to guarantee each boat is of the highest quality.
From the design stage to the construction and finishing stages, the team at HH Catamarans focuses on providing a truly custom experience for each and every customer.
The entire manufacturing process is carefully planned and managed to ensure that each boat is built to the exact specifications of the customer.
The production process begins with the design phase, where each boat is designed and engineered to meet the customers exact specifications.
The construction phase then follows, where experienced craftsmen use the latest techniques and materials to construct the boat.
All components are carefully inspected for quality assurance, and any necessary modifications or repairs are made.
The boat is then moved to the finishing area, where the team applies a range of treatments to ensure the boat is protected from the elements.
From painting and varnishing to the installation of hardware and electronics, the team utilizes the latest techniques and materials to ensure the boat is safe and sea-worthy.
Once the boat is complete, it is subjected to rigorous testing and inspection to ensure it meets the customers specifications.
With over 20 years of experience in the industry, HH Catamarans is dedicated to providing the best sailing experiences possible.
The team at HH Catamarans is passionate about creating the perfect sailing experience for each and every customer, and their attention to detail and commitment to quality is evident in every boat they build.
Cutting-edge Technology
When it comes to luxury sailing catamarans, HH Catamarans stands out for its use of cutting-edge technology.
Located in Cape Town, South Africa, their state-of-the-art production facility is designed to ensure each and every boat is of the highest quality.
From the initial design process to the final assembly, HH Catamarans utilizes the latest technology available to ensure their boats are built to the exact specifications of the customer.
By utilizing advanced computer numeric control (CNC) machinery, HH Catamarans is able to create custom-made boat components with unparalleled precision.
The CNC machines are programmed with specific instructions and then the components are machined with robotic arms to exact specifications.
This helps to ensure that the components fit perfectly together and that the boat is built to the highest standards.
In addition, the cutting-edge technology used by HH Catamarans allows for the use of the latest materials available.
Using a combination of lightweight, high-strength composites and traditional building materials, HH Catamarans can create a boat that is both lightweight and durable.
This makes it possible for the customer to customize their boat to their exact specifications while still ensuring a high quality end product.
By utilizing cutting-edge technology and the latest materials available, HH Catamarans is able to guarantee an unparalleled sailing experience.
So if youre looking for a luxury sailing catamaran, look no further than HH Catamarans.
Quality Materials

The quality of the materials used to construct HH Catamarans is second to none.
Each boat is constructed with the highest grade carbon fiber and Kevlar components, ensuring that the boats are lightweight yet incredibly strong and durable.
The carbon fiber and Kevlar components are sourced from trusted suppliers, ensuring that only the best materials are used.
The hulls are also constructed with a combination of marine grade stainless steel and aluminum, making them incredibly strong and resistant to corrosion.
Additionally, each boat is treated with a special sealant to provide extra protection from the elements.
With these high-quality materials, HH Catamarans are built to last and will provide years of reliable performance.
Customization Benefits
For those who want the ultimate sailing experience, HH Catamarans offers customization options that are perfect for customers looking to make their boat truly their own.
The production facility in Cape Town, South Africa is equipped to create catamarans tailored to anyones exact specifications.
From the size and shape of the boat, to the interior and exterior design, HH Catamarans give customers the opportunity to create a sailing experience that truly reflects their individual style and preferences.
The experienced team at HH Catamarans puts in the extra effort to ensure that each boat is built to the highest quality standards.
They use only the best materials and the latest technologies to provide customers with a product that is of the utmost quality.
The process is meticulous and thorough, and all boats are tested for optimal performance before they are allowed to leave the facility.
Customers can also rest assured that their boat will always be in safe hands.
The team at HH Catamarans has over 20 years of experience in the industry and is dedicated to providing the best sailing experiences possible.
From providing customers with detailed instruction manuals to offering comprehensive warranties, HH Catamarans is committed to making sure every customer is satisfied with their experience.
Whether youre looking for a boat for leisure, sailing competitions, or just a weekend adventure, HH Catamarans has the perfect boat for you.
With their customization options and dedication to quality and safety, HH Catamarans is the perfect choice for those looking for a truly unique and enjoyable sailing experience.
Experienced Craftsmanship

When it comes to manufactured products, quality is always a top priority.
HH Catamarans understands this better than anyone.
Thats why their state-of-the-art production facility in Cape Town, South Africa is staffed with some of the most experienced and skilled craftsmen in the business.
Every boat is built to the exact specifications of the customer, ensuring that each and every one is of the highest quality.
In addition, the facility utilizes the latest technology and the best materials available to ensure that the boats are as durable and reliable as possible.
Testimonials
For over 20 years, HH Catamarans have been a leader in the luxury sailing catamaran industry.
The company is committed to providing the highest quality sailing experience, and the testimonials from customers prove it.
The state-of-the-art production facility in Cape Town, South Africa, is where every HH Catamaran is meticulously crafted.
Utilizing the latest technology and the best materials available, each boat is designed to the exact specifications of the customer.
This ensures that each boat is tailored to the individual, creating a truly custom experience.
The reviews from customers who have purchased and sailed HH Catamarans are overwhelmingly positive.
From enthusiastic racers to leisure sailors, everyone has praised the quality and performance of the catamarans.
Many customers have noted the exceptional customer service they received, including the attention to detail and the hands-on approach that HH Catamarans takes with every boat.
One customer, a sailing enthusiast from the United States, said: I was so impressed with the quality of the boat and the customer service that I received. The entire process was smooth and the boat sailed like a dream. I cant recommend HH Catamarans enough.
Another customer, a former racer from Europe, said: I raced for many years and have never sailed anything like this. The boat is fast and light and handles so well. I cant believe the performance Im getting. Im so glad I chose HH Catamarans.
These are just a few of the many glowing reviews that HH Catamarans has received over the years.
This is a testament to the craftsmanship, quality, and commitment to excellence that goes into every boat.
Their boats are built with the latest technology and the best materials available, and they are dedicated to providing the best sailing experiences possible.
With HH Catamarans, you can be sure that you are getting the highest quality boat that money can buy.
Final Thoughts
For those looking for a reliable and luxurious sailing experience, HH Catamarans is the perfect choice.
Their state-of-the-art production facility in Cape Town, South Africa, allows for the use of cutting-edge technology and quality materials to build each boat to the exact specifications of the customer.
If you’re looking for a custom catamaran that you can rely on, look no further than HH Catamarans.
James Frami
At the age of 15, he and four other friends from his neighborhood constructed their first boat. He has been sailing for almost 30 years and has a wealth of knowledge that he wants to share with others.
Recent Posts
When Was Banana Boat Song Released? (HISTORICAL INSIGHTS)
The "Banana Boat Song" was released in 1956 by Harry Belafonte. This calypso-style song, also known as "Day-O," became a huge hit and remains popular to this day for its catchy tune and upbeat...
How to Make Banana Boat Smoothie King? (DELICIOUS RECIPE REVEALED)
To make a Banana Boat Smoothie King smoothie at home, start by gathering the ingredients: a ripe banana, peanut butter, chocolate protein powder, almond milk, and ice. Blend the banana, a scoop of...

HH44 Catamaran: The sailing TIE-Fighter
- April 19th, 2024
- Sailing Yacht
Safe the best for last, as they say, right? And as such I´d like to write my final article from this year´s La Grande Motte Multihull show about a very special catamaran. HH Catamarans is neither a newcomer on the boating market – actually, the company was founded some 12 years ago by the renowned boatbuilders Mr. Hudson and Mr. Hakes – hence the name “HH” Catamarans. Nor is their no-compromise approach new.

Honestly, I´ve seen them around but never really approached this brand or boat. Maybe that is because “HH” is an awkward name to speak, but surely because I did not really know what HH Catamarans was all about and frankly, what an awesome build their boats really are! In this, join me for a really cool walkthrough in a yacht that sets the bar a bit higher. Quite a bit!
Emerging Player: HH Catamarans
First things first: Yes, these are boats which are built in China. But, like with so many other things, it is not the origin of a product that is deciding but the briefing and budget given to the makers. In terms of HH Catamarans, the company has set up a state-of-the-art production plant in Xiamen that is owned and run by the company (not a rented production facility!). I haven´t been there but from what one can see online and by talking to the guys present at the HH Cats stand, this is the best from the best. Most advanced CNC , infusion and Carbon Fiber processing technology on the market. Cheap China? Not at all! This 44-footer comes with a plus one million price tag: An HH Catamaran is absolute top shelf luxury.

As apparently the stand and the catamaran was full the whole boat show, I walked by several times hoping for a calm spot to not being interfered with when taking pictures. Which was really hard. Even before opening and after closing times, the cat was full of people checking it out. Which is a good sign. And I can understand why it attracts so many people: Nearing myself from bow, the design and lines are really breathtaking!

The extra-slim hulls and the negative stems make for a fine, slicing entry. The freeboard is very high and distance from the middle section to the waterline pleasantly high: A sign for a very seakind and fast catamaran. I liked the angled shapes very much, instantly I am reminded of the “Star Wars” starship design of the famous TIE-Fighters by the Empire – a daring look for sure. The high class paint of the hull sets it apart from the white deck-salon. A starship, ready to fly.

This enthusiasm changes a bit when I look from a stern angle at the boat. Again, I am reminded of another starship, this time Captain Jean-Luc Picard´s ENTERPRISE D, which looks awesome seen from some angles and doesn´t work anymore from others. The reason for this strange look of the HH 44 are the closed aft sections. The boat appears to have been sort of “cut off” or “sawn away” at the stern – but later more to this, because there is a not so stupid reason.
A hidden gem
Anyways, right on the last day of the “Multicoque 2024” it was my last chance to do the walkthrough and so I went over. Again, even for a traditionally lame last boat show Sunday, the yacht was full of people. So I thank all the guys who allowed me to have them on my pictures here, and so I started my tour.

The HH 44 is the smallest entry level catamaran of the range. The shipyard offers a staggering palette of eight models, ranging from 44 over 50, 52, 60, 66, 80 and a huge 88 feet flybridge super-catamaran. The model shown at La Grande Motte was a used boat, so not brand new anymore, but there were no visible signs of wear. Also, the HH 44 is offered in two principal versions: A cruising catamaran and a high-performance cruiser with daggerboards as displayed at La Grande Motte. Setting my foot into the salon, I quickly realized that this is truly a hidden gem.
A starship for sure!
To stay a bit with the starship-theme, it doesn´t feel like being on a boat. Her design – lightweight sandwich and painted carbon structures – is kept in shiny gloss-white and hard black contrasts. Only a few other colors, like the LED-lighting or slightly crème-colored leather cushion derive from the black/white design. I like it, it really feels like being on a starship.

The salon offers a classy layout with a nice wide L-settee around a reasonably sized dinner table. The windows to the front, the sides and abaft are huge and offer a true 360-degree roundsight. Having a lightweight build utilizing the latest material for stiffness, there are literally no bigger solid walls, it really feels like as if the roof is hovering above the deck.

To make a connection from the “inside” to the “outside”, which is the large aft cockpit under a rigid roof, the large galley window can be folded up and secured under the roof, the sliding door is also removed. In this, a ship´s cook facing backwards will have most fun when providing a meal. Dishes and food can quickly be shuffled out or hauled back in after a meal. Right onto the worktop where a large single sink is located. That this catamaran is a different level indeed can be seen at some really nice details.

For example, the integrated steps to go onto the roof are – at the inside – nicely stitched and wrapped in padded leather. Wow! I absolutely loved how nicely the sunshades work which are made of up to three moving fans going seamlessly up and down. Everything is made of a nice, “heavy” quality – there are literally no cheap plastic clasps installed in the boat.

For a 44-footer, die salon made a great impression on me. The layout is classy and very practical. It holds also a fine balance between providing as much (free) space as possible and at the same time having a safe (less empty volume) room to roam about even in heavy seas violently moving the boat. Comparing the HH 44 salon to “our” Excess 14 , which has roughly the same measurements, this one has less room and feels more “filled”, but on the other hand, comes with a very cruising- and owners-sailed optimized layout.
Design meets practical solutions
Looking at some key features, the distinction between an owner-optimized and vacation-optimized boat becomes apparent. For example the nav-station. This is an indisputable feature in a cruising catamaran, but of course, for boats predominantly used as vocational ships which as well must work fine in charter business , a dedicated nav-station will be as small as possible. This is different from a catamaran or boat (same goes for monohulls) which are intended and thought-through for sailor and owners-couple usage.

If you liked the huge role model nav station on the Outremer 52 , you will simply love the one on the HH 44! The desk is big enough so that two persons can take a seat on the lightweight, very practical poufs . I personally like the pivoting stool on the Outremer 52 more, but I´m sure the yard could fit something like this here as well. Also, all electronic displays and controls of the boat to be found outside are mounted as daughter displays in here. A fully operational control-bridge – best for a heavy weather watch!

Another deciding detail – this time much, much better solved than on the (much bigger) Outremer 52 and many other catamarans I´ve seen is the galley. It´s a U-shape, which not just provides so much extra stowage, but also a safe standing position to prepare food or doing the dishes. A ship´s cook can wedge in here and there´s no danger of falling through an all-open salon.

The boat is loaded with such amenities and practical solutions. The point is that you will never have the feeling that something has be done afterwards or as some sort of concession to some weird client´s requests, but it feels like the boat has been constructed around these things. Best seen where the large washing/drying machine is installed. They haven´t taken out a cabinet and just somehow fitted a washing machine, the whole area was planned to fit it. And to look nice, on top.
A Cathedral of light: Cabins aboard the HH 44
Let´s stay down below for a while because this is there the HH Catamaran really gets exciting. First of all, the black/white design in combination with huge and manifold windows and deck opening hatches makes for a wonderfully light suffused interior. There are windows literally everywhere you look – and a friendly light atmosphere. Many other boats are like “traps”, rather boosting seasickness than curing it.

This light-concept is best understood when checking the aft sections of the hulls: Huge rectangular bed which utilized all of the area between the hulls´ walls instead of island beds (which in my opinion are nice to look at in a catalogue but are a waste of space and unsafe in heavy seas). But the best are the windows … just look at this:

Owners and VIP-guests sleeping aft will enjoy a sunroom-like openness. I cannot remember having seen a boat´s cabin that offers such a huge amount of transparent area, being here whilst underway on the blue Ocean must be a tremendous experience. The only downside – as with so many boats – is that the hull windows are so high that you cannot look out whilst laying in bed. I guess that´s a safety issue, but it would have had an extra boosting comfort effect for sure.

Have no fear for your privacy, all windows on the HH 44 are tempered so that nobody can peep inside. This is especially important for the aft cabin´s windows which are directly en par with the cockpit: Essentially, any helmsman would have a front row seat and look through a +70 inch TFT-screen onto the owner´s berth. Normally, you don´t want this. The beds aren´t just big, spacy and cozy. Underneath, parts of the really advanced propulsion system are installed.
Hybrid propulsion and autonomous energy generation
Sustainability in boat building is a huge thing currently and I support this. Big companies are investing a lot in research and development, smaller startups try out their ideas and approaches. Of course, full electric or hydrogen-based propulsion is a thing of the future, but the first brands have launched their hybrid boats already. The HH 44 is such a yacht and the shipyard calls their concept the “Eco Drive”.

It´s basically the proven, rigid and reliable Diesel engine with a linear electric motore directly attached. This electric drive with two 10 kW also works as an alternator so that, when under Diesel engines, the large batteries are constantly reloaded. The Diesel engines (Vetus) are fitted directly underneath the aft beds. This is a rather uncommon approach and I have a lot of questions regarding heat, possible (dangerous) fumes, noise and vibrations and last not least questions like maintenance (inside the cabin) to possible exchange of an engine, but apparently HH found a solution to this.

The interesting aspect of the HH Catamarans “Eco Drive” concept is the interaction of the ensemble. Diesel-mode is clear, all electric mode is also clear. Furthermore, the alternators – when sailing and the props aren´t locked – recuperation mode is possible. Meaning by having the props rotate when sailing, they function like a hydro-generator. Also, there is a very clever “mix”-mode, as I call it. When you need Diesel-Power but also sleep, only one of the Diesels can be operated whilst the other is in recuperation mode.

Entering via a big removable door or wall piece from the forward guest cabin, there is full access to the battery and charger-room. The HH 44 is equipped with a set of 48 Volts lithium batteries with a combined power of over 43 kW hours, which is very impressive. This capacity is more than enough to ensure a cruising range (at 7 knots) of over 600 nautical miles or the utilization of all possible amenities for onboard comforts, like fridges, freezers, washing machines and even an AC.

Apart from than, the whole rooftop of the catamaran is completely covered with solar panels . The maximum power generation of these is 4.200 Watt-peak, which is also a lot when sailing or anchoring in sun-rich areas. The HH 44, like his bigger sisters, is a proven concept and a safe offshore-capable system. I found especially impressive how openly and honest the shipyard declares that they consider all-electric propulsion for not ready now. For the sake of seamanship and safety at sea, this is a brave and trust-building standpoint, better than offering something that is not ready now.
Luxury amenities and full-cruising capabilities
So, with such a rich abundancy of electric power and a long lasting range of almost complete autonomy, this catamaran is set to re-define the combination of luxury cruising with performance sailing. Luxury, that´s often a matter of being able to use the same household appliances which make our daily life at shore so convenient.

The HH 44 offers all of them, and even more. For example, in the very roomy and tasteful designed owner´s bathroom I was happy to discover an electric towel dryer. Such a small appliance that can make life so much easier. A washing machine, dishwasher in the galley up and many more little “helpers” not only add to the impressive price tag here, but also and foremost add to the label “luxury sailing” which is truly earned.

HH Catamarans utilizes latest production techniques. This can be seen by looking at the bare numbers: The HH 44 has a displacement of 10.2 tons (empty) and 14.5 tons with maximum load. Compared to the Nautitech 44 for example, that’s 1 ton lighter. Even more, almost 3 tons lighter than the 12.8 tons of the Excess 14 . How is this achieved? Carbon, lightweight sandwich layups and even prepreg-applications are used to build the boat.

Here and there the shipyard offers a glimpse onto these facts by having bare glossy painted Carbon there to admire, for example in the bathrooms. People who know will easily recognize the thumb-metallic sound when knocking on the materials, which is a totally different sound from ordinary GRP layups.

Both boats are made for four persons who will love their aft cabins, but there´s also another guest cabin in the front with a single bed. At least here a small window nearly at the height of the head of the occupant is offered. I guess this is the cabin that will remain unoccupied anyway or utilized otherwise as additional stowage. Let´s check the performance data, now that we´ve seen her interiors.
Performance through High-Tech
In the 44/45 footer class there isn´t much to compare the HH 44 to. So let´s stick to the Nautitech Open 44, the Excess 14 and the Outremer 45 . The upwind sails area of the HH 44 is said to be 116 square meters, whereas Nautitech, Excess and Outremer clock in with 105, 135 and and 106 square meters. Being the lightest of them four boats sporting the second biggest area of canvas up in the wind, it should be clear which one performs best.

The Excess 14 is an excellent, easy to sail cruising catamaran which exceeds the projected sailing performance by the shipyard by far. But it is not a performance cat – as well as the Nautitech, both have no daggerboards which gives both the Outremer and the HH Catamaran a much better directional stability and upwind performance with significantly lessened leeway. I haven´t sailed the HH 44 (yet) but I´d say a match race between her and the Outremer 45 would be a great feat.

The HH 44 has rounded (C-shape) daggerboards made of carbon fibers, hence provide a huge safety margin, high stability with flexing capability and are easy to operate due to their light weight. Besides these features, walking the deck and inspecting the running rigging, I notice so many great details, like the Carbon shrouds with soft shackles or the tall 90 cm stanchions which provide maximum safety.

The HH 44 is a classy sports catamaran with two full-sized helm stations in the cockpit. The starboard side features the primary plotter and all control panels for anchor windlass, all electric winches (which can also be operated by foot) and some secondary displays for wind and log-data. Like on the Outremer 52, the steering wheels are mounted on a pivoting stand.

So in active “fun” sailing mode, the wheels are put to the outer face of the hulls, granting perfect view over the leeward hull. In cruising mode or during bad weather phases, the wheel is put to middle position (as shown in the pictures) to grant a dry stand for the helmsman underneath the hardtop and they can even pivot further into the inside of the cockpit, maybe useful in long motoring sessions.

The handling of all lines and winches is ergonomically perfect, all is well protected. I must say that for my taste a bit more “exposure” to the elements wouldn´t had been bad as I deemed the forward vision through the cabin windows an bit obstructed. Excess and Outremer have much more exposed helm stations in this matter. On the other side, aboard the HH 44 safety is apparently of utmost importance and a such this explains the decision for the positioning the helmstations this way.
A perfect ship?
Praise for the HH 44 is unison high. These boats win awards like Tiger Woods in his golden days. This year the catamaran was nominated for the prestigious “Multihull of the Year”-award. And as rumors go, they haven´t won because of the – surely justified, but ridiculously – high price of well over 1.5 million Euros. I can clearly see why the yachting magazines and blogs are full of admiration for this boat: Her finishing and building quality is close to flawless.

So I leave the boat after my intense time aboard. I leave her over one of the foldable bathing platforms, which also brings me back to the beginning of this article. Comparing the HH 44 to the ENTERPRISE D, with a “best view” and some more awkward angles. The closed stern with a foldable bathing platform is the reason for the strange looks of the HH 44. Now that I understood that safety is the main thing on this boat – I can see the advantage of having such a closed stern.

This is a view I could grow into and make my peace with. Yes, the high-active fully exposed Outremer 45 helm station is super exciting and makes for the most adventurous shots, but at the same time, standing a watch up there in really bad weather is clearly much more dangerous than on the HH 44. In the end, this catamaran shows how high class boatbuilding goes if tooling, machinery, material choice, intense high-class labour and of course a later price to be paid is all but secondary. The full order books of HH Catamarans speak for themselves, as well as the opening of a second high-tech production facility in Cebu. Impressive!
You might as well be interested in these related articles:
Carbon overflow: Gunboat!
At the Outremer shipyard
Sea Trial of the Excess 14 catamaran
Yachting World
- Digital Edition

HH Catamarans – a new range of performance cruisers from China
- Elaine Bunting
- January 15, 2016
A range of fast-paced, sleek and modern-looking boats from Hudson Yacht & Marine based in south-west China will include cats from 55ft to 115ft, reports Elaine Bunting

HH Catamarans is a name you may not have heard of (yet), but behind this new brand is one of the largest-scale investments and boldest thinking in some years. The plans are ambitious, with a range of big, fast, luxurious catamarans up to superyacht scale.
The company is Hudson Yacht & Marine, based in south-west China, which sees its main market in Europe and the US, hence its appearance in Annapolis.
At the new facility in Xiamen, an island city lying between Hong Kong and Shanghai, the first is being built of what is to be a range of catamarans from 55ft to 115ft: the HH55, HH66, HH77, HH88 and HH115.

Rendering of the HH88
Four HH66s have been sold and are already in production. The first is due to launch in February for an Asian owner, and tooling for the HH55 is underway.
If the appearance of these resembles the Gunboat range more than the average production cruising cat, that is hardly surprising: the designs are the work of Morrelli & Melvin, the design team responsible for 18 Gunboats, and whose expertise in performance multihulls over the years spans A Class and Nacra catamarans to the late Steve Fossett’s PlayStation and, more recently, BMW Oracle Racing.
All will be fast-paced, sleek and modern-looking boats aimed at fast passagemaking and comfortable open plan ‘indoor/outdoor’ living. The HH55 and HH66 are styled as ‘a light and strong raceboat in disguise’. The HH66 is in composite construction, primarily aimed at cruising but, according to Morrelli & Melvin, “able to kick it up a notch”. So it is ultra light, and has C-shape daggerboards and T-foil rudders.

The HH55 is available in two configurations: forward cockpit and centre steering or dual aft steering and either in full-on performance-mode carbon composite construction or a less costly epoxy/E-Glass alternative. It, too, features C-shape daggerboards and T-foil rudders.
NZ builder brought in
Besides commissioning Morrelli & Melvin for the designs, owner Hudson Wang brought in New Zealand boatbuilder Paul Hakes four years ago. Hakes, a well known racing boat builder very experienced in building in pre-preg carbon, admits that he was “quite taken aback” by the scale of the company’s commitment to building boats – to date it has spent US$50m on building a boatyard. In that time Hakes has built several of the Judel Vrojlik-designed HH42, the best known example of which is Richard Matthews’s Oystercatcher XXX .
Hudson sees yacht manufacture as part of a serial manufacturing operation. The company’s products are wide-ranging. It produces around 20 per cent of baseball bats bought in the US, makes aircraft escape slides, barbecues and coolers, and employs some 4,000 people, of which 400 are in the boatyard. Its history in boats goes back to building J/80s and RIBs.
Tooling for the HH55 is also well underway. Paul Hakes tells us that the yard has finished a new fit-out hall and now has capability to have four or five HH66s and five to six HH55s in build at a time.

Preliminary drawings for the HH88 have been done and sufficient structural detail to allow price estimates. Designer Gino Morrelli says that the company is in talks with two potential owners.
Morrelli emphasises that the range could also go beyond the 115-footer currently planned. “We think the yard has capability to go to 150ft and they’ve built their new building to get that out the door, as that is where we think we will be in five to six years.”
Each of these boats can be highly customised, and renderings show very modern interiors. The zingy hull colours illustrated emphasise the message that Hudson is aiming to appeal to owners not hidebound by tradition, and perhaps migrating from motorboats.
The fact that the business has put its weight so strongly behind multihull production is yet another indication of growing interest in this area of sailing. “As far as the sailing market is concerned, the share of multihulls is growing, and bigger boats are coming out [of the downturn] faster than smaller boats,” says Morrelli.
www.hhcatamarans.com and www.morrellimelvin.com
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources
Nominee Spotlight: HH Catamarans HH44
- By Andrew Parkinson
- October 4, 2023
Over the past several years, Jason and Nikki Wynn have become an internet sensation of sorts, documenting their ‘round the world cruising endeavors on their sailing YouTube channel “Gone with the Wynns,” which has grown to over a half a million subscribers, becoming the third most popular (and growing) sailing channel on YouTube today. Beginning this fall, they’ll be broadcasting their adventures from the decks of a sweet new ride—the eco-conscious and carbon-reinforced HH44 by HH Catamarans.

Poised to appeal to early tech adopters, world cruisers and serious sailors alike, the HH44 is a disruptive new entry in the catamaran market, and it’s ready to make waves as a strong 2024 Boat of the Year contender at its US premiere in Annapolis.
This new model from HH Catamarans is available in two versions: OC (Ocean Cruising) and SC (Sports Cruising). The HH44-OC is a fast, comfortable, family-friendly cruiser that skews toward ease of operation for bluewater cruising. It shares the same hull and interior fit and finish quality as the sportier HH44-SC but features an aluminum mast, e-glass longeron, white gelcoat finish and mini-keels as standard instead of daggerboards. The HH44-SC integrates the very latest in race boat technology but remains equally as comfortable as a family cruiser. This is a “no-compromise-boat” with C-shaped carbon daggerboards, a carbon rig, a painted hull finish, emissions-free motoring, cutting-edge solar integration and an EcoDrive as standard equipment.
Designed for hybrid propulsion and solar power, the HH44 was conceived from the ground up to work with a parallel electric/diesel hybrid, a 4,232 watt solar array on the cabin top and hydro-regeneration while sailing. HH’s EcoDrive provides all the benefits of an electric boat: silent fume-free motoring at 7.5kts, instant torque for maneuvering, and hydro-regeneration while sailing, while also providing the reliability of trusty diesel engines as a backup. For technology shy owners, traditional standalone diesel engines with shaft drives are also offered.
The 4,232 watts of custom integrated solar come standard, as does an electric parallel hybrid with shaft drives, folding transoms, dual swing helm stations, forward opening salon windows, line tunnels, EVA foam decking and carbon fiber design detailing throughout.
Steer the boat from the outboard position with the wind in your hair and increased visibility of your sail plan. A fold-down helm seat stows out of the way or easily deploys when needed. Or, rotate the helm(s) inboard and steer from the protection of the three-seat sofa on the aft beam.

An angular cabin allows the two large, forward-facing windows to open fully from inside the 187 square-foot salon. Ceiling height is over 6’6” throughout. Comfort underfoot has been enhanced with non-skid EVA foam decking as standard.

Carbon and epoxy construction creates the strongest yacht possible without adding weight. All lines run under the deck to create an uncluttered walkway. Stanchions are 900mm tall for safety underway, and a continuous, unbroken toe rail runs the length of the deck with all hull and deck-joints fused and hidden.
An emphasis on craftsmanship and fit-and-finish is evident throughout, with foam core furniture and meticulous joinery, top of the line fixtures and Bosch electric appliances standard. Cabinet locks are cleverly hidden in the modern design and an optional pocket TV can deploy and spin to face the viewer. Optional RGB rope lighting throughout can be dimmed or change colors depending on your vision needs while night sailing or for setting the mood at anchor.

HH Catamarans HH44 Specifications
- More: 2024 Boat of the Year , Boat of the Year , catamaran , hh catamarans , Sailboats
- More Sailboats

For Sale: 1983 Little Harbor 44

Sailboat Preview: ClubSwan 28 by Nautor Swan

Sailboat Review: Vision 444

Sailboat Preview: Lagoon 43

When the Wind Goes Light

Sailor & Galley: Ice Cream, Anytime
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding

- € 0.00 0 items

Description
The first HH44 was launched in 2023 and premiered at the Cannes International Yachting Festival. This innovative design is the “baby” of the HH Catamarans range and has some interesting features such as her closed transoms, swing aft helms and a side boarding gate aft.
She’s a very pretty cat and will turn heads in the marina. This is HH’s first hybrid electric-powered catamaran although you can also opt for standard diesel power with shaft drives.
There are 2 versions, like much of the HH range. The Sports Cruising model: HH44-SC and the Ocean Cruising model: HH44-OC. The SC version is a “no-compromise-boat” with C-shaped carbon daggerboards, a carbon rig, a painted hull finish and 4,232 watts of solar with EcoDrive.
The OC saves you some money with the same hull, interior fit and finish quality as the sportier SC but with an aluminium mast, e-glass longeron, white gelcoat finish and mini-keels as standard.
Many of the ideas on this boat have been driven by a desire to maximise solar generation. There are 4,232W of peak solar on the cabin top alone with an option for more on the davits.
To maximise the solar, they have positioned the helms aft in a traditional sporty set-up. That way, there’s plenty of surface area up top to load on solar.
To help you stay protected in weather, these swing inboard, under the long coach-roof.
There are foldaway seats that tuck into the sides allowing you to either steer the boat from an outboard position with the wind in your hair and your sails’ tell-tales in full view.
Or swing the helms inboard and steer from the protected three-seat sofa on the aft beam.
To make it easy to board the boat in the marina, there is a side gate aft for when you come in along the dock.

The HH44 has been designed to sail. The whole idea behind this catamaran is to get sailing in light winds (you should match wind speed on a beam reach) and to maximise your SOG over a wide range of conditions.
So she has a self-tacking staysail, a solent, a fractional reacher and a furling gennaker. The boom is very low over the coach-roof which keeps the centre of effort from the mainsail low.
There is a traveller aft on the coach-roof to manage your mainsail shape. The HH44 points well into the wind (45 TWA) thanks to her C-shaped daggerboards which provide a bit of lift at speed.
All the lines come back to the helm, so she is set up for short-handed sailing.
- Light, rigid and fast, the HH44 is a great sailor
- Swing aft helms give you flexibility while opening up the living space in the aft cockpit
- The finish on this boat is excellent
- Those closed transoms create a safe enclosed living space. They’ll also save you money in the marina
- A great looking boat that should hold her value well in the market due to the high demand
- The EcoDrive strikes a great balance between electric motoring with back-up diesels for safety
- With those aft helms, visibility is reduced towards the opposite bow, although the sight lines through the salon windows is good.
- This is not a cheap yacht
- The forward cabin is cosy. There is an option for a Pullman berth here (or convert to a workspace)
- The bow lockers seem small, although they are deep
Light Construction
Carbon and epoxy have been used to build as strong and stiff a yacht as possible while minimising the weight.
All of the lines run under the decks, so you have clear walkways around the boat. Stanchions are 900mm tall and a continuous, unbroken toe rail runs the length of the deck with all hull and deck joints fused and hidden.
Living Space
Moving inside, you’ll notice that the aft cockpit and salon forms one fully protected space with a large sofa on the aft beam and her closed transoms make this a safe family boat.
The angular cabin has two large, forward-facing windows that open fully from the the generously sized (187 sq ft or 17.4m2) salon. The standing height is over 2m (6’6”) high throughout.
One of the things that sets the HH44 apart from her competition is the quality of the finish on this semi-custom yacht. She has foam core furniture and exceptional joinery throughout, and Bosch electric appliances as standard.
There are two options for a BBQ, one which replaces the aft sofa with a large LPG BBQ & Dive Tank station or you can mount an LPG Grill in the aft fishing rod holder, keeping the aft sofa. There is an outlet on the aft beam so you can run an electric BBQ.
In the salon, there is an L-shaped sofa with a table forward to starboard and a large nav station/workstation to port.
Tuck yourself into the U-shaped galley behind the nav station or pull out some cold ones from the fridge on the starboard side. The ventilation at anchor is excellent with those huge forward windows.

The starboard hull is the owner’s side and consists of the master cabin aft and a walk-in shower and head forward. The finish has an Italian feel to it and it is very light down here with a large window aft in the owner’s cabin.
This is a 44 foot performance cat, so there is not as much room down her as you’d find in a cruising cat, but she has ample space in the aft cabin and the storage is well organised.
HH offers three different forward cabin combinations. One is the standard layout with a single berth.
The second has a Pullman berth above the standard bed that folds away when not needed.
A third option does away with the beds and replaces them with a large work bench with shelves (for pantry storage or tools) and an extra Fridge/Freezer unit.
If you go for the option with the EcoDrive, the House Bank is powerful enough to run the A/C overnight without the need to run a generator. There is enough power to run the A/C in the master cabin for over three days.
EcoDrive, her Electric/Diesel Parallel Hybrid System The HH44 was designed from scratch to work with a parallel electric/diesel hybrid, with a minimum of 4,232W of peak solar array on the cabin top and hydro-regeneration while sailing.
EcoDrive gives you silent fume-free motoring at 7.5kts, fast torque for manoeuvring, and hydro-regeneration while sailing. Plus you have parallel, trusty diesel engines for safety.
A diesel engine is paired with a large electric motor, much like an alternator sits on a traditional diesel engine. A belt links the two units and a camshaft allows you to flip between the two power systems, giving you good redundancy. And remember, you have 2 of these systems on board!
The system is designed to offer from 1.5 to 3 hours of electric propulsion: more than enough time to exit the marina or anchorage and hoist the sails.
This boat has been designed to get sailing in light winds which ultimately is the key to an eco-friendly sailing yacht. And you will be recharging your batteries as you sail.
You can also fit the HH44 with traditional standalone diesel engines with shaft drives.
The HH44 is an innovative design that will appeal to sailors setting out across long distances who want to sail more and beat well to windward when needed. This yacht is in a different price league to something like an Aventura 37 of course, but there are two options here: the Sports Cruising and the Ocean Cruising models.
She’s a comfortable boat, although there is a trade-off on space down below particularly in the forward cabins.
With the EcoDrive option and a bow locker full of sails, you’ll be able to minimise your diesel usage on this boat while crossing oceans safely and quickly.
What is the price of an HH44? How much do they cost? The sportier HH44-SC starts at $1,325,000. Meanwhile the HH44-OC version starts at $957,000 USD. The total cost will vary depending on your options, but you should budget an additional $300k, perhaps more for the SC.
How much solar is there on the HH44? The HH44 has a generous 4,232W of peak solar as standard on the SC on the cabin top. You can fit 1,200W watts over the Davits, but this comes with a weight penalty.
What is the length of the boat with transoms up? With the transoms up, the LOA from davits to Bow Sprit is 14.23m (46.68 feet), so fine for a 15m berth.
What size tender can you carry? The optimum sized tender is 3-3.5m (10-11 foot). The davits are carbon fibre and will soak up a high load.
Technical Specification
Related Catamarans

Seawind 1600

McConaghy MC50
Browse, search and find your perfect catamaran!
The Unique Burial of a Child of Early Scythian Time at the Cemetery of Saryg-Bulun (Tuva)
<< Previous page
Pages: 379-406
In 1988, the Tuvan Archaeological Expedition (led by M. E. Kilunovskaya and V. A. Semenov) discovered a unique burial of the early Iron Age at Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva. There are two burial mounds of the Aldy-Bel culture dated by 7th century BC. Within the barrows, which adjoined one another, forming a figure-of-eight, there were discovered 7 burials, from which a representative collection of artifacts was recovered. Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather headdress painted with red pigment and a coat, sewn from jerboa fur. The coat was belted with a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles. Besides that, a leather quiver with arrows with the shafts decorated with painted ornaments, fully preserved battle pick and a bow were buried in the coffin. Unexpectedly, the full-genomic analysis, showed that the individual was female. This fact opens a new aspect in the study of the social history of the Scythian society and perhaps brings us back to the myth of the Amazons, discussed by Herodotus. Of course, this discovery is unique in its preservation for the Scythian culture of Tuva and requires careful study and conservation.
Keywords: Tuva, Early Iron Age, early Scythian period, Aldy-Bel culture, barrow, burial in the coffin, mummy, full genome sequencing, aDNA
Information about authors: Marina Kilunovskaya (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Vladimir Semenov (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Varvara Busova (Moscow, Russian Federation). (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Kharis Mustafin (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Technical Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Irina Alborova (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Biological Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Alina Matzvai (Moscow, Russian Federation). Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected]
Shopping Cart Items: 0 Cart Total: 0,00 € place your order
Price pdf version
student - 2,75 € individual - 3,00 € institutional - 7,00 €

Copyright В© 1999-2022. Stratum Publishing House
- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis

The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.
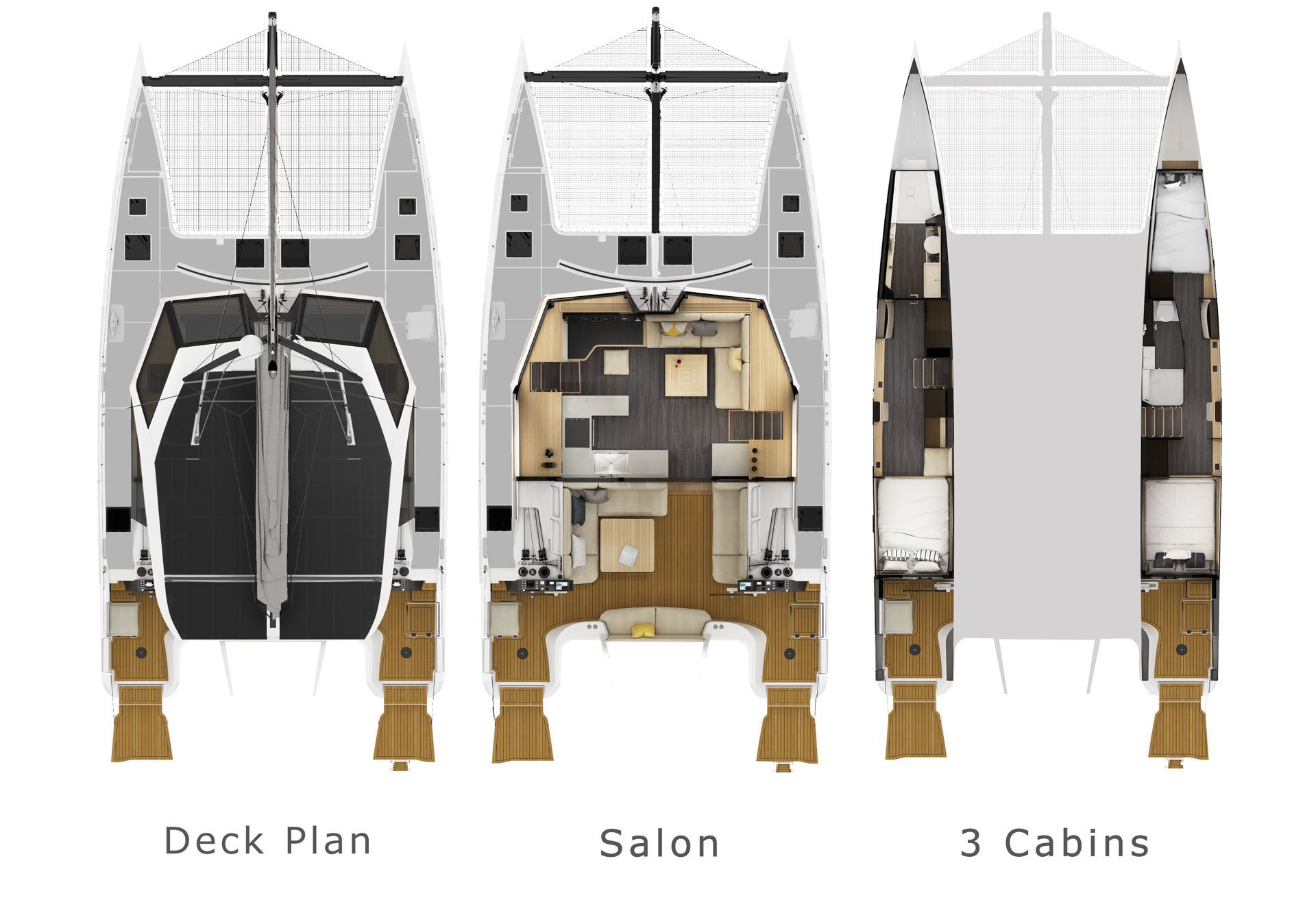
Experts in carbon fiber construction, we offer a five year hull warranty and we expect our boats to be sailing the world's oceans for 50+ years. HH Catamarans' award winning designs are built to exacting specifications using the most advanced construction methods in the industry. We deliver semi-custom cruising yachts tailored to each owner ...
HH Catamarans are built by a team of professional boat builders in a state-of-the-art production facility in Xiamen, China. HH Catamarans parent company, Hudson Yacht Group, is dedicated to building the highest quality, most technologically advanced, luxury cruising catamarans in the world. With an investment of over $50 million USD, the newly ...
Unmatched Strength. HH Catamarans offers an unmatched combination of strengths: a dedicated team of in-house designers and engineers, and partnerships with renowned naval architects around the world; two wholly-owned, state-of-the-art production facilities; a master boatbuilding team led by industry veterans; and an intricate network of the ...
HH Catamarans are made in the United States, in Clearwater, Florida. HH Catamarans has a state-of-the-art, climate-controlled facility, where the catamarans are constructed with the highest quality materials. The company takes pride in their craftsmanship and attention to detail, and uses the latest in cutting edge technology to ensure the ...
I've just flown over to Xiamen, China to see our boat which is in construction. Lots of decisions to be made and a huge amount learned. The factory is huge! ...
Hudson Yacht Group introduced a new generation of luxury, high-performance cruising catamarans. Faster, stronger, and more stable in heavy seas than anything in their class, HH Catamarans are the ultimate choice for those looking for a dual purpose yacht, demanding only the best. Built to order, HYG is currently producing the HH44, HH50, HH52 ...
HH Catamarans. 6,606 likes · 4 talking about this. Award-winning catamarans offering the ultimate synthesis of luxury and performance, from 44'-88'.
Shipyard Walkthrough by Paul Hakes, Chief Operating Officer at HHCatamarans.Focus on: HH Catamarans - HH50HH Ocean Serie - OC50HH Catamarans- HH88Presented b...
HH Catamarans. HH Catamarans is a yacht brand that currently has 7 yachts for sale on YachtWorld, including 6 new vessels and 1 used yachts, listed by experienced boat and yacht brokers mainly in the following countries: Australia, Sint Maarten (Dutch part), United States and British Virgin Islands. The selection of models featured on ...
The HH 44 is the smallest entry level catamaran of the range. The shipyard offers a staggering palette of eight models, ranging from 44 over 50, 52, 60, 66, 80 and a huge 88 feet flybridge super-catamaran. The model shown at La Grande Motte was a used boat, so not brand new anymore, but there were no visible signs of wear.
HH Catamarans Sales. Sales & Service. [email protected] +1 386 414 6700. Learn More Blue Sailing, DE. Sales & Service. [email protected] +49 421 34660250. Learn More Inspiration Marine, UK. Sales & Service. [email protected] +44 (0) 2380 457 008. Learn More ...
A range of fast-paced, sleek and modern-looking boats from Hudson Yacht & Marine based in south-west China will include cats from 55ft to 115ft, reports Elaine Bunting. HH Catamarans is a name you ...
This new model from HH Catamarans is available in two versions: OC (Ocean Cruising) and SC (Sports Cruising). The HH44-OC is a fast, comfortable, family-friendly cruiser that skews toward ease of operation for bluewater cruising. It shares the same hull and interior fit and finish quality as the sportier HH44-SC but features an aluminum mast, e ...
Hudson Yacht Group. HH Catamarans' parent company, Hudson Yacht Group employs 250 people and 600sqm between three main production halls. HH50-06, OC50-02 with HH88-01 at the far end. The newest shed alone is 200m long by 60m wide, with three mezzanine floors, four 5 ton gantry cranes, 2 industrial elevators and a 40m long EPA compliant spray ...
2020 HH Catamarans 66. US$3,950,000. SOMA Sailing LLC | Simpson Bay, Sint Maarten (Dutch part) Request Info.
HH44. The first HH44 was launched in 2023 and premiered at the Cannes International Yachting Festival. This innovative design is the "baby" of the HH Catamarans range and has some interesting features such as her closed transoms, swing aft helms and a side boarding gate aft. She's a very pretty cat and will turn heads in the marina.
HH50 - Style, Speed and Simplicity — HH Catamarans. The HH50 is for those seeking the perfect balance of performance and luxury in a size that can be easily managed by a couple. If you are looking for the ultimate blue-water capable catamaran, look no further than the 2021 "Boat of the Year," the HH50.
Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather ...
In 1938, it was granted town status. [citation needed]Administrative and municipal status. Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Elektrostal Urban Okrug.
Main page; Contents; Current events; Random article; About Wikipedia; Contact us; Donate; Pages for logged out editors learn more
Chris has worked with HH since HH6601 launched in 2016. Chris has captained luxury performance cruising catamarans for 10+ years, and in addition to his on-water expertise, brings a wealth of project management and customer service skills to the program.
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...
The HH52 forward cockpit configuration can also be ordered as a 50/50 e-glass/carbon "Ocean Cruising" version or a 100% carbon-fiber "Sports Cruising" version. The forward helm station and pit provides a central, protected location to operate all sail controls from. This is a superb configuration for easy, single handed sailing.

Lindsey Vonn goes sailing with Team USA and joins grinder Anna Weis on the winches
The Associated Press
June 21, 2024, 8:26 PM
- Share This:
- share on facebook
- share on threads
- share on linkedin
- share on email
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River on Friday aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team.
The retired skiing champion was the “sixth sailor” with Team USA for a jaunt off Manhattan before all 10 crews held practice races ahead of this weekend’s Mubadala New York Sail Grand Prix. It’s the penultimate regatta in Season 4 of tech billionaire Larry Ellison’s global league.
While there certainly will be some boardroom work involved for Vonn — she envisions helping with brand strategy and partnerships — being on the water was the place to be.
“For me, part of the excitement about being on the board is just being involved with another adrenaline sport,” Vonn said in a phone interview with The Associated Press.
The wind wasn’t strong enough to do much foiling, which is what makes the F50 catamarans among the world’s fastest boats.
The wind did pick up just after Vonn got off the boat.
“Just my luck,” she cracked. “It wasn’t what I hoped for. As someone that’s missing speed as a retired athlete, I was really hoping to go fast. But to be actually doing something, or at least they let me feel like I was doing something, was exciting. … Downhill’s a little bit faster. But again, I’m retired so I’ll take what I can get.”
She was thrilled to work alongside grinder Anna Weis, turning the winches that help the wing trimmer do his job.
“It was fun,” Vonn said. “I was grinding with Anna and kind of following their lead. I was a little bit of a fish out of water, to some degree, but it was really fun. Grinding is so hard and what Anna does as a woman, I think, is really, really incredible. I don’t think many people know how difficult a role like that really is, so I just have a lot of respect for her and the team. To have a coed team like that, it’s amazing.”
As part of the Women’s Pathway program, every SailGP team must have a woman onboard. Weis, who competed in the Tokyo Olympics in the foiling Nacra 17 catamaran class, has done the most races as a grinder of any woman in SailGP, and she also trims the jib. Her job requires strength, cardiovascular endurance and finesse.
“She’s such an amazing young woman who’s incredibly strong,” Vonn said. “She’s a great example for the next generation.”
With women’s sports reaching a tipping point, Vonn mentioned the work Billie Jean King has done over the decades in championing women’s equality in sports, and how current women athletes, including in SailGP, “are showing people what is possible. And again, it’s a combination of the past paving the way for the present and the present really taking the opportunity and maximizing it.”
Vonn was outfitted in full protective gear, including a crash helmet. Team USA had a dramatic capsize in practice racing in Bermuda in early May that was caused by a crew error. While there were no serious injuries, the boat was damaged to the point the team missed the regatta.
“Since the capsize of a couple of weeks ago, I wanted to make sure I actually listened to the safety protocol this time,” said Vonn, who also sailed with an America’s Cup crew in 2016 off Manhattan before an exhibition regatta.
“I saw the video of it. It was pretty crazy,” she said. “Honestly, I think things like that are really exciting. Obviously, again, it was very expensive, but that’s what makes it exciting. Those are the type of things that make the sport really interesting.”
Vonn retired from skiing in 2019 after winning three Olympic medals, including one gold, and four overall World Cup titles. She was the first woman to win 82 World Cup races.
Team USA was purchased in November by a group of investors from the sports, technology and entertainment worlds. They include former Alabama linebacker Dallas Turner, who was drafted by the Minnesota Vikings at No. 17 overall; actress/producer Issa Rae; founding Uber engineer Ryan McKillen; and professional sailor Mike Buckley.
On Friday, Team USA announced a multiyear partnership with Tommy Hilfiger starting in 2025 that will include boat branding and crew uniforms.
The Americans are out of the running for the $2 million, winner-take-all season championship race July 14 in San Francisco. New Zealand sits atop the 10-boat fleet with an 11-point lead over Spain, with three-time defending champion Australia another point back in third.
Bernie Wilson has covered sailing for the AP since 1991.
AP sports: https://apnews.com/hub/sports
Copyright © 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, written or redistributed.
Related News

Bryce Duke, Dominic Iankov rally Montreal to 4-2 victory over Union

Seattle Storm swept past Dallas Wings 97-76

Will Smith’s double ignites seven-run 11th inning as the Dodgers beat the Giants 14-7
Recommended.

'I kept it very secret': One trans woman's journey transitioning in the military after 'Don't Ask, Don't Tell' repeal

DC United ties Red Bulls 2-2 after Cristian Dájome gets red card, is sent off field

The Unique Burial of a Child of Early Scythian Time at the Cemetery of Saryg-Bulun (Tuva)
<< Previous page
Pages: 379-406
In 1988, the Tuvan Archaeological Expedition (led by M. E. Kilunovskaya and V. A. Semenov) discovered a unique burial of the early Iron Age at Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva. There are two burial mounds of the Aldy-Bel culture dated by 7th century BC. Within the barrows, which adjoined one another, forming a figure-of-eight, there were discovered 7 burials, from which a representative collection of artifacts was recovered. Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather headdress painted with red pigment and a coat, sewn from jerboa fur. The coat was belted with a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles. Besides that, a leather quiver with arrows with the shafts decorated with painted ornaments, fully preserved battle pick and a bow were buried in the coffin. Unexpectedly, the full-genomic analysis, showed that the individual was female. This fact opens a new aspect in the study of the social history of the Scythian society and perhaps brings us back to the myth of the Amazons, discussed by Herodotus. Of course, this discovery is unique in its preservation for the Scythian culture of Tuva and requires careful study and conservation.
Keywords: Tuva, Early Iron Age, early Scythian period, Aldy-Bel culture, barrow, burial in the coffin, mummy, full genome sequencing, aDNA
Information about authors: Marina Kilunovskaya (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Vladimir Semenov (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Varvara Busova (Moscow, Russian Federation). (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Kharis Mustafin (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Technical Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Irina Alborova (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Biological Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Alina Matzvai (Moscow, Russian Federation). Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected]
Shopping Cart Items: 0 Cart Total: 0,00 € place your order
Price pdf version
student - 2,75 € individual - 3,00 € institutional - 7,00 €

Copyright В© 1999-2022. Stratum Publishing House

COMMENTS
Capsize is very unlikely in most cruising catamarans, but it does happen occasionally so, as with most seamanship issues, the smart move is to be on top of the subject and prepared for the worst.
The cat was 9 m long, and the owner had modified the boat by adding keels. The study consists of a data set of over 120 incidents reported, of which only 33 are catamarans showing that catamaran capsizing is something very uncommon. The reason for a catamaran sailboat capsizes; 28% Gust of wind. 28% Wind.
It is extremely hard to capsize a modern cruising cat. Either a basic disregard for seamanship or extreme weather is required. ... I have sailed about 70,000nm on cruising catamarans, a Canadian built Manta 38 (1992, 39ft x 21ft) with fixed keels and my present boat, a Walter Greene Evenkeel 38 (1997, 38ft x 19ft 6″) with daggerboards. I came ...
Summary. A catamaran's stability is attributed to its center of gravity, its freeboard, and its pendulum-like behavior. However, despite its stability and speed, a catamaran can still capsize due to strong winds and capsizing waves. There are factors that can contribute to the likelihood of a capsize happening, such as wind speed, wave height ...
Kickstarter https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/elcanoandplukky/the-elcano-challengePart 1 of this series go check it outhttps://youtu.be/OjbLv_ucT9QTo cont...
Catamarans are a popular choice among sailing enthusiasts due to their sleek design, stability, and impressive speed. However, even the most experienced sailors can fall victim to catamaran capsizing if they fail to understand the causes, risks involved, and how to prevent mishaps. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of understanding catamaran capsizing to ensure that you can ...
1 - the bad tack, 2 - the sideways , 3 - the sideways on the wire , 4 - the gybe on the wire , 5 - newton's cradle , 6 - pitchpole sitting in , 7 - pitchpol...
I've read quite a few threads recently relating to catamaran capsize, and as I am now seriously looking to purchase one (a Lagoon 380), I'm curious how far planning for a capsize should go, and what people would do in the event. Not the least of my thoughts is that we are a cruising family with two young boys (10 and 7 when we leave) and would need them to know what to do.
Many multihull capsizes are a result of a series of issues - a squall, overpowered rig, inability to quick release, turning the wrong way to depower. On a cruising catamaran these are reduced, but good seamanship dictates an awareness of what to do when the unexpected occurs. Avoid getting caught 'in irons'
This week we answer the question often speculated but seldom discussed - what is the risk of capsize on a catamaran? We get hit by a rogue wave on what shou...
Although they can theoretically (and practically) capsize, cruising catamarans are the favourite type of boat among blue water sailors. Every year, dozens of family crews set off on their Lagoons, Fountaine Pajots, Nautitechs, Outremers and other series-produced catamarans on long voyages across the Atlantic or even around the world.
August 15, 2010. On July 31, 2010 the Atlantic 57 Catamaran, Anna, with a crew of two, was capsized by a violent squall 125nm from Tonga in the South Pacific. This news came as a shock to me and most of the owners of Atlantic Catamarans, as well as sailors of other cruising catamarans. Fortunately neither the captain nor crew was injured beyond ...
Catamaran Capsize. Earlier today Sydney (Aust) time, a Catamaran reportedly 11.7m, capsized off Newcastle with three persons reported dead and two rescued. A terrible tragedy. My wind app says seas 2.5m and winds around 25kts today. Thoughts and condolences to families and friends, and to those involved in the rescue.
Catamaran capsize. GILow: Our Community: 71: 14-07-2019 06:17: Catamaran capsize preparation: terah: Multihull Sailboats: 19: 23-01-2017 09:21: Capsize Ratio: Scott k: General Sailing Forum: 30: 14-03-2013 06:05: EPIRB Proves Its Worth in Sudden Capsize of Catamaran: foolishsailor: Health, Safety & Related Gear: 27: 12-08-2012 00:13: OUTREMER ...
In short: The crew of the US F50 were thrown overboard in a spectacular capsize during a pre-race practice session in Bermuda. The cause of the accident was found to have been from one of the crew ...
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River on Friday aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team. The retired skiing champion was the "sixth sailor" with Team USA for a jaunt off Manhattan before all 10 crews held practice races ahead of this weekend's ...
Elektrostal is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located 58 kilometers east of Moscow. Elektrostal has about 158,000 residents. Mapcarta, the open map.
These speeds — combined with an occasional capsize — give the event the look of a Formula 1 auto race, an appeal the league hopes will broaden its reach beyond sailing aficionados.
Location: cruising SW Pacific. Boat: Jon Sayer 1-off 46 ft fract rig sloop strip plank in W Red Cedar. Posts: 21,304. Re: Catamaran Capsize. Quote: I recently sailed a 43 ft cat south from Port Stevens to Pittwater in a similar wind strength & swell size, but it was not a port beam swell with an offshore wind.
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team ... "Since the capsize of a ...
HH Catamarans are built by a team of professional boat builders in a state-of-the-art production facility in Xiamen, China. HH Catamarans parent company, Hudson Yacht Group, is dedicated to building the highest quality, most technologically advanced, luxury cruising catamarans in the world. With an investment of over $50 million USD, the newly
Lindsey Vonn went sailing on the Hudson River on Friday aboard a foiling catamaran, enjoying one of the perks of joining the board of directors of the United States SailGP team. The retired skiing ...
Location: Now limited to seasonal NE sailing. Boat: PT-11. Posts: 1,541 Re: Catamaran capsize. Quote: Originally Posted by smj. ... Catamaran capsize. Quote: Originally Posted by conchaway. A well built mono will not sink when capsized ( all things being sealed). I would NEVER suggest, because of being deemed mean-spirited, that when a cat goes ...
State Housing Inspectorate of the Moscow Region Elektrostal postal code 144009. See Google profile, Hours, Phone, Website and more for this business. 2.0 Cybo Score. Review on Cybo.
Re: Catamaran capsize. Yep, people sometimes have a one sided view of Wharrams, but there are also some very nice high quality ones around too, as well as some still not terrible but more simple versions that are getting people out cruising.
Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather ...