- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources

Guide to Sailing Ropes
- By Jen Brett
- Updated: June 16, 2020

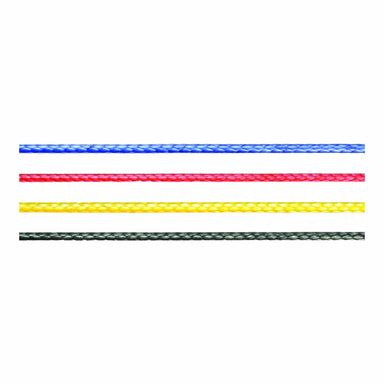
Replacing the running rigging on your sailboat seems like it should be fairly simple, and a decade or two ago, it was. As with electronics, safety gear, and even sails, technology has significantly improved cordage. The downside to all these improvements is that not only are there more options than ever, but you may feel like you need a materials-science degree in order to choose the right sailing ropes for your new jib halyard. Here, we’ll take a look at the types of sailing ropes and what the newer, high-tech materials can do for your boat.
When it comes time to choose new sailing rope for the lines aboard your boat, you’ll need to consider the type of sailing that you’ll be doing (a year in the tropics? racing to Bermuda?), the hardware that you currently have (clutches, sheaves), what qualities you feel are important (soft hand, ease in splicing, weight, durability), and your budget. The type of sails you have is another consideration. “If you’ve already made the investment in laminate sails, then you should really consider upgrading your running rigging to a low-stretch material,” says Brian Fisher of Rig Pro, in Portsmouth, Rhode Island. “But even if you have Dacron sails, you can benefit from a cordage upgrade.”
Starting at the top, you should check over your sheaves before replacing your halyards, and if you’re going from wire to rope halyards, you’ll need to change to rope sheaves. (Wire halyards use a V-shaped sheave; rope sheaves are U-shaped.) While you’re aloft, look for any sharp edges that could chafe through your new line, especially if you’re going from wire to rope halyards.
What’s the best halyard rope? There are plenty of choices for new halyards, from basic polyester double-braid to all the high-tech materials. Whatever you choose will probably be a compromise between such factors as amount of stretch, cost, weight, and ease of handling.
Long the workhorse on many a cruising boat, polyester (Dacron) double-braid is still a good choice for many onboard applications. Polyester is long lasting, resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and costs a fraction of high-tech rope; however, it’s somewhat stretchy and heavier than more modern materials, and if there’s one area on board that could benefit from an upgrade to lightweight low-stretch line, it’s the halyards.
Most cruising boats have a roller-furling headsail , and many have in-mast furling mainsails as well. Since these remain hoisted for possibly months at a time, a lightweight low-stretch line will offer better halyard tension and sail shape over the long run. This is true for non-roller-furling sails as well, especially if you’re heading out on a long passage where the sails will be set for a while. Here Fisher recommends using a Spectra/Dyneema-cored line, since it’s extremely strong, lightweight, and doesn’t absorb water. An alternative would be a Vectran-cored line, which stretches even less and doesn’t creep; however, it’s heavier than Spectra/Dyneema and absorbs water. When switching from polyester to a high-tech line, it’s usually possible to downsize the line by a few millimeters since these fibers are so strong. This is a definite advantage for bigger cruising boats, since polyester line can be quite bulky at larger diameters.
If the price tag of Spectra/Dyneema-cored or Vectran-cored line is a little steep, all the major rope manufacturers currently make “mid-level” blended-core ropes that would be well suited to the cruising environment (and easier on the wallet). A few examples are New England Ropes’ VPC, with a Vectran and polyolefin core, and T-900, with a Dyneema and Technora core; and Yale’s Vizzion, with a braided composite core of Vectran LCP and filament olefin.
Both high-tech lines and the mid-level blends typically have polyester covers, which provides extra UV protection and a nice hand, although there are also covers available that blend the polyester with materials such as Technora, for its abrasion-resistant and heat-dissipating qualities. If weight saving is a major issue aboard your boat, note that many of the high-tech ropes available are core dependent, and the cover can be stripped off. On the majority of cruising boats, however, the effect would be negligible.
Like halyards, sheets are an area where Spectra/Dyneema-cored lines can improve performance and even your sailing experience. “Since you can downsize your line when you switch from polyester, you end up with smaller, lighter piles in your cockpit and less weight pulling at your sail,” says Fisher. He offers an example of genoa halyards on an Oyster 46, which are 69 feet long. In this application, polyester double-braid lines would measure 3/4-inch in diameter, with a breaking strength of 16,000 pounds and a weight of 11 pounds. A Spectra/Dyneema-cored line would have a 1/2-inch diameter, a breaking strength of 20,000 pounds, and a weight of only 4.6 pounds. And only the polyester cover would absorb water, offering additional weight savings as well as more pleasant tacking.
It’s worth noting that if you’re replacing your running rigging, the time’s right to inspect your deck hardware, too. Since polyester line has more give, it absorbs more of the load from the sails. If you make the switch to high-tech line, be sure that your deck hardware is appropriately sized and reinforced.
Spinnaker sheets are well suited for a high-tech upgrade as well, since a lightweight, small-diameter line that’s also very strong will offer better performance. Examples of good choices for this application are Samson’s WarpSpeed, featuring a Dyneema core and a polyester cover, and New England Ropes’ Flight Line, which has a Dyneema core and a polypropylene cover.
Rope construction for the mainsheet is much a matter of personal preference. Single-braid is usually softer, has a nice hand, and doesn’t kink, but it could snag more than a double-braid line and doesn’t have the additional abrasion resistance of a cover. Yale Cordage’s Ph.D. rope is a single-braid construction made from polyester-coated Spectra. According to Yale, the polyester coating gives the rope a nice feel and good grip on winches, while the Spectra core gives it strength and weight savings.
All the Rest
While halyards and sheets have been the focus here, there are plenty of other places aboard that could benefit from a high-tech sailing rope makeover: runners, the outhaul, the traveler, the boom vang, even lifelines. If a major high-tech cordage upgrade is in your future, it may be wise to consult with a rigger to ensure that the chosen material is suitable to the application on your particular boat and that your lines are appropriately sized. “I’ve seen several situations in which customers have forgotten to take into account proper line size with regard to the winches and rope clutches on their boats,” notes Andrew Spiro of The Ship’s Store and Rigging, in Portsmouth, Rhode Island. “It’s simple, but just because you can use a smaller-diameter line with the same strength, they forget that the winches and clutches are limited to certain sizes. The result is often slipping.”
Always on the forefront of technology, raceboats have been using high-tech fibers for years in many applications on board, even standing rigging, and as these fibers have improved and their acceptance has grown, more and more wire is being traded out in favor of these lightweight alternatives. Cruisers can also reap benefit from these advances.
Jen Brett is CW’s senior editor.
Rope Guide for Sailboats
Aramids (Twaron, Technora, Kevlar): Like other high-tech fibers, aramids are strong and stretch little, but they also have the benefit of being resistant to heat. You’ll find aramids in both double-braid cores as well as blended with other fibers in the covers.
Colligo Dux: A relative newcomer to sailboat rigging, Colligo Dux is pre-stretched and heat-treated Dyneema. This process, however, produces an extremely strong rope with virtually no creep that is suitable for service in standing rigging.
H.M.P.E. (Dyneema, Spectra, Amsteel): High-modulus polyethylene has many benefits for running-rigging applications: It’s very strong, lightweight, doesn’t absorb water, has decent resistance to ultraviolet radiation, and it can float. On the downside, it has more creep (see “Rope Speak,” page 80) than other high-tech fibers.
L.C.P. (Vectran): Liquid-crystal polymer fiber possesses high-strength and low-stretch qualities and suffers virtually no creep. L.C.P. is one of the strongest core materials, although it doesn’t have the U.V. resistance of H.M.P.E., and it’s a little bit heavier.
Nylon: Strong yet stretchy nylon is commonly used in applications for which shock absorption is important, such as in dock lines and anchor lines.
P.B.O. (Zylon): Polybenzoxazole is extremely low stretch and high strength. It’s also ungodly expensive and lacks the durability that most cruisers desire. As such, P.B.O. is usually only found on high-end raceboats.
Polyester (Dacron): For decades, polyester has been the go-to rope for cruising-boat halyards and sheets. It’s cost efficient, strong, and resists ultraviolet radiation.
Polypropylene: Usually used in applications like ski and dinghy tow ropes, polypropylene is lightweight and can float. Alone, polypropylene isn’t usually seen in cruising-boat lines since it’s very susceptible to UV degradation, but it’s sometimes combined with other fibers that benefit from its lightweight, low-cost qualities.
- More: DIY Sailboat Projects , Gear , How To , sail handling , sails & rigging , sails and rigging
- More How To

DIY Tips for Repairing Nonskid

Shaft Bearing Maintenance Tips

When the Wind Goes Light

How We Built Our Own Bulwarks

Hurricane Beryl Relief Efforts: How You Can Help

Gary Jobson To Talk U.S. Prospects in Upcoming World Sailing Competitions

For Sale: 2005 Tayana 48

Make Downwind Sailing Fun Again. Turn Off That Motor and Unfurl Your Kite!
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

Rope, rigging & deck gear: how to choose the right rope
- Toby Heppell
- April 12, 2021
Rope continues to develop every year. We take a look at the plethora of options on the market

Rope is one of the most important tools for the cruising sailor
There was a time when selecting the correct boat rope for a specific task was scarcely more complicated than choosing a larger diameter for higher loads.

Choose ropes according to their role to hit the right balance between price and performance
But as new materials have been developed – offering differing characteristics, woven in different ways, with or without a jacket – deciding on which rope is right for you can be something of a minefield.
Typically, the better a rope performs in any number of areas, the higher the price tag, so for most sailors there is something of a cost-benefit analysis to be made when deciding which product to buy.
It is wise to ask yourself what specific improvement you are paying for and whether, ultimately, it is worth the additional expense.
It is also worth noting that, though we tend to equate cheaper with lower performance, that is not always the case.
Sometimes picking up a more expensive rope assuming it will behave better due to the higher price tag can leave you with an inferior product for a specific task.
On the other hand, due to the cost price of the materials they use, manufacturers don’t tend to vary hugely in terms of outright price charged for a given product.
As such, if you manage to find a rope that is significantly cheaper than everyone else online, it is worth being fairly cautious.
Rope is our most important tool and for most cruising sailors, a knowledge of the basic types established half a century ago has been enough to get by.
Traditionally, we’ve accepted what manufacturers or riggers gave us, perhaps made a decision about nylon rather than polyester for the anchor, and that’s been the end of the matter.
But progress in the past decade or so has been meteoric, driven largely by race boats. Some of these developments lie beyond the needs of cruisers, but the critical elements are right up our alley.
What’s changed and why
We’re now relatively used to seeing the term ‘high-modulus’ in reference to ropes.

English Braids’ R5 is made with yarn sourced from recycled plastic
These have been used at the highest end of sailing for well over 20 years, though until relatively recently were only available at eye-watering prices.
The term ‘high-modulus’ refers to Young’s Modulus of Elasticity.
The higher the value of this figure, the less a rope will stretch.
As it happens, most high-modulus ropes are also exceedingly strong – at least equivalent to wire – and can withstand far more load than any ropes previously.
Not only are these ropes unbelievably strong and light, they also repel water, so won’t get heavier when wet.
The same may not apply to the cover, depending on what this is made of.
The essentials remain the same as they have for a generation, though, with the high-modulus option best seen as an important bolt-on.
Polyester three-strand rope
Once the mainstay of yacht ropes, three-strand polyester is now largely used for shorelines.
Stretch is relatively low, price is not too steep and abrasion resistance is reasonable, so if that’s how you like your shorelines, it’ll do nicely.

Octo-plait gives plenty of flexibility
If you prefer more flexibility, try polyester multi-plait or ‘octo-plait.’ It seems to resist chafe better than three-strand, and if one strand does wear through, there are another seven to go.
Polypropylene three-strand rope
This is a cheap and not-too-cheerful option for shorelines.
It chafes easily, is degraded rapidly by sunlight and isn’t as strong as other rope variants.
Where polypropylene excels is in its ability to float.
As long as you have bought the best you can find (the really cheap line won’t coil at all), it will make a great heaving line as it isn’t too heavy to throw and won’t sink into your propeller.
Nylon, whether three-strand or multi-plait, is the strongest of the non-hi-tech ropes and is set aside from the others by its remarkably low elastic modulus.
This means that if it takes a snatch load, it will elongate rather than break, making it the top choice for anchor rodes and snubbers ever since it was invented.
For shorelines, many prefer polyester or really meaty polyprop because, the argument goes, you don’t want them stretching to leave the boat hanging off the dock.

Marlow’s classic braid-on-braid is very popular
However, nylon can be a better option because it soaks up any snatching and, so long as you’ve bought nylon that’s big enough for your boat, stretch won’t be an issue.
Nylon is also a very good option for gybe preventers. The less a preventer stretches, the more likely it is to damage the boom in a crash gybe .
Nylon has long been the default rope for all running rigging in cruising yachts.

Something with a bit of give is ideal for mooring
It might be ‘braid-on-braid’, with similar outer and inner parts, as sold by most manufacturers, or it could be a low-stretch polyester braidline (LSP) with a loosely laid three-strand core, such as Marlowbraid.
The stretch reduction of this can be as much as 40 per cent, which is well worth the extra you’ll pay.
Much of the braid-on-braid now sold is pre-stretched at the factory, which creates rope that’s an improvement on non pre-stretched lines, but it’s not as good as LSP, so is less than ideal for halyards on all but the smallest yachts.
With respectable strength, easy splicing and good price, braid-on-braid is the logical option for working sheets, kicker tackle, pole guys and the like.
It starts off soft to handle, but it can stiffen up over the years until the friction it creates passing round a block becomes so heavy that the boat’s winches are inadequate.
It also chafes relatively easily and it stretches a lot compared with more modern alternatives.
Buy Marlow Rope’s doublebraid rope on Amazon (UK)
Buy Kingfisher Braid on braid from Force 4
Buy Liros braid on braid from Force 4
Note: We may make a small commission on purchases made via the links on this feature. In no way does that affect our editorial independence.
Cores and modern rope.
Modern ropes are made of two components – a core that accounts for up to 95% of the rope’s strength, plus a protective outer cover (or jacket) that provides abrasion resistance, protection from sunlight and, where appropriate, improved holding in a clutch, jammer or cleat.
The cover can also be designed for better handling comfort.

Without a protective outer layer, modern rope will deteriorate in UV light
On racing boats this will usually be sacrificed in favour of a performance benefit, be it holding capability or resistance, but for the cruising sailor, striking a balance between performance and comfort is a key concern.
Broadly speaking, when talking about modern ropes, there are four or five major fibres involved – primarily Dyneema, Technora, Kevlar and polyester.
Until recently, Vectran was also used frequently, but its low resistance to ultra-violet light means there are now better fibres on the market.
These materials are blended together in different ways to produce both cores and covers that are optimised for each function on the boat.
Dyneema focus
Dyneema is perhaps the most important fibre currently used to manufacture ropes and is a proprietary brand name of DSM, which developed and sells it.
As such, brands selling Dyneema products will almost always feature the Dyneema name and/or trademark.
Dyneema is not the be all and end all of ropes but it does cover most areas and is a reliable purchase thanks to the above reasons.
All of the ‘big four’ manufacturers working in the UK – English Braids, Kingfisher, Liros, and Marlow – feature Dyneema in their performance products.

Dyneema comes in a variety of types and strengths
Dyneema lines come in different types too.
So simply specifying a Dyneema line of an appropriate size is not sufficient. Dyneema sells four different types of fibre for the marine sector: SK75, 78, 90 and 99.
SK75 has been around a while and combines strength with lightweight.
SK78 is a higher-end product with lower creep (permanent long-term elongation that arises from extended periods under load), while Dyneema SK90 has more strength, but with slightly more creep.
Continues below…

How to tie a soft shackle
Soft shackles can be used almost anywhere you currently use a conventional shackle. Look on any boat and you will…

How to make a Brummel Lock Splice for low-friction rings
Low friction rings are a robust and cost-effective addition to your boat. Graham Snook explains how to make a Brummel…

Why you should regularly check your deck fittings
What’s really going on under your deck fittings? Ben Sutcliffe-Davies investigates the hidden weaknesses

Spinnaker masterclass: tailored downwind sailing
There’s more than one way to rig, hoist, set and drop your spinnaker. Choosing the right setup and skills is…
In recent years Dyneema SK99 has been making significant inroads into the racing world and is now used by all major manufacturers.
SK99 has become one of the class leaders in the rope rigging field and offers a breaking load of almost a tonne in 3mm rope!
For most cruising sailors, however, the latter would be overkill, says Nigel Saddington of Kingfisher Rope.
‘I would say that 78 has superseded 75 and 99 has superseded 90 right now. But even then, to be honest, for most sailors and in most circumstances, I would say 78 is sufficient for almost all needs.’
Buy Marlow Excel Fusion Rope – SK75 Dyneema core – from Force 4
Buy Liros Magic Edge Rope – SK75 Dyneema – from Force 4
Effect on deck fittings
Nigel points to some concerns he has with the very top end of the Dyneema ropes being produced.
He notes that as a commercial product, its strength and stiffness are the qualities that make it a good rope but also make it a rope to be used with care.
This is because the loads that can be carried, even in a relatively small-diameter line, are high enough to warrant extra consideration with regards to which clutches and sails it is being used with.

Though super-strong modern ropes are ideal on race boats, their deck gear is set up to handle loads it will be working under
This is a theme that seems to pop-up time and again in recent years; as modern materials become stronger, so the rest of the kit on board needs to be up-spec’d in order to keep up.
Though it is impressive how much load can be carried by the highest-performing ropes, in relatively small diameters you still need something wide enough for your clutch to hold, and you will also want to ensure that your deck gear is rated high enough to deal with the loads.
Saving a halyard at the cost of losing a clutch might not be such a good idea.
That basic core of modern ropes isn’t the only area where there have been developments, however.
Here, a Dyneema mix is a popular option which has the benefit of being extremely light and, perhaps because it floats, is as resistant to water as the Dyneema inside – great for lightweight spinnaker sheets that stay light even after they’ve been dunked a few times.
The downside is that it doesn’t last very long because of the vulnerability of polypropylene to UV degradation.
The ‘entry-level’ coat is polyester of similar specification to the standard braid-on-braid most of us use.
This is relatively loosely woven, making for easy splicing.
Although the resulting rope’s performance is streets ahead of its braid-on-braid equivalent, it is prone to chafe and is more likely to slip around the core.
In other words, the clutch catches the cover but the core can slide through until equilibrium is reached.

Many modern fibres do not melt, making them fray easily when cut
Next up the scale comes Technora, a para-aramid fibre woven far more tightly.
A coat of this is a little more expensive than a basic polyester cover, but the improvement in performance and chafe-resistance is huge.
If your halyards are wearing through and need replacing, it’s a no-brainer.
Finally, if you want to see your ropes in the dark, you can specify a cover that has a light-positive strand.
This works on the same principle as those garden lights that soak up power by day then illuminate when it’s dark.
The rope won’t dazzle you, but you’ll certainly appreciate being able to see it so easily at night.
What ropes to use in running rigging
On most cruisers, sheets and other ropes that are constantly adjusted and not under tremendous load can sensibly be braid-on-braid for economy, ease of splicing and soft feel.
Lines that are set up tightly then left are a different story, however.
On a boat with pretensions to performance, high-modulus ropes can make a dramatic difference.

A clutch needs to be closely matched with a rope’s breaking strain and diameter
Reef pennants are a case in point.
A Dyneema pennant can be a size or two smaller than the standard braidline item, yet will be just as strong and will stay tight once set up.
Main halyards should definitely be made out of some variety of Dyneema, ideally with a Technora coat or its equivalent.
Wire halyards are a thing of the past now, particularly when rope can cope with almost the same loads for its size, with few of the drawbacks.
Headsail halyards should also ideally be top-quality rope, but on roller forestays it can be easier to maintain luff tension than on a mainsail.
So, if funds are tight, upgrade the main halyard first and see how you get on.
Creep stretch and elasticity definitions
Initial loading will result in elastic extension.
This happens upon loading and is immediately recoverable upon release of the load (elastic contraction).
After the elastic extension of the initial loading, the rope will experience what is known as viscoelastic extension.
This is further extension over time and is fairly limited.

It’s not a question of ‘best’ or ‘cheapest’, but buying rope with the right properties for the task
Unlike elastic stretch, viscoelastic stretch will only recover slowly over time once the load is released.
Finally there is creep, which is permanent, non-recoverable and time-dependent.
Creep occurs at the yarn molecular level when the rope is under constant load.
Once the load is released and elastic and viscoelastic extension recovered, the rope will ultimately have experienced an element of permanent extension.
This is a factor of both creep and ‘bedding in’, which is when individual fibre components in the rope and/or splice settle into their preferred position when under load.
Enjoyed reading Rope, rigging & deck gear: how to choose the right rope?
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.
The Ultimate Guide to Sailboat Rigging Rope

What is sailboat rigging rope?
Sailboat rigging rope is the lifeline of a sailboat , connecting the sails to the mast and allowing the boat to harness the power of the wind.
Essentially, it is a specialized type of rope that is designed to withstand the forces and stresses encountered while sailing.
Why is a rope called a line on a boat?
In nautical terms, a line refers to a rope that has a specific purpose or is used for a particular function.
For example, a halyard line is used to hoist a sail, while a sheet line controls the position of the sail.
By using the word “line” instead of “rope,” sailors were able to clearly communicate their intentions and actions on a boat.
What ropes are used for ship rigging?
When it comes to sailboat rigging ropes, there are a variety of types available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Let’s explore some of the most common types and their uses.
Polyester ropes.
Polyester ropes are popular for their durability, strength, and resistance to UV rays and saltwater corrosion. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, from halyards and sheets to control lines and running rigging.
Dyneema ropes
Dyneema ropes, also known as high-performance ropes, are incredibly strong and lightweight. They are perfect for high-load applications such as rigging and running backstays, where strength and low stretch are crucial.
Sta-Set ropes
Sta-Set ropes are made from polyester and are known for their flexibility and ease of handling. They are commonly used for general-purpose applications like halyards, sheets, and control lines.
Wire ropes, made from stainless steel, provide excellent strength and resistance to abrasion. They are commonly used for standing rigging , such as shrouds and stays, where stiffness and stability are required.
Vectran ropes
Vectran ropes offer high strength and low stretch properties, making them suitable for applications that require minimal elongation, such as halyards and control lines.
- Boat Rigging: Everything You Need to Know
- Line or Rope of Your Boats (explained)
- Choosing The Right Mooring Lines Or Dock Lines For Your Boat
- What’s the Difference Between a Spring line, a Breast line, and a Dock Line?
Which type of rope used in rigging is the strongest?
- One of the strongest types of rope used in rigging is Dyneema.
This high-performance rope is incredibly strong and lightweight, making it perfect for high-load applications. Its low stretch characteristics also contribute to its strength, ensuring minimal elongation under heavy loads.
- Stainless steel wire ropes are also known for their exceptional strength.
Made from corrosion-resistant stainless steel, these ropes provide excellent tensile strength and resistance to abrasion.
What are the three ropes on a boat?
On a sailboat, three primary ropes play essential roles in controlling and maneuvering the boat.
The first rope is called the halyard, and it is used to raise and lower the sails.
The halyard connects to the top of the sail and allows you to adjust its position and tension. Common options for Halyard include polyester, nylon, and dyneema.
The second rope is known as the sheet. Sheets are used to control the angle and position of the sails in relation to the wind.
There are typically separate sheets for the main sail and jib or genoa. By adjusting the tension and angle of the sheets, you can optimize the sail’s performance and power.
Common options for sheets include polyester, nylon, and blended ropes.
Control line
The third rope is the control line.
Control lines are used for various purposes, such as adjusting the shape of the sails, controlling the boom, or operating the boat’s various systems.
They are typically found on larger boats with more complex rigging setups.
Generally, control lines need to be strong and durable, with good grip and flexibility. Common options include polyester, nylon, and braided ropes.
How do i choose a rigging rope?
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Assess your sailing needs
Consider the size of your boat, the sailing conditions you typically encounter, and your rigging setup. This will help you determine the strength and durability requirements for your rigging rope .
2. Research different rope materials
Look into the characteristics and benefits of materials like polyester, Dyneema, and stainless steel. Understand how each material performs in terms of strength, UV resistance, and corrosion resistance.
3. Determine the appropriate size
Based on your boat size and rigging setup, identify the ideal thickness and strength of rope needed. Larger boats and high-performance rigs will generally require thicker and stronger ropes, while smaller boats may benefit from lighter options.
4. Consider flexibility and handling
Ensure that the rope you choose is easy to work with and provides a good grip. It should be flexible enough to maneuver but not overly stretchy.
5. Consult with experts
If you’re unsure about any aspect of choosing a rigging rope, don’t hesitate to seek advice from professionals or experienced sailors. They can provide valuable insights and help you make the best decision for your specific needs.
What size rope do i need for my boat?
The size of the rope you need will depend on the size of your boat, the specific rigging setup, and the intended use of the rope.
For example a 20 foot sailboat , you would typically need a halyard rope that is around 5/16 to 3/8 inches in diameter. The length of the rope should be long enough to reach from the masthead to the cockpit, allowing for proper hoisting and trimming of the sails.
Generally, a sheet rope with a diameter of 5/16 inch or 3/8 inch should suffice for most sailboats. As a general guideline, the length of the rope should be at least twice the length of your boat. This will allow for proper handling and maneuvering of the sail.
Why is a line called a sheet?
The term “sheet” likely comes from the old English word “sceata,” which means corner or border. The ropes were called sheets because they controlled the corners or edges of the sail.
Over time, the term “sheet” became associated with any rope that controls the position or angle of a sail.
How long should boat lines be?
Boat lines are ropes used for various purposes, such as docking, anchoring, and securing the boat.
A general guideline is to ensure that boat lines are at least 2-3 times the length of your boat. This will provide enough length to handle different docking scenarios and ensure the safety of your vessel.
It’s also a good idea to have a variety of lengths available to accommodate different situations.
Common Problems and Solutions for Sailboat Rigging Ropes
Here are some common problems you may encounter with sailboat rigging ropes and their troubleshooting solutions:
1. Fraying or wear
If you notice any signs of fraying, it’s important to replace the rope immediately to avoid accidents. Regularly inspect your ropes for wear and tear and replace them as needed.
2. Tangling or kinking
To prevent tangling or kinking, always store your rigging ropes neatly coiled and avoid knots or tangles. If your rope becomes tangled, carefully untangle it to restore its proper function.
3. Stiffness or difficulty in maneuvering
If your rope becomes stiff or difficult to maneuver, it may need lubrication. Apply a suitable lubricant to the moving parts of the rope to restore smooth operation.
4. Slippage
If your rope slips or loses tension, you may need to adjust the knot or connection. Ensure that all knots are properly tied and secure, and adjust the tension as needed.
5. Corrosion or rust
Stainless steel wire ropes are resistant to corrosion, but they can still develop rust over time. Regularly inspect your stainless steel ropes for any signs of rust and replace them if necessary.
6. Overloading
Avoid overloading your ropes beyond their recommended weight limits. Be aware of the maximum load capacity of your ropes and use appropriate ropes for heavier loads.

Standing Rigging (or ‘Name That Stay’)
Published by rigworks on november 19, 2019.
Question: When your riggers talk about standing rigging, they often use terms I don’t recognize. Can you break it down for me?
From the Rigger: Let’s play ‘Name that Stay’…
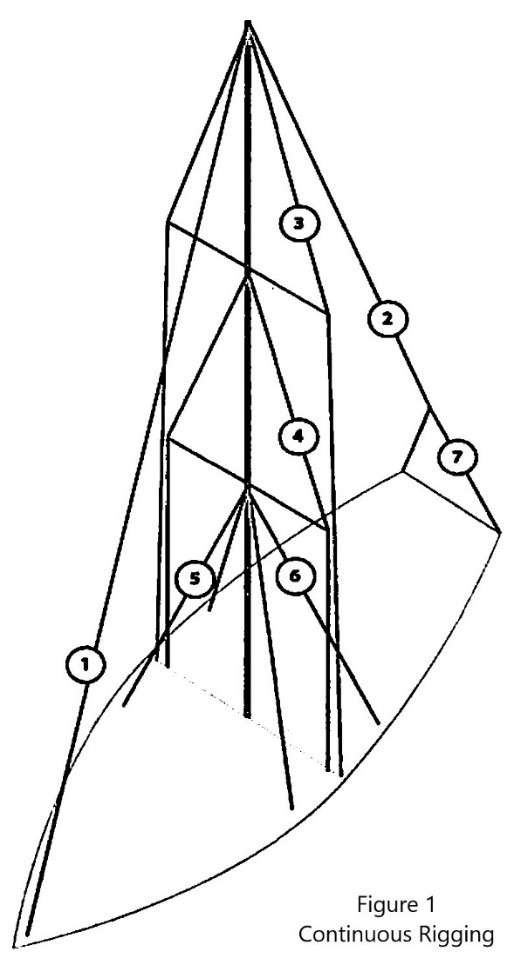
Forestay (1 or HS) – The forestay, or headstay, connects the mast to the front (bow) of the boat and keeps your mast from falling aft.
- Your forestay can be full length (masthead to deck) or fractional (1/8 to 1/4 from the top of the mast to the deck).
- Inner forestays, including staysail stays, solent stays and baby stays, connect to the mast below the main forestay and to the deck aft of the main forestay. Inner forestays allow you to hoist small inner headsails and/or provide additional stability to your rig.
Backstay (2 or BS) – The backstay runs from the mast to the back of the boat (transom) and is often adjustable to control forestay tension and the shape of the sails.
- A backstay can be either continuous (direct from mast to transom) or it may split in the lower section (7) with “legs” that ‘V’ out to the edges of the transom.
- Backstays often have hydraulic or manual tensioners built into them to increase forestay tension and bend the mast, which flattens your mainsail.
- Running backstays can be removable, adjustable, and provide additional support and tuning usually on fractional rigs. They run to the outer edges of the transom and are adjusted with each tack. The windward running back is in tension and the leeward is eased so as not to interfere with the boom and sails.
- Checkstays, useful on fractional rigs with bendy masts, are attached well below the backstay and provide aft tension to the mid panels of the mast to reduce mast bend and provide stabilization to reduce the mast from pumping.
Shrouds – Shrouds support the mast from side to side. Shrouds are either continuous or discontinuous .
Continuous rigging, common in production sailboats, means that each shroud (except the lowers) is a continuous piece of material that connects to the mast at some point, passes through the spreaders without terminating, and continues to the deck. There may be a number of continuous shrouds on your boat ( see Figure 1 ).
- Cap shrouds (3) , sometimes called uppers, extend from masthead to the chainplates at the deck.
- Intermediate shrouds (4) extend from mid-mast panel to deck.
- Lower shrouds extend from below the spreader-base to the chainplates. Fore- (5) and Aft-Lowers (6) connect to the deck either forward or aft of the cap shroud.
Discontinuous rigging, common on high performance sailboats, is a series of shorter lengths that terminate in tip cups at each spreader. The diameter of the wire/rod can be reduced in the upper sections where loads are lighter, reducing overall weight. These independent sections are referred to as V# and D# ( see Figure 2 ). For example, V1 is the lowest vertical shroud that extends from the deck to the outer tip of the first spreader. D1 is the lowest diagonal shroud that extends from the deck to the mast at the base of the first spreader. The highest section that extends from the upper spreader to the mast head may be labeled either V# or D#.
A sailboat’s standing rigging is generally built from wire rope, rod, or occasionally a super-strong synthetic fibered rope such as Dyneema ® , carbon fiber, kevlar or PBO.
- 1×19 316 grade stainless steel Wire Rope (1 group of 19 wires, very stiff with low stretch) is standard on most sailboats. Wire rope is sized/priced by its diameter which varies from boat to boat, 3/16” through 1/2″ being the most common range.
- 1×19 Compact Strand or Dyform wire, a more expensive alternative, is used to increase strength, reduce stretch, and minimize diameter on high performance boats such as catamarans. It is also the best alternative when replacing rod with wire.
- Rod rigging offers lower stretch, longer life expectancy, and higher breaking strength than wire. Unlike wire rope, rod is defined by its breaking strength, usually ranging from -10 to -40 (approx. 10k to 40k breaking strength), rather than diameter. So, for example, we refer to 7/16” wire (diameter) vs. -10 Rod (breaking strength).
- Composite Rigging is a popular option for racing boats. It offers comparable breaking strengths to wire and rod with a significant reduction in weight and often lower stretch.
Are your eyes crossing yet? This is probably enough for now, but stay tuned for our next ‘Ask the Rigger’. We will continue this discussion with some of the fittings/connections/hardware associated with your standing rigging.
Related Posts

Ask the Rigger
Do your masthead sheaves need replacing.
Question: My halyard is binding. What’s up? From the Rigger: Most boat owners do not climb their masts regularly, but our riggers spend a lot of time up there. And they often find badly damaged Read more…
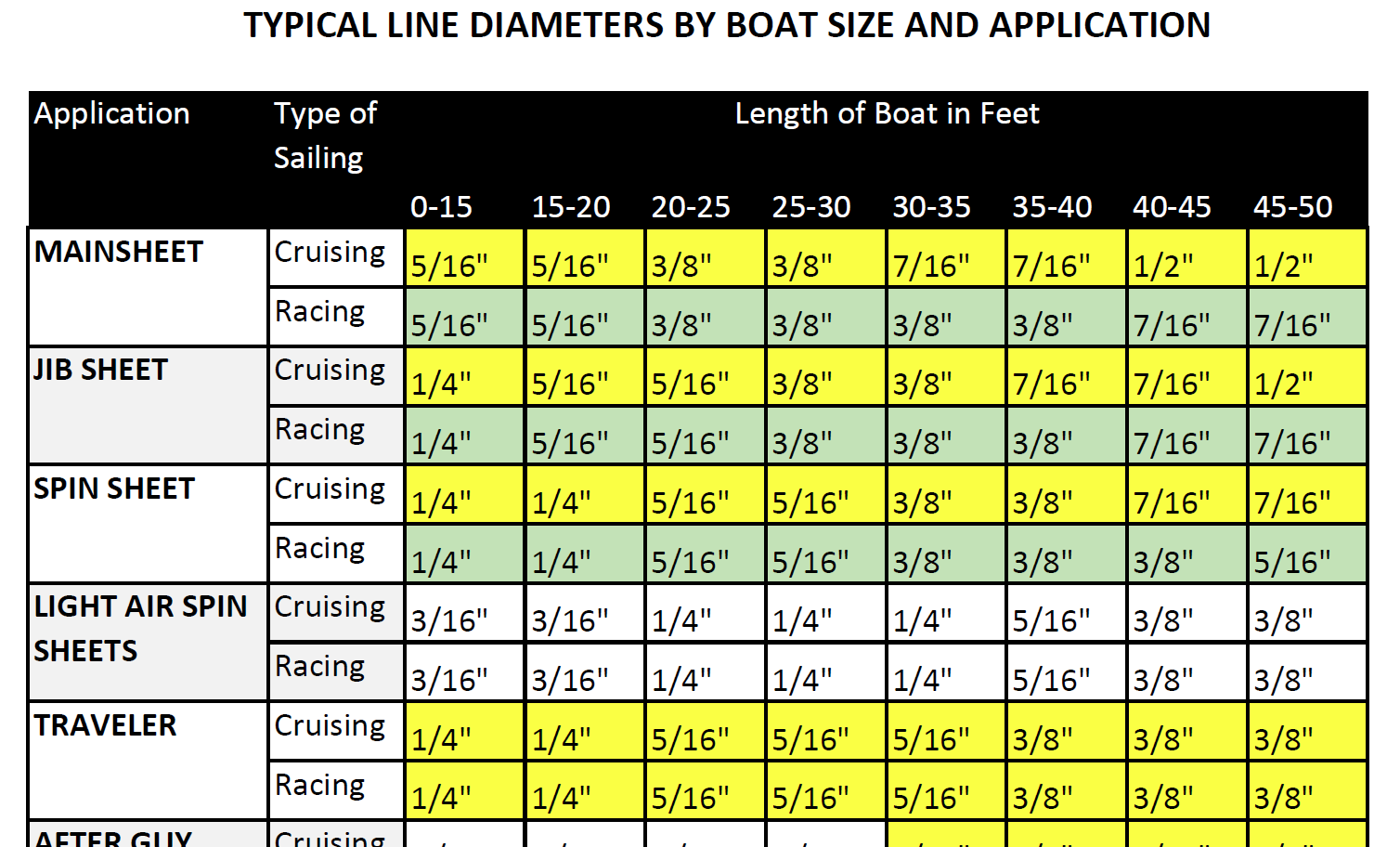
Selecting Rope – Length, Diameter, Type
Question: Do you have guidelines for selecting halyards, sheets, etc. for my sailboat? From the Rigger: First, if your old rope served its purpose but needs replacing, we recommend duplicating it as closely as possible Read more…

Spinlock Deckvest Maintenance
Question: What can I do to ensure that my Spinlock Deckvest is well-maintained and ready for the upcoming season? From the Rigger: We are so glad you asked! Deckvests need to be maintained so that Read more…
- Rock Climbing
- Home & Crafting
- Recreation & Sports
- Cargo & Towing
- Polypropylene
- Double Braid
- Diamond Braid
- Solid Braid
- Mission Rope
- Tracer Rope
- Teufelberger
- New England Ropes
- Maxim Climbing Ropes
- Samson Rope
- I'd like to search by sized at width Find my Rope
Collections
Sailboat rigging lines.

Multi-purpose double braid line that holds up to the elements.

Economical spun polyester static rope

Strong and thin sporting rope made from dyneema.

Pre-stretched ArmourCoated Dyneema rope

High strength and stretch performance for a polyester braid-on-braid

Dyneema SK78 rope unrivalled in strength and low elongation
Polyester option for windsurf downhauls and outhauls

Low stretch and zero creep

The first and best dedicated line for continuous loop dinghy control lines

High strength and minimal creep

Ideal for halyards, sheets and high strength control lines.

Blended Dyneema and Polypropylene cover

Designed to be spliced for halyard tails and lazy jacks

Vectran/Technora cover ensures heat and abrasion resistance

Lightweight and high strength, single braid Dyneema

Made with bio-based Dyneema fiber

Low stretch with outstanding heat resistance

High performance sheet performing well in ratchet blocks
- Best selling
- Alphabetically, A-Z
- Alphabetically, Z-A
- Price, low to high
- Price, high to low
- Date, old to new
- Date, new to old

Available Mon-Fri, 9am–5pm ET

Pick up the phone and talk to one of our rope specialist to find your answers.
(888) 619-ROPE (7673)

Phone not your thing? Send us a message via chat and we will be happy to help.
Ask us anything

Send us an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Running Rigging On A Sailboat Explained
The running rigging on a sailboat consists of all the lines used to hoist, lower, and control the sails and sailing equipment. These lines usually have different colors and patterns to easily identify their function and location on the vessel.
Looking at the spaghetti of lines with different colors and patterns might get your head spinning. But don’t worry, it is actually pretty simple. Each line on a sailboat has a function, and you’ll often find labels describing them in the cockpit and on the mast.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the functions of every component of the running rigging. We’ll also look at the hardware we use to operate it and get up to speed on some of the terminology.
The difference between standing rigging and running rigging
Sometimes things can get confusing as some of our nautical terms are used for multiple items depending on the context. Let me clarify just briefly:
The rig or rigging on a sailboat is a common term for two parts, the standing , and the running rigging.
- The standing rigging consists of wires supporting the mast on a sailboat and reinforcing the spars from the force of the sails when sailing. Check out my guide on standing rigging here!
- The running rigging consists of the halyards, sheets, and lines we use to hoist, lower, operate and control the sails on a sailboat which we will explore in this guide.
The components of the running rigging
Knowing the running rigging is an essential part of sailing, whether you are sailing a cruising boat or crewing on a large yacht. Different types of sailing vessels have different amounts of running rigging.
For example, a sloop rig has fewer lines than a ketch, which has multiple masts and requires a separate halyard, outhaul, and sheet for its mizzen sail. Similarly, a cutter rig needs another halyard and extra sheets for its additional headsail.
You can dive deeper and read more about Sloop rigs, Ketch Rigs, Cutter rigs, and many others here .
Take a look at this sailboat rigging diagram:
Lines are a type of rope with a smooth surface that works well on winches found on sailboats. They come in various styles and sizes and have different stretch capabilities.
Dyneema and other synthetic fibers have ultra-high tensile strength and low stretch. These high-performance lines last a long time, and I highly recommend them as a cruiser using them for my halyards.
A halyard is a line used to raise and lower the sail. It runs from the head of the sail to the masthead through a block and continues down to the deck. Running the halyard back to the cockpit is common, but many prefer to leave it on the mast.
Fun fact: Old traditional sailboats sometimes used a stainless steel wire attached to the head of the sail instead of a line!
Jib, Genoa, and Staysail Halyards
The halyard for the headsail is run through a block in front of the masthead. If your boat has a staysail, it needs a separate halyard. These lines are primarily untouched on vessels with a furling system except when you pack the sail away or back up. Commonly referred to as the jib halyard.
Spinnaker Halyard
A spinnaker halyard is basically the same as the main halyard but used to hoist and lower the spinnaker, gennaker, or parasailor.
The spinnaker halyard is also excellent for climbing up the front of the mast, hoisting the dinghy on deck, lifting the outboard, and many other things.
A sheet is a line you use to control and trim a sail to the angle of the wind . The mainsheet controls the angle of the mainsail and is attached between the boom and the mainsheet traveler . The two headsail sheets are connected to the sail’s clew (lower aft corner) and run back to each side of the cockpit.
These are control lines used to adjust the angle and tension of the sail. It is also the line used to unfurl a headsail on a furling system. Depending on what sail you are referring to, this can be the Genoa sheet , the Jib sheet , the Gennaker sheet , etc.
The outhaul is a line attached to the clew of the mainsail and used to adjust the foot tension. It works runs from the mainsail clew to the end of the boom and back to the mast. In many cases, back to the cockpit. On a boat with in-mast furling , this is the line you use to pull the sail out of the mast.
Topping lift
The topping lift is a line attached to the boom’s end and runs through the masthead and down to the deck or cockpit. It lifts and holds the boom and functions well as a spare main halyard. Some types of sailboat rigging don’t use a topping lift for their boom but a boom vang instead. Others have both!
Topping lifts can also be used to lift other spars.
A downhaul is a line used to lower with and typically used to haul the mainsail down when reefing and lowering the spinnaker and whisker poles. The downhaul can also control the tack of an asymmetrical spinnaker, gennaker, or parasailor.
Tweaker and Barber Haul
A tweaker is a line, often elastic, attached to the sheet of a headsail and used to fine-tune the tension on the sheet.
Barber haul
A barber haul is a line attached to a headsail’s sheet to adjust the sheeting angle to the wind. It is often used to pull the clew further toward the center or outboard than the cars allow.
Boom Preventer
A boom preventer is a line attached to the boom’s end when sailing off the wind. Its function is to hold the spar in place and prevent it from swinging wildly.
If the boat were to get an accidental gybe, it could cause serious damage to the rigging or even harm people on board. It is important for the rigger to be cautious when setting up the boom preventer.
Running Backstay
Running backstays is similar to a normal backstay but uses a line instead of a hydraulic tensioner. Some rigs have additional check stays or runners as well.
Bonus tip: Reefing
The term reefing is used when reducing the effective sailing area exposed to the wind of a given sail. Headsails are usually reefed by partially furling them in, and they often have marks for what we refer to as 1st, 2nd, and 3rd reefs.
The mainsail is reefed similarly with an in-mast furling or in-boom furling system.
On a traditional mast, we use a system called slab reefing. The system has reefing lines running through the boom to reinforced points on the luff and leech, allowing you to pull the sail down to the boom and effectively reduce the sail area.
Having at least two reefing points in the mainsail is normal, but most cruising sailboats have 3. The 3rd is used for the heaviest conditions, giving you only a tiny bit of sail area exposed to the wind.
You want to reef your sails before the wind increases to a point where your boat gets overpowered.
It is essential to practice your reefing technique . You will find yourself in situations with rapidly increasing winds where you need to reduce your sails quickly.
Rule of thumb: If you think setting a reef might be a good idea, do it.
Shaking a reef is the term used when we sail with a reefed sail and want to increase the sail area back to full.
Hardware used for sail handling and the running rigging
Furling system.
Most sailboats have their headsail on a furling system. A furling system is a tube that runs along the forestay from the bottom furler drum to the masthead swivel.
This system allows you to roll the headsail around the forestay, making furling the sail in and out accessible. It is also convenient when reefing the sail when the wind picks up, as you can easily do this from the safety of the cockpit. These furling systems come in manual versions and electric versions.
In-mast furling
In-mast furling is a system that rolls the mainsail in and out of the mast. To unfurl the mainsail, we use the outhaul .
In-boom furling
In-boom furling is a system that rolls the mainsail in and out of the boom. This system has been costly and has mostly been seen on big yachts earlier. They are becoming more affordable and common on smaller boats, though. To unfurl this setup, we use the main halyard.
A Stack pack is also called a Lazy Bag or Lazy Pack. It is a bag with a zip attached to the boom where the mainsail is stored when unused. It protects the mainsail from UV rays from the sun and weather elements. It is a very nice and tidy way to store the mainsail and reefing lines if you don’t have in-mast or in-boom furling.
Lazy Jacks is a system of lines running from the stack pack to the mast. The Lazy Jacks guide the mainsail up and down from the Stack Pack and prevent it from falling down on the deck. It is also possible to rig Lazy Jacks without a Stack Pack.
A block is a pulley with a sheave wheel. Blocks are used to change the direction of a pull on a line or rope and give a mechanical advantage. They have many uses, especially onboard sailboats.
A winch is a metal drum that gives you a mechanical advantage to control and tighten lines. These can be operated by turning a rope around it and pulling manually or by a winch handle to get more force. Most modern winches are self-tailing, which means they lock the line on so you can winch the line without holding on to it. Some boats even have electrical winches operated by a button.
Mainsheet Traveler
The mainsheet traveler is a horizontal track that the mainsheet is attached to through a series of blocks. The traveler enables you to adjust and lock the boom at an angle and also plays a critical part in trimming the mainsail.
Most cruising sailboats have their traveler attached to the top of the coachroof in front of the spray hood. A racing boat typically has the traveler in the cockpit near the helm to give the helmsman better control over the mainsheet.
The cars are basically a pulley or block attached to a track on the port and starboard deck that your headsail sheets run through. Cars are used to control the angle of the sheet between the clew and the deck. The cars are handy when you trim the sail to set the right balance of tension between the foot and leech, depending on your point of sail.
The jammer is used to lock a line in place. Most sailboats use these for locking the halyards, mainsheet, outhaul, reef lines, traveler lines, boom vang lines, etc. You can pull or winch a line through a closed jammer, but it won’t run away if you let go of it unless you open the lock.
As I explained earlier, it is normal to have most or all of the lines led back to the cockpit, and they are usually run through a series of jammers.
The jammers are often labeled with the name of the line it locks, which makes it easier to remember which line goes where.
Spinnaker Pole
A spinnaker pole is a spar used to wing out a headsail when sailing off the wind, particularly the spinnaker. The spinnaker pole should have the same length as the distance between the mast and the forestay measured along the deck. We use a fore and aft guy and the pole’s topping lift to rig a pole correctly.
The rigging varies depending on the layout of the boat, but it usually looks like this:
- One line runs from the bow to the end of the pole.
- An aft line runs from near the stern to the end of the pole.
- A topping lift is used to raise and lower the pole.
Whisker Pole
A whisker pole is similar to the spinnaker pole and is rigged similarly. It is typically built lighter and attached to a track on the mast. These can be found in fixed lengths or adjustable lengths. Ideally, the length should be the same as the foot of the headsail you intend to pole out.
Boom Vang/Rod Kicker
The Boom Vang has a few different names. Rod-kicker, kicking strap, or kicker. It is used to tension the boom downwards. When you are sailing downwind and have the boom far out, the mainsheet won’t pull the boom down as much as inboard, and you can then use the vang to adjust the twist and shape of the mainsail.
Mooring line
A mooring line is a traditional rope lead through a fairlead to the vessel’s cleat and a mooring buoy, key, or pontoon.
Final words
Congratulations! By now, you should have a much better understanding of how the running rig on a sailboat functions. We’ve covered the different lines, their purpose, and the hardware used to operate them. I hope you’ve enjoyed this guide and learned something new.
Now it’s time to take what you’ve learned and put it into practice by getting out on the water, setting sail, and getting hands-on experience with the lines.
Or you can continue to my following guide and learn more about the different types of sails .
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


Beginner’s Guide: How To Rig A Sailboat – Step By Step Tutorial
Alex Morgan

Rigging a sailboat is a crucial process that ensures the proper setup and functioning of a sailboat’s various components. Understanding the process and components involved in rigging is essential for any sailor or boat enthusiast. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to rig a sailboat.
Introduction to Rigging a Sailboat
Rigging a sailboat refers to the process of setting up the components that enable the sailboat to navigate through the water using wind power. This includes assembling and positioning various parts such as the mast, boom, standing rigging, running rigging, and sails.
Understanding the Components of a Sailboat Rigging
Before diving into the rigging process, it is important to have a good understanding of the key components involved. These components include:
The mast is the tall vertical spar that provides vertical support to the sails and holds them in place.
The boom is the horizontal spar that runs along the bottom edge of the sail and helps control the shape and position of the sail.
- Standing Rigging:
Standing rigging consists of the wires and cables that support and stabilize the mast, keeping it upright.
- Running Rigging:
Running rigging refers to the lines and ropes used to control the sails, such as halyards, sheets, and control lines.
Preparing to Rig a Sailboat
Before rigging a sailboat, there are a few important steps to take. These include:
- Checking the Weather Conditions:
It is crucial to assess the weather conditions before rigging a sailboat. Unfavorable weather, such as high winds or storms, can make rigging unsafe.
- Gathering the Necessary Tools and Equipment:
Make sure to have all the necessary tools and equipment readily available before starting the rigging process. This may include wrenches, hammers, tape, and other common tools.
- Inspecting the Rigging Components:
In the upcoming sections of this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to rig a sailboat, as well as important safety considerations and tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you will be able to rig your sailboat correctly and safely, allowing for a smooth and enjoyable sailing experience.
Key takeaway:
- Rigging a sailboat maximizes efficiency: Proper rigging allows for optimized sailing performance, ensuring the boat moves smoothly through the water.
- Understanding sailboat rigging components: Familiarity with the various parts of a sailboat rigging, such as the mast, boom, and standing and running riggings, is essential for effective rigging setup.
- Importance of safety in sailboat rigging: Ensuring safety is crucial during the rigging process, including wearing a personal flotation device, securing loose ends and lines, and being mindful of overhead power lines.
Get ready to set sail and dive into the fascinating world of sailboat rigging! We’ll embark on a journey to understand the various components that make up a sailboat’s rigging. From the majestic mast to the nimble boom , and the intricate standing rigging to the dynamic running rigging , we’ll explore the crucial elements that ensure smooth sailing. Not forgetting the magnificent sail, which catches the wind and propels us forward. So grab your sea legs and let’s uncover the secrets of sailboat rigging together.
Understanding the mast is crucial when rigging a sailboat. Here are the key components and steps to consider:
1. The mast supports the sails and rigging of the sailboat. It is made of aluminum or carbon fiber .
2. Before stepping the mast , ensure that the area is clear and the boat is stable. Have all necessary tools and equipment ready.
3. Inspect the mast for damage or wear. Check for corrosion , loose fittings , and cracks . Address any issues before proceeding.
4. To step the mast , carefully lift it into an upright position and insert the base into the mast step on the deck of the sailboat.
5. Secure the mast using the appropriate rigging and fasteners . Attach the standing rigging , such as shrouds and stays , to the mast and the boat’s hull .
Fact: The mast of a sailboat is designed to withstand wind resistance and the tension of the rigging for stability and safe sailing.
The boom is an essential part of sailboat rigging. It is a horizontal spar that stretches from the mast to the aft of the boat. Constructed with durable yet lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber, the boom provides crucial support and has control over the shape and position of the sail. It is connected to the mast through a boom gooseneck , allowing it to pivot. One end of the boom is attached to the mainsail, while the other end is equipped with a boom vang or kicker, which manages the tension and angle of the boom. When the sail is raised, the boom is also lifted and positioned horizontally by using the topping lift or lazy jacks.
An incident serves as a warning that emphasizes the significance of properly securing the boom. In strong winds, an improperly fastened boom swung across the deck, resulting in damage to the boat and creating a safety hazard. This incident highlights the importance of correctly installing and securely fastening all rigging components, including the boom, to prevent accidents and damage.
3. Standing Rigging
When rigging a sailboat, the standing rigging plays a vital role in providing stability and support to the mast . It consists of several key components, including the mast itself, along with the shrouds , forestay , backstay , and intermediate shrouds .
The mast, a vertical pole , acts as the primary support structure for the sails and the standing rigging. Connected to the top of the mast are the shrouds , which are cables or wires that extend to the sides of the boat, providing essential lateral support .
The forestay is another vital piece of the standing rigging. It is a cable or wire that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat, ensuring forward support . Similarly, the backstay , also a cable or wire, runs from the mast’s top to the stern of the boat, providing important backward support .
To further enhance the rig’s stability , intermediate shrouds are installed. These additional cables or wires are positioned between the main shrouds, as well as the forestay or backstay. They offer extra support , strengthening the standing rigging system.
Regular inspections of the standing rigging are essential to detect any signs of wear, such as fraying or corrosion . It is crucial to ensure that all connections within the rig are tight and secure, to uphold its integrity. Should any issues be identified, immediate attention must be given to prevent accidents or damage to the boat. Prioritizing safety is of utmost importance when rigging a sailboat, thereby necessitating proper maintenance of the standing rigging. This ensures a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
Note: <p> tags have been kept intact.
4. Running Rigging
Running Rigging
When rigging a sailboat, the running rigging is essential for controlling the sails and adjusting their position. It is important to consider several aspects when dealing with the running rigging.
1. Choose the right rope: The running rigging typically consists of ropes with varying properties such as strength, stretch, and durability. Weather conditions and sailboat size should be considered when selecting the appropriate rope.
2. Inspect and maintain the running rigging: Regularly check for signs of wear, fraying, or damage. To ensure safety and efficiency, replace worn-out ropes.
3. Learn essential knot tying techniques: Having knowledge of knots like the bowline, cleat hitch, and reef knot is crucial for securing the running rigging and adjusting sails.
4. Understand different controls: The running rigging includes controls such as halyards, sheets, and control lines. Familiarize yourself with their functions and proper usage to effectively control sail position and tension.
5. Practice proper sail trimming: Adjusting the tension of the running rigging significantly affects sailboat performance. Mastering sail trimming techniques will help optimize sail shape and maximize speed.
By considering these factors and mastering running rigging techniques, you can enhance your sailing experience and ensure the safe operation of your sailboat.
The sail is the central component of sailboat rigging as it effectively harnesses the power of the wind to propel the boat.
When considering the sail, there are several key aspects to keep in mind:
– Material: Sails are typically constructed from durable and lightweight materials such as Dacron or polyester. These materials provide strength and resistance to various weather conditions.
– Shape: The shape of the sail plays a critical role in its overall performance. A well-shaped sail should have a smooth and aerodynamic profile, which allows for maximum efficiency in capturing wind power.
– Size: The size of the sail is determined by its sail area, which is measured in square feet or square meters. Larger sails have the ability to generate more power, but they require greater skill and experience to handle effectively.
– Reefing: Reefing is the process of reducing the sail’s size to adapt to strong winds. Sails equipped with reefing points allow sailors to decrease the sail area, providing better control in challenging weather conditions.
– Types: There are various types of sails, each specifically designed for different purposes. Common sail types include mainsails, jibs, genoas, spinnakers, and storm sails. Each type possesses its own unique characteristics and is utilized under specific wind conditions.
Understanding the sail and its characteristics is vital for sailors, as it directly influences the boat’s speed, maneuverability, and overall safety on the water.
Getting ready to rig a sailboat requires careful preparation and attention to detail. In this section, we’ll dive into the essential steps you need to take before setting sail. From checking the weather conditions to gathering the necessary tools and equipment, and inspecting the rigging components, we’ll ensure that you’re fully equipped to navigate the open waters with confidence. So, let’s get started on our journey to successfully rigging a sailboat!
1. Checking the Weather Conditions
Checking the weather conditions is crucial before rigging a sailboat for a safe and enjoyable sailing experience. Monitoring the wind speed is important in order to assess the ideal sailing conditions . By checking the wind speed forecast , you can determine if the wind is strong or light . Strong winds can make sailboat control difficult, while very light winds can result in slow progress.
Another important factor to consider is the wind direction . Assessing the wind direction is crucial for route planning and sail adjustment. Favorable wind direction helps propel the sailboat efficiently, making your sailing experience more enjoyable.
In addition to wind speed and direction, it is also important to consider weather patterns . Keep an eye out for impending storms or heavy rain. It is best to avoid sailing in severe weather conditions that may pose a safety risk. Safety should always be a top priority when venturing out on a sailboat.
Another aspect to consider is visibility . Ensure good visibility by checking for fog, haze, or any other conditions that may hinder navigation. Clear visibility is important for being aware of other boats and potential obstacles that may come your way.
Be aware of the local conditions . Take into account factors such as sea breezes, coastal influences, or tidal currents. These local factors greatly affect sailboat performance and safety. By considering all of these elements, you can have a successful and enjoyable sailing experience.
Here’s a true story to emphasize the importance of checking the weather conditions. One sunny afternoon, a group of friends decided to go sailing. Before heading out, they took the time to check the weather conditions. They noticed that the wind speed was expected to be around 10 knots, which was perfect for their sailboat. The wind direction was coming from the northwest, allowing for a pleasant upwind journey. With clear visibility and no approaching storms, they set out confidently, enjoying a smooth and exhilarating sail. This positive experience was made possible by their careful attention to checking the weather conditions beforehand.
2. Gathering the Necessary Tools and Equipment
To efficiently gather all of the necessary tools and equipment for rigging a sailboat, follow these simple steps:
- First and foremost, carefully inspect your toolbox to ensure that you have all of the basic tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Make sure to check if you have a tape measure or ruler available as they are essential for precise measurements of ropes or cables.
- Don’t forget to include a sharp knife or rope cutter in your arsenal as they will come in handy for cutting ropes or cables to the desired lengths.
- Gather all the required rigging hardware including shackles, pulleys, cleats, and turnbuckles.
- It is always prudent to check for spare ropes or cables in case replacements are needed during the rigging process.
- If needed, consider having a sailing knife or marlinspike tool for splicing ropes or cables.
- For rigging a larger sailboat, it is crucial to have a mast crane or hoist to assist with stepping the mast.
- Ensure that you have a ladder or some other means of reaching higher parts of the sailboat, such as the top of the mast.
Once, during the preparation of rigging my sailboat, I had a moment of realization when I discovered that I had forgotten to bring a screwdriver . This unfortunate predicament occurred while I was in a remote location with no nearby stores. Being resourceful, I improvised by utilizing a multipurpose tool with a small knife blade, which served as a makeshift screwdriver. Although it was not the ideal solution, it allowed me to accomplish the task. Since that incident, I have learned the importance of double-checking my toolbox before commencing any rigging endeavor. This practice ensures that I have all of the necessary tools and equipment, preventing any unexpected surprises along the way.
3. Inspecting the Rigging Components
Inspecting the rigging components is essential for rigging a sailboat safely. Here is a step-by-step guide on inspecting the rigging components:
1. Visually inspect the mast, boom, and standing rigging for damage, such as corrosion, cracks, or loose fittings.
2. Check the tension of the standing rigging using a tension gauge. It should be within the recommended range from the manufacturer.
3. Examine the turnbuckles, clevis pins, and shackles for wear or deformation. Replace any damaged or worn-out hardware.
4. Inspect the running rigging, including halyards and sheets, for fraying, signs of wear, or weak spots. Replace any worn-out lines.
5. Check the sail for tears, wear, or missing hardware such as grommets or luff tape.
6. Pay attention to the connections between the standing rigging and the mast. Ensure secure connections without any loose or missing cotter pins or rigging screws.
7. Inspect all fittings, such as mast steps, spreader brackets, and tangs, to ensure they are securely fastened and in good condition.
8. Conduct a sea trial to assess the rigging’s performance and make necessary adjustments.
Regularly inspecting the rigging components is crucial for maintaining the sailboat’s rigging system’s integrity, ensuring safe sailing conditions, and preventing accidents or failures at sea.
Once, I went sailing on a friend’s boat without inspecting the rigging components beforehand. While at sea, a sudden gust of wind caused one of the shrouds to snap. Fortunately, no one was hurt, but we had to cut the sail loose and carefully return to the marina. This incident taught me the importance of inspecting the rigging components before sailing to avoid unforeseen dangers.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Rig a Sailboat
Get ready to set sail with our step-by-step guide on rigging a sailboat ! We’ll take you through the process from start to finish, covering everything from stepping the mast to setting up the running rigging . Learn the essential techniques and tips for each sub-section, including attaching the standing rigging and installing the boom and sails . Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner, this guide will have you ready to navigate the open waters with confidence .
1. Stepping the Mast
To step the mast of a sailboat, follow these steps:
1. Prepare the mast: Position the mast near the base of the boat.
2. Attach the base plate: Securely fasten the base plate to the designated area on the boat.
3. Insert the mast step: Lower the mast step into the base plate and align it with the holes or slots.
4. Secure the mast step: Use fastening screws or bolts to fix the mast step in place.
5. Raise the mast: Lift the mast upright with the help of one or more crew members.
6. Align the mast: Adjust the mast so that it is straight and aligned with the boat’s centerline.
7. Attach the shrouds: Connect the shrouds to the upper section of the mast, ensuring proper tension.
8. Secure the forestay: Attach the forestay to the bow of the boat, ensuring it is securely fastened.
9. Final adjustments: Check the tension of the shrouds and forestay, making any necessary rigging adjustments.
Following these steps ensures that the mast is properly stepped and securely in place, allowing for a safe and efficient rigging process. Always prioritize safety precautions and follow manufacturer guidelines for your specific sailboat model.
2. Attaching the Standing Rigging
To attach the standing rigging on a sailboat, commence by preparing the essential tools and equipment, including wire cutters, crimping tools, and turnbuckles.
Next, carefully inspect the standing rigging components for any indications of wear or damage.
After inspection, fasten the bottom ends of the shrouds and stays to the chainplates on the deck.
Then, securely affix the top ends of the shrouds and stays to the mast using adjustable turnbuckles .
To ensure proper tension, adjust the turnbuckles accordingly until the mast is upright and centered.
Utilize a tension gauge to measure the tension in the standing rigging, aiming for around 15-20% of the breaking strength of the rigging wire.
Double-check all connections and fittings to verify their security and proper tightness.
It is crucial to regularly inspect the standing rigging for any signs of wear or fatigue and make any necessary adjustments or replacements.
By diligently following these steps, you can effectively attach the standing rigging on your sailboat, ensuring its stability and safety while on the water.
3. Installing the Boom and Sails
To successfully complete the installation of the boom and sails on a sailboat, follow these steps:
1. Begin by securely attaching the boom to the mast. Slide it into the gooseneck fitting and ensure it is firmly fastened using a boom vang or another appropriate mechanism.
2. Next, attach the main sail to the boom. Slide the luff of the sail into the mast track and securely fix it in place using sail slides or cars.
3. Connect the mainsheet to the boom. One end should be attached to the boom while the other end is connected to a block or cleat on the boat.
4. Proceed to attach the jib or genoa. Make sure to securely attach the hanks or furler line to the forestay to ensure stability.
5. Connect the jib sheets. One end of each jib sheet should be attached to the clew of the jib or genoa, while the other end is connected to a block or winch on the boat.
6. Before setting sail, it is essential to thoroughly inspect all lines and connections. Ensure that they are properly tensioned and that all connections are securely fastened.
During my own experience of installing the boom and sails on my sailboat, I unexpectedly encountered a strong gust of wind. As a result, the boom began swinging uncontrollably, requiring me to quickly secure it to prevent any damage. This particular incident served as a vital reminder of the significance of properly attaching and securing the boom, as well as the importance of being prepared for unforeseen weather conditions while rigging a sailboat.
4. Setting Up the Running Rigging
Setting up the running rigging on a sailboat involves several important steps. First, attach the halyard securely to the head of the sail. Then, connect the sheets to the clew of the sail. If necessary, make sure to secure the reefing lines . Attach the outhaul line to the clew of the sail and connect the downhaul line to the tack of the sail. It is crucial to ensure that all lines are properly cleated and organized. Take a moment to double-check the tension and alignment of each line. If you are using a roller furling system, carefully wrap the line around the furling drum and securely fasten it. Perform a thorough visual inspection of the running rigging to check for any signs of wear or damage. Properly setting up the running rigging is essential for safe and efficient sailing. It allows for precise control of the sail’s position and shape, ultimately optimizing the boat’s performance on the water.
Safety Considerations and Tips
When it comes to rigging a sailboat, safety should always be our top priority. In this section, we’ll explore essential safety considerations and share some valuable tips to ensure smooth sailing. From the importance of wearing a personal flotation device to securing loose ends and lines, and being cautious around overhead power lines, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and awareness needed for a safe and enjoyable sailing experience. So, let’s set sail and dive into the world of safety on the water!
1. Always Wear a Personal Flotation Device
When rigging a sailboat, it is crucial to prioritize safety and always wear a personal flotation device ( PFD ). Follow these steps to properly use a PFD:
- Select the appropriate Coast Guard-approved PFD that fits your size and weight.
- Put on the PFD correctly by placing your arms through the armholes and securing all the straps for a snug fit .
- Adjust the PFD for comfort , ensuring it is neither too tight nor too loose, allowing freedom of movement and adequate buoyancy .
- Regularly inspect the PFD for any signs of wear or damage, such as tears or broken straps, and replace any damaged PFDs immediately .
- Always wear your PFD when on or near the water, even if you are a strong swimmer .
By always wearing a personal flotation device and following these steps, you will ensure your safety and reduce the risk of accidents while rigging a sailboat. Remember, prioritize safety when enjoying water activities.
2. Secure Loose Ends and Lines
Inspect lines and ropes for frayed or damaged areas. Secure loose ends and lines with knots or appropriate cleats or clamps. Ensure all lines are properly tensioned to prevent loosening during sailing. Double-check all connections and attachments for security. Use additional safety measures like extra knots or stopper knots to prevent line slippage.
To ensure a safe sailing experience , it is crucial to secure loose ends and lines properly . Neglecting this important step can lead to accidents or damage to the sailboat. By inspecting, securing, and tensioning lines , you can have peace of mind knowing that everything is in place. Replace or repair any compromised lines or ropes promptly. Securing loose ends and lines allows for worry-free sailing trips .
3. Be Mindful of Overhead Power Lines
When rigging a sailboat, it is crucial to be mindful of overhead power lines for safety. It is important to survey the area for power lines before rigging the sailboat. Maintain a safe distance of at least 10 feet from power lines. It is crucial to avoid hoisting tall masts or long antenna systems near power lines to prevent contact. Lower the mast and tall structures when passing under a power line to minimize the risk of contact. It is also essential to be cautious in areas where power lines run over the water and steer clear to prevent accidents.
A true story emphasizes the importance of being mindful of overhead power lines. In this case, a group of sailors disregarded safety precautions and their sailboat’s mast made contact with a low-hanging power line, resulting in a dangerous electrical shock. Fortunately, no serious injuries occurred, but it serves as a stark reminder of the need to be aware of power lines while rigging a sailboat.
Some Facts About How To Rig A Sailboat:
- ✅ Small sailboat rigging projects can improve sailing performance and save money. (Source: stingysailor.com)
- ✅ Rigging guides are available for small sailboats, providing instructions and tips for rigging. (Source: westcoastsailing.net)
- ✅ Running rigging includes lines used to control and trim the sails, such as halyards and sheets. (Source: sailingellidah.com)
- ✅ Hardware used in sailboat rigging includes winches, blocks, and furling systems. (Source: sailingellidah.com)
- ✅ A step-by-step guide can help beginners rig a small sailboat for sailing. (Source: tripsavvy.com)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how do i rig a small sailboat.
To rig a small sailboat, follow these steps: – Install or check the rudder, ensuring it is firmly attached. – Attach or check the tiller, the long steering arm mounted to the rudder. – Attach the jib halyard by connecting the halyard shackle to the head of the sail and the grommet in the tack to the bottom of the forestay. – Hank on the jib by attaching the hanks of the sail to the forestay one at a time. – Run the jib sheets by tying or shackling them to the clew of the sail and running them back to the cockpit. – Attach the mainsail by spreading it out and attaching the halyard shackle to the head of the sail. – Secure the tack, clew, and foot of the mainsail to the boom using various lines and mechanisms. – Insert the mainsail slugs into the mast groove, gradually raising the mainsail as the slugs are inserted. – Cleat the main halyard and lower the centerboard into the water. – Raise the jib by pulling down on the jib halyard and cleating it on the other side of the mast. – Tighten the mainsheet and one jibsheet to adjust the sails and start moving forward.
2. What are the different types of sailboat rigs?
Sailboat rigs can be classified into three main types: – Sloop rig: This rig has a single mast with a mainsail and a headsail, typically a jib or genoa. – Cutter rig: This rig has two headsails, a smaller jib or staysail closer to the mast, and a larger headsail, usually a genoa, forward of it, alongside a mainsail. – Ketch rig: This rig has two masts, with the main mast taller than the mizzen mast. It usually has a mainsail, headsail, and a mizzen sail. Each rig has distinct characteristics and is suitable for different sailing conditions and preferences.
3. What are the essential parts of a sailboat?
The essential parts of a sailboat include: – Mast: The tall vertical spar that supports the sails. – Boom: The horizontal spar connected to the mast, which extends outward and supports the foot of the mainsail. – Rudder: The underwater appendage that steers the boat. – Centerboard or keel: A retractable or fixed fin-like structure that provides stability and prevents sideways drift. – Sails: The fabric structures that capture the wind’s energy to propel the boat. – Running rigging: The lines or ropes used to control the sails and sailing equipment. – Standing rigging: The wires and cables that support the mast and reinforce the spars. These are the basic components necessary for the functioning of a sailboat.
4. What is a spinnaker halyard?
A spinnaker halyard is a line used to hoist and control a spinnaker sail. The spinnaker is a large, lightweight sail that is used for downwind sailing or reaching in moderate to strong winds. The halyard attaches to the head of the spinnaker and is used to raise it to the top of the mast. Once hoisted, the spinnaker halyard can be adjusted to control the tension and shape of the sail.
5. Why is it important to maintain and replace worn running rigging?
It is important to maintain and replace worn running rigging for several reasons: – Safety: Worn or damaged rigging can compromise the integrity and stability of the boat, posing a safety risk to both crew and vessel. – Performance: Worn rigging can affect the efficiency and performance of the sails, diminishing the boat’s speed and maneuverability. – Reliability: Aging or worn rigging is more prone to failure, which can lead to unexpected problems and breakdowns. Regular inspection and replacement of worn running rigging is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a sailboat.
6. Where can I find sailboat rigging books or guides?
There are several sources where you can find sailboat rigging books or guides: – Online: Websites such as West Coast Sailing and Stingy Sailor offer downloadable rigging guides for different sailboat models. – Bookstores: Many bookstores carry a wide selection of boating and sailing books, including those specifically focused on sailboat rigging. – Sailing schools and clubs: Local sailing schools or yacht clubs often have resources available for learning about sailboat rigging. – Manufacturers: Some sailboat manufacturers, like Hobie Cat and RS Sailing, provide rigging guides for their specific sailboat models. Consulting these resources can provide valuable information and instructions for rigging your sailboat properly.
About the author
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

The history of sailing – from ancient times to modern adventures
History of Sailing Sailing is a time-honored tradition that has evolved over millennia, from its humble beginnings as a means of transportation to a beloved modern-day recreational activity. The history of sailing is a fascinating journey that spans cultures and centuries, rich in innovation and adventure. In this article, we’ll explore the remarkable evolution of…

Sailing Solo: Adventures and Challenges of Single-Handed Sailing
Solo Sailing Sailing has always been a pursuit of freedom, adventure, and self-discovery. While sailing with a crew is a fantastic experience, there’s a unique allure to sailing solo – just you, the wind, and the open sea. Single-handed sailing, as it’s often called, is a journey of self-reliance, resilience, and the ultimate test of…

Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Practices on the boat
Eco Friendly Sailing Sailing is an exhilarating and timeless way to explore the beauty of the open water, but it’s important to remember that our oceans and environment need our protection. Sustainable sailing, which involves eco-friendly practices and mindful decision-making, allows sailors to enjoy their adventures while minimizing their impact on the environment. In this…

Ex-Display & Sample Sale
- Search for:
No products in the basket.
- Base Layers
- Technical T-Shirts
- Sailing Jackets
- Sailing Trousers
- Dinghy Footwear
- Sweatshirts
- Holebrook Samples
- Pelle Samples
- Changing Robes
- Cleaners & Proofers
- Scarves / Snood
- Dinghy Equipment
- Hi-fits / Trousers
- Hiking Equipment
- Hiking Shorts
- Spray Tops / Smocks
- Full Wetsuits
- Shorty Wetsuits
- Long John Wetsuits
- Wetsuit Tops
- Wetsuit Shorts & Trousers
- Summer Wetsuits
- Winter Wetsuits
- Children’s Wetsuits
- Men’s Wetsuits
- Women's Wetsuits
- Wetsuit Sale
- Technical Clothing
- Casual Clothing
- Hats, Gloves, Socks & Scarves
- Watersports
- Accessories Sale
- Amazing Bundle Deals
- Cables & Accessories
- Fixed GPS/plotters
- GPS Antennas
- Handheld GPS/Plotters
- Marine Cameras
- Mounting/Brackets
- Radar Scanners
- Sailing Watches
- Thermal Cameras
- Waterproof Cases
- Accessories
- Fish Finder Sonar
- Depth Instruments
- Multifunction Systems
- Speed Instruments
- Weather Instruments
- Wind Instruments
- Autopilot Accessories
- Cockpit Autopilots
- Onboard Autopilots
- Navigation Charts
- Plotting Aids
- Entertainment Accessories
- Entertainment Systems
- Speakers & Subs
- Electronics
- 4G and WIFI
- Handheld VHF Radio
- Mounted VHF Radio
- VHF Antennas
- Walkie Talkies
- Buoyancy Aids
- Lifejackets
- Children’s Life Jackets
- Commercial Lifejackets
- Harnesses/Bosuns Chair
- Lifejacket Accessories
- Safety Knives
- Safety Lights
- Safety Lines
- PLB & AIS
- Satellite Communicators
- Fire Safety Stick
- Fire Extinguishers
- GPS Tracker
- Liferaft Accessories
- Recovery Devices
- Survival Suit
- Cones & Balls
- Dye Markers
- Horns & Whistles
- RADAR Reflectors
- Bungs & Bailers
- Battery Management
- Chargers & Alternators
- Electrical Other
- Leisure Batteries
- Plugs & Connectors
- Shore Power
- Wind Generator
- USB & Phone Chargers
- Blocks & Terminals
- Circuit Breakers
- Seals / Outlets / Plugs
- Switches & Panels
- Wires & Cables
- Deck Lights
- Interior Lighting
- Navigation Lights
- Searchlights
- Head Torches
- Freshwater Pumps
- Macerator Pumps
- Service Kits
- Toilets/Waste
- Spray Guns & Connectors
- Toilet Accessories
- Toilet Parts
- Waste Tanks
- Ball Valves
- Inlet & Skin Fittings
- Metal Plumbing Fittings
- Plastic Plumbing Fittings
- Diverter Valves
- Non Return Valves
- Deionised Water
- Filters & Purification
- Taps & Sinks
- Water Heaters
- Water Tanks
- Gas Connectors
- Gas Fittings
- Bow Thruster
- Bungs And Self Bailers
- Cleats and Fairleads
- Deck Filler
- Deck Flooring & Protection
- Eye Bolts & U Bolts
- Grab Rail / Handles
- Hooks and Clips
- Latches & Catches
- Shackles & Swivels
- Tiller Extenders & Joints
- Track & Cars
- Winch Handles
- Fans & Windscoops
- Hatch & Inspection Covers
- Hatch Shades
- Hatches & Portlights
- Plastic Hatches
- Yacht / Keelboat Rope
- Dinghy Rope
- Dockline / Mooring Rope
- General Purpose Rope
- Watersports Rope
- Fender Rope
- Rope Accessories
- Furling & Reefing
- Mast, Spars & Sails
- Pins & Rings
- Rigging Screws, Adjusters & Tensioners
- Splicing & Whipping
- Thimbles & Stoppers
- Galvanising Paints
- Thinners & Solvents
- Paint Brushes
- Glue & Adhesives
- Mixing Pots & Accessories
- Resins & Epoxy
- Sealants & Caulking
- Boat Cleaner
- Cleaning Equipment
- Fabric Cleaners & Proofers
- General Cleaners
- Metal Cleaners
- Onboard Cleaner
- Polishes & Waxes
- Vinyl Cleaner
- Teak Cleaner
- All Zinc Anodes
- Zinc Shaft / Prop
- Zinc Engine / Outdrive
- All Aluminium Anodes
- Aluminium Hull
- Aluminium Shaft / Prop
- Aluminium Engine / Outdrive
- All Magnesium Anodes
- Magnesium Hull
- Magnesium Shaft / Prop
- Magnesium Engine / Outdrive
- Bow Thruster Anodes
- Hanging Anodes
- Bolts & Fixings
- Backing Pads
- Lubricants & Grease
- Power Tools
- Marine Prepacks
- Dehumidifiers
- Blowers & Exhaust
- Engine Oil & Additives
- Oil Extractors & Filters
- Shaft Bearings
- Pumps & Inflation
- Tender Accessories
- Petrol Engines
- Boat Fender
- Dock Fender
- Edging Strip
- Hooks & Pumps
- Mooring Buoy
- Step Fenders
- Anchor Bags
- Anchor Connectors
- Anchor Lines
- Anchor Windlass
- Compensators
- Personal Craft
- Engine Covers
- Fuel Tanks & Lines
- Fuel Connectors
- Kill Switches
- Propeller Bags
- Straps & Ratchets
- Flag Staff & Holder
- Lighters & Matches
- Cabinet Fridges
- Cooling Kits
- Portable Fridge/freezers
- Chandlery Misc
- Cup Holders
- Sail Knives
- Seats & Cushions
- Games & Toys
- Gift Vouchers
- Nautical Gifts
- Novelty Hats
- Anemometers
- Clocks & Barometers
- Teak Fittings
- Weather Stations
- Galley Equipment
- Tumblers & Glasses
- Water Bottles & Flask
- Inflatable Paddleboards
- Hard Paddleboards
- Inflatable Kayaks
- Handles / Bridles
- Throw Lines
- Swim Accessories
- Sea Scooter
- Free Delivery on UK mainland orders over £100 excl. Highlands / rural areas
Boat Ropes & Rigging
Whether you’re renewing your entire boat rigging or replacing ropes for safety, comfort or better colour-coding, we have miles of the finest quality lines in stock and ready to ship, including dinghy ropes , fender ropes , yacht ropes and docklines and mooring ropes . Our inventory includes synthetic and natural boat ropes in all sizes and materials from top brands like Marlow and Seago. Complete your selection with essential rope accessories like hot knives and rope cutters .
Showing 1–36 of 72 results

Seago Dockline

Marlow Doublebraid Rope

Marlow 3 Strand Polyester Rope

Marlow Blue Ocean Dockline

Marlow Blue Ocean Doublebraid Rope

Trem Spliced Polyester Fender Rope with Eyelet

Marlow Excel D12 Rope
Marlow 8 Plait Marstron Floating Rope
Marlow Excel Pro

Marlow D2 Club Rope – Dyneema® SK75 / Polypropelene Core

Marlow Shockcord

Marlow Excel Fusion Rope
Marlow Excel Racing Rope

Marlow Marlowbraid Rope

Blue Performance Bulkhead Sheet Bag

Marlow Excel Marstron+

Marlow Excel Control Rope

Trem Anchor Line

Seago Liros Handy Anchor Lines

Halyard Line With Spliced Shackle

Halyard Line With Spliced Snap Shackle

Seago Spliced Fender Lines Pair 8mm

Talamex Fenderline 8mm 2 Pack

Trem Tidy Bungies

Marlow Excel Pro/Racing Hi Brites Reels

Marlow Dockline

Marlow Multiplait Nylon Rope

Marlow 8 Plait Standard Rope

Marlow Excel R8 Rope

Barton Line Tamer

Marlow 3 Strand Pre-Stretched Rope

Hot Knife Rope Cutter

Seago Rope Cutter Mains Powered

Marlow Guard Rail Netting

Marlow 8 Plait Pre-Stretched Rope
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?
Email address *
A password will be sent to your email address.
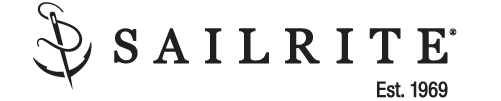
- [[html title]]
How to Select Rope for Your Boat
How to choose the right marine rope, what are my priorities.
To determine what priorities you need for your rope, you’ll need to think about the rope’s application, what type of sailing you do and your budget.
- Application: The application in which the line will be used is obviously a big factor for which type of rope you should purchase. The application will help you determine which rope criteria (strength, stretch and UV resistance) are your biggest priorities. Most rigging applications will require high strength and low stretch as priorities.
- Type of Sailing: Are you a racer or a cruiser? The main use of your boat will directly affect the main use of your lines. Racers will need lines that are lightweight and meet their class regulations, while cruisers may place more importance on longevity and ease of handling.
- Budget: It’s important to set a budget and to not overspend on your line. You could easily buy the most expensive, highest quality line, but for many sailors the fanciest line available is probably overkill. You might never use the line to its full extent, so it’s just not worth the expenditure.
Fiber Choices
After you’ve determined the traits that will be your line priorities, it's time to take a look at which fiber will meet those requirements. Many of a rope’s performance properties lie inherently within its fibers. Here are the most common rope fibers and what they are known for.
- Polyester: An excellent choice for applications where strength, low stretch and durability are important, as in most running rigging applications. Also, polyester has a moderate price tag, which makes it a good fit for a variety of uses and users.
- Nylon: One of the original synthetic fibers, nylon has great shock absorption properties, wear, UV resistance and strength. Also with a moderate price, nylon ropes are great for dock and anchor lines.
- HMPE (Dyneema®): High Modulus Polyethylene (HMPE) is another high performance fiber with very high strength and very low stretch. These ropes also repel water, float, and are ideal for lightweight running rigging for serious racers or on larger yachts. HMPE ropes do have a few drawbacks, however. They have a low melting point, which makes these ropes susceptible to friction. When left under sustained loads, HMPE ropes have been known to creep or elongate. Polypropylene: This is a lower to moderately priced line that is great for applications where a lightweight or affordable line is important. Polypropylene line floats in water and is a good choice for light air spinnaker sheets. The drawbacks to polypropylene are that it is not very strong or UV resistant, has high stretch, and melts at a low temperature.
Rope Construction
A rope’s construction can make it better suited to a particular application. It also can enhance the strength of the fiber. Here are three main types of construction:
- Single Braid: This type of line has a flexible and supple construction that absorbs twist and does not kink, making it great for mainsheets, furling lines and large dock lines.
- 3-Strand: 3-Strand is durable, long-lasting, flexible and easy to handle. Plus, this line won’t harden with age. Use nylon 3-Strand for anchor, dock, mooring and tow lines or polyester 3-strand for running rigging on traditional cruising boats.
- Double Braid: A braided core inside a braided cover. This produces an easy-to-handle rope that is strong and durable. Double braid lines are used in running rigging and dock lines.
Make Your Choice
The fiber and construction of the line can be selected in different combinations to best meet your needs. Be aware that the selection process often involves some trade-offs, whether they be performance or cost-based. Gauge your priorities to decide which combination would work best for your boat.
Now that you have a good idea of what fiber and construction type suits your needs, you should be ready to make your rope selection. Sailrite® stocks a wide array of high-quality New England Ropes. See our full selection of rope for your vessel in our Cordage category.
Is this the formula you use to select rope or do you use another method? Share your thoughts in the comments!
Stay in the loop! Never miss sale announcements, how-to blogs, new product launches, helpful tutorials and more!
Free Shipping Over $99 - 366 Day Returns - Expert Advice

- Call Us +1-503-285-5536
- Sign in & Register
- Recently Viewed
West Coast Sailing offers a full selection of marine grade sailing line and rigging including One Design rigging, pre cut line, line kits, and line by the foot for halyards, sheets, control lines, and more. Shop running rigging and standing rigging today from trusted brands including Marlow, Robline, Samson, Kingfisher, New England Ropes, and more.

- Qty in Cart

Laser / ILCA 8:1 Cunningham TecPRO (Complete)

Laser / ILCA Vang Complete TecPRO (Allen Vang Block)

J/80 Main Halyard w/ Shackle

J/70 Backstay Flicker

Thistle Main Halyard Tapered (6mm Excel)

Thistle Spinsheet Continuous Tapered (6mm Excel Racing)

Melges 24 4:1 Main Halyard Vectran

Melges 24 Jib Sheet (Continuous/Tapered)

J/24 Spinnaker Sheet (Ultra Lite)

J/22 Twings (Pair) with Ring
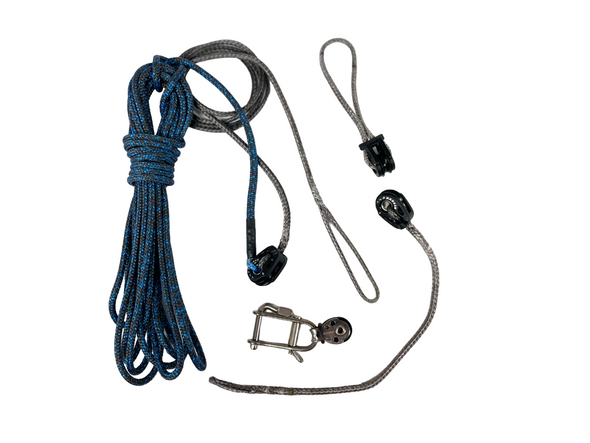

Laser / ILCA Outhaul TecPRO 6:1 (Complete)

10mm Marlow D2 Racing

8mm Marlow D2 Racing

Laser / ILCA Vang Control PRO

Laser / ILCA 8:1 Cunningham PRO (Complete)
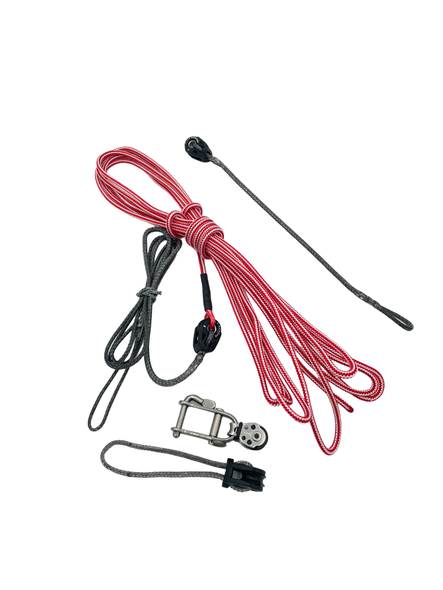

Laser / ILCA Outhaul PRO 6:1 (Complete)
- Total: items /
- Add all to cart
Adding your products to cart
Sailboat line & rigging - halyards, sheets, control lines & more.
Line is a critical part of any sailboat, from small dinghy to super yacht and everything in between. West Coast Sailing offers a wide variety of line and marine rope for every sailor from leading line manufacturers. Whether you're looking for a new control line for your Laser vang, jib sheet for your J24, replacement halyard for your cruising boat, or a high strength low stretch line for a high performance application, we've got what you need to get you back on the water. Shop by common application, diameter, material, and more with options available from Robline, Marlow, Alpha Ropes, and New England Ropes. All line sold by the foot with line kits for select boats and small diameter mini spools available.
Shop By Boat
West Coast Sailing offers custom rigging, line kits, and pre cut line for many popular one design dinghies and keelboats. These products make it simple to get the right line for your sailboat and you can be confident they will work great.
- Shop Line Kits
- Shop One Design Rigging
- Shop Pre Cut Line
Shop By Line Type
Line has come a long way in the past few decades, and current options offer great value and performance. We offer a variety of h igh tech Lines, which generally feature a non-stretch core for strength, durable cruising lines, which are typically polyester and less expensive but still strong and durable, or Dyneema, Spectra, & Vectran for non-stretch control line, halyard, and sheet applications. Shockcord bungee and floating Polypropylene also available. Scroll down this page for recommendations for line material based on your boat size and application.
- Shop by Line Type
Shop By Diameter
West Coast Sailing carries over 80 different lines from 6 of the best rope manufacturers in diameters ranging from 1mm all the way up to 12mm. Use our handy category filters to narrow in on the specific diameter of lines that work for your application, and then pick the one that meets your exact criteria for performance, color, or price.
- Shop by Line Diameter
Additional Line Options & Services
In addition to per foot line, pre cut line, line kits, and custom rigging, West Coast Sailing also offers mini spools, splicing equipment, and custom rigging services. If you can dream it, our team can build it!
- Shop Mini Spools
- Shop Splicing Tools
- Shop Custom Rigging
Line Fiber Type / Material Guide
| Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Poor | Poor | Fair | |
| Poor | Poor | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Good | |
| Excellent | Poor | Fair | Excellent | Poor | Good | Good | |
| Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Fair | Good | |
| Excellent | Fair | Fair | Poor | Poor | Excellent | Fair | |
| Good | Good | Good | Excellent | Good | Fair | Excellent | |
Line Application Guide - Dinghy
|
| | ||||||
| Good | Better | Best | |||||
| Good | Better | Best | |||||
| Good | Better | ||||||
| Good | Best | Best | |||||
| Good | Best | Best | |||||
| Good | Best | Best | |||||
| Better | Better | ||||||
Line Application Guide - Racing
|
| | ||||||
| Good | Better | Best | |||||
| Good | Better | Best | |||||
| Good | Best | ||||||
| Good | Best | Better | Good | Best | |||
| Good | Best | ||||||
| Better | Best | Good | Best | ||||
| Good | Better | Better | Good | Best |
Line Application Guide - Performance Cruising
|
|
| | |||||
| Good | Better | Better | Best | ||||
| Good | Better | Better | Best | ||||
| Good | Better | Best | |||||
| Good | Good | Better | Better | Best | |||
| Good | Good | Better | Best | ||||
| Good | Good | Better | Best | ||||
| Good | Good | Better | Better | Better | |||
Line Diameter Guide
Recommended Diameter by Application & Boat Length
|
|
| |||||
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | |
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | |
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | |
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | |
| 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | 12mm / 1/2 in | |
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | 12mm / 1/2 in | |
| 6mm / 1/4 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 8mm / 5/16 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | |
| 5mm / 3/16 in | 6mm / 1/4 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 9mm / 3/8 in | 11mm / 7/16 in | |
|
| 1mm = 3/64 inch | 2mm = 5/64 inch | 3mm = 1/8 inch | 4mm = 5/32 inch | 5mm = 3/16 inch | 6mm = 1/4 inch |
| 7mm = 9/32 inch | 8mm = 5/16 inch | 9mm = 3/8 inch | 10mm = 25/64 inch | 11mm = 7/16 inch | 12mm = 1/2 inch | |
If you are replacing an existing line, the easiest way to determine what diameter you need is to match what you already have. This can be done with a caliper or by close estimation with a tape measure. For example, if you've previously used a 7mm halyard and it has performed well, another 7mm line is likely a great choice. In most applications, there is some flexibility in the exact diameter that can be used. Most blocks, for example, have an 'ideal' diameter (ie, the line diameter that runs most effectively though the block's sheave) but also have a range so that you can run a slightly thinner or slightly thicker line. If you have a halyard that is getting hung up in your rig, stepping down 1-2mm might help the halyard run more efficiently. If you have a larger boat or rig and want to run a thinner halyard, consider a double braid line that features a Dyneema or Spectra core for strength. A similar approach can be applied to replacing sheets, control lines, and other line on your sailboat.

Double Braid vs Single Braid
Two terms you will often see in line descriptions are 'double braid' and 'single braid', which refer to the way the line is constructed. At the most basic level, a double braid line has a cover and a core whereas a single braid does not, but there are other important distinctions to consider when making a line selection.
Single Braids are made up of either 8 or 12 strands that are braided into a circular pattern, half clockwise and half counter clockwise. This produces a line that is supple, absorbs twists, and tends not to kink. There are two types of single braid lines: performance single braids and polyester/blended single braids. Performance single braids are made from fibers with very low stretch and designed to handle extreme loads - think Dyneema, Spectra, or Vectran. Polyester/blended single braids, sometimes called hollow braid, are soft and easy to grip, built for sheets and hand-adjusted control lines. These are less common than performance single braid lines but recommended in a few specific applications.
Double Braids , sometimes called braid on braid, have a braided core within a braided outer jacket or cover. This creates a strong, durable, smooth-running line that is easy to handle. Double braids are used for the vast majority of all running rigging on sailboats including sheets, halyards and control lines for both cruising or racing. There are two types to consider: polyester double braids and high-tech double braids. Polyester double braids, found most commonly on recreational and cruising sailboats, have a polyester cover with polyester core. These are low maintenance, affordable, and long-lasting, while offering relatively low stretch and high working loads. For additional strength and minimal stretch, consider high-tech double braids. These lines typically feature a Dyneema or Spectra core (non-stretch) inside a polyester or polyester/dyneema blend cover for additional durability. They are more expensive but often the go to choice for high performance racing boats.
Sailing Programs & Clubs - West Coast Sailing offers special program pricing on purchases for sailing programs, yacht clubs, and community sailing organizations. Visit our YC & Program Purchasing page for more details.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive discounts, new product announcements, and upcoming sales.

Lines & Rigging

(419) 873-8300
- Jute, Natural & Pro-Manila Rope
- Cotton Rope
- Polyester Rope
- Polypropylene Rope
- Accessory Cord
- Amsteel & Aramid Fiber Rope
- Static Rope
- Shock/Bungee Cord
- Arborist Rope
Sailing & Boating Rope
- Pulling Products
- Macramé Rope
- Landscaping
- Multi-Purpose Rope
- Solid Braid
- Double Braid
- Hollow Braid
- Custom Splicing
- Climbing Hardware
- Decorative Hardware
- Rope Clamps & Ends
- Rope Ladders
- Custom Knotwork
- Dog Leash Snaps
- Rope Search
- GSA Ordering
- Safety Tag Lines & Lanyards
- Handmade Dog Leashes
- Exercise Climbing Ropes
- Retail, Design and Exhibit
- On Location Rope Splicing
- Custom Cut to Length
- Photo Gallery
- Project Help
- Custom Project Forms
- Rope Safety Info
- Mr. Twisty - Blog
UPGRADE YOUR SAILING LINES.
We offer the some of the best lines in the sailing and boating industry. From our High Performance Running Rigging to our Value Performance Running Rigging lines, we have something to fit every budget and need.
Need a custom dock line? We've got you covered. All of our dock lines are hand spliced to ensure the best quality and craftsmanship in the market. Call us today or order through our Dock Line category. Don't let the name fool you. The only thing that's pre-made about these is the ordering process. These are made to order!
High Performance Running Rigging
Value performance running rigging.

AmSteel-Blue Dyneema
Strong as steel cable for it's size. This rope is easily spliced and has almost zero stretch. Rope Construction: AmSteel®-Blue is a torque-free, 1...
Dynatru - UHMWPE
Dynatrū is a high strength rope perfect for industrial applications. Manufactured with ultra-strong UHMWPE fiber and coated with a special agent fo...
Excel Racing Dinghy Control Line
This rope has a braided polyester cover over a braided Dyneema® core (except for the 3mm size in which the Dyneema® core is NOT braided). High str...
The pre-stretched, bio-based D12 78 core makes D2 Racing a high-strength, lightweight all-round performer. It is colour coded with the cover ensuri...
D2 Club has been developed to provide an upgrade to polyester sheets and halyards offering the benefit of reduced weight and reduced elongation tha...
Blue Ocean Double Braid Polyester
BLUE OCEAN® DOUBLEBRAID is the next generation of innovation in Marlow's Blue Ocean® product range. Made using Marlow's trademarked Blue Ocean® yar...
Marlow Double Braid Polyester
Marlow's heat set Doublebraid offers industry leading strength and stretch performance for a polyester braid-on-braid. Flexibility and soft feel en...
Sta-Set Sailing Line
Looking for the classic low cost running rigging? You found it here. Sta-Set has been used on more sailboats than probably any other line. This pro...
Vintage Sta-Set
A great choice if you need something that looks like old time jute or hemp rope, but still need a modern sailing line. Rope Construction: This is ...
- Best selling
- Alphabetically, A-Z
- Alphabetically, Z-A
- Price, low to high
- Price, high to low
- Date, old to new
- Date, new to old
Added to your cart:

Marine Wire Rope

Strength in Challenging Environments
Our high quality marine wire rope products are engineered for strength, appearance, abrasion resistance, elongation, exceptional corrosion resistance, and performance. Applications include sailboat rigging, dock railings, winch cables, and crane ropes, all designed to stand up to the challenges of the marine environment. Whether you are refitting your sailboat or re-stocking your tow ropes, Strand Core has the marine wire rope size and construction you need.
Strand Core offers type 302 / 304 and type 316 stainless products for both fresh and salt water applications. Sizes range from 3/32" to 5/8", in 1x19, 7x7, 6x19, and 6x37 constructions. Click on a product line below for more information. Other constructions and alloys are available by request.
Marine Wire Rope Data Sheet
1x19 Stainless Steel Strand
Smooth outside and resists compressive forces. Excellent strength and appearance for sailboat stayed rigging. Used in Dockside railings and other waterfront architectural applications
7x7 Stainless Steel Aircraft Cable
Performs well when strength & moderate flexibility are concerns. Primarily used in sailboat lifeline and sailboat running rigging, boat lift winches and other single line hoisting operations.
6x19 Stainless Steel Wire Ropes
Excellent Corrosion resistance combined with flexibility and strength. Used on marine towing and marine crane operations.
Product Information
Packaging information, technical information, get a marine wire rope quote.

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 554fc3bb-4719-11ef-8113-4e07900282f1
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.
Shop by Material
Shop by construction, shop closeouts.
- Running Rigging
- Standard Rigging
- Rigging Inspection
- Refit & Service
- Custom Splicing Order
- OEM/Manufacturing
- Small Business Discount
- Wholesale Account
- Davey & Company
- Langman Rope
- Marlow Ropes
- New England Ropes
- Samson Rope
- Sterling Rope
- Teufelberger
- Veteran & Active Duty Discount
- First Responder Discount
- Universities, Camps, Non-Profits
- Government & Municipality
- Shipping & Returns
- RopeFest 2024
Sailing & Recreational Marine
- Sailing Lines
- Hardware & Equipment
- Pre-Spliced Goods
- Rigging & Sail Making Tools
- Sail Handling
- Closeouts/Shorts/Specials
| Hot! 0.3 USD | 1.95 USD | 1.95 USD | 0.5 USD |
| 1.59 USD | 2.95 USD | 0.5 USD | On Sale Now! $ 0.48 0.48 USD |
| Going Fast! 0.35000000000000003 USD | 0.45 USD | 0.37 USD | 27.0 USD |
| 193.65 USD | 88.9 USD | 16.05 USD | 76.68 USD |
| 225.0 USD | 1.7 USD | 2.0 USD | 0.6 USD |
We use cookies to provide you a better user experience on this website. Cookie Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. 3. Fisheries Supply is your premier supplier of sailing and rigging rope from top brands like Samson, Marlow, Robline and New England Rope. We offer a full range of sailing lines to replace any or all the running rigging on your boat such as halyards, sailboat sheets or control lines. Whether you're a racer, a local cruiser, or an ocean ...
Colligo Dux: A relative newcomer to sailboat rigging, Colligo Dux is pre-stretched and heat-treated Dyneema. This process, however, produces an extremely strong rope with virtually no creep that is suitable for service in standing rigging. ... Polyester (Dacron): For decades, polyester has been the go-to rope for cruising-boat halyards and ...
Nylon has long been the default rope for all running rigging in cruising yachts. Something with a bit of give is ideal for mooring. It might be 'braid-on-braid', with similar outer and inner . parts, as sold by most manufacturers, . or it could be a low-stretch polyester braidline (LSP) with a loosely laid .
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision: 1. Assess your sailing needs. Consider the size of your boat, the sailing conditions you typically encounter, and your rigging setup. This will help you determine the strength and durability requirements for your rigging rope. 2.
New England Ropes V100. If you are looking for a bit' more performance you may want to look at New England Ropes Endura (Spectra Core) or V-100 (Vectran Core). These are very low stretch lines and offer the ability to strip the cover off as seen on many racing boats. If you do decide to taper your halyards (or strip the cover) for performance ...
Boom Vang - Boom length x 2. Cunningham - Boom length x 1. Reefing Line (reef 1) - Boom length x 2.5. Reefing Line (reef 2) - Boom length x 3. If your running rigging leads back to the cockpit, remember to account for that in your length. And if in doubt, too long is always better than too short! Guidelines for Rope Diameter and Type ...
Our sailboat rigging include mainsail halyards, spinnaker halyards, and Genoa halyards that are made from a double braid polyester line, double braid Dyneema line or Vectran. Our mainsheets are also made from durable double braid polyester and hybrid fibers with blend of Dyneema and Technora. This material has the best reputation in the industry.
A sailboat's standing rigging is generally built from wire rope, rod, or occasionally a super-strong synthetic fibered rope such as Dyneema ®, carbon fiber, kevlar or PBO. 1×19 316 grade stainless steel Wire Rope (1 group of 19 wires, very stiff with low stretch) is standard on most sailboats. Wire rope is sized/priced by its diameter which ...
D12 MAX 78 Rigging Rope. Dyneema SK78 rope unrivalled in strength and low elongation. Starting from $361.73. 1.8 mm. Marlow Ropes. Kiteline Freestyle Sporting Rope. Strong and thin sporting rope made from dyneema. Starting from $117.99. 3/16".
By Robin Iversen January 12, 2024. The running rigging on a sailboat consists of all the lines used to hoist, lower, and control the sails and sailing equipment. These lines usually have different colors and patterns to easily identify their function and location on the vessel. Looking at the spaghetti of lines with different colors and ...
PLEASE NOTE: THIS VIDEO HAS BEEN UPDATED WITH ENHANCED GRAPHICS AND IMPROVED SOUND. CHECK IT OUT HERE https://youtu.be/tRgWtPaCQQcA beginners guide to sailbo...
5. Secure the mast using the appropriate rigging and fasteners. Attach the standing rigging, such as shrouds and stays, to the mast and the boat's hull. Fact: The mast of a sailboat is designed to withstand wind resistance and the tension of the rigging for stability and safe sailing. 2.
Marlow Guard Rail Netting. £ 3.30 / metre. Marlow 8 Plait Pre-Stretched Rope. £ 1.00 - £ 1.95 / metre. 1. 2. Buy boat ropes and rigging online from Marine Super Store's unbeatable range, including Marlow and Seago marine ropes. FREE UK delivery over £100.
Use nylon 3-Strand for anchor, dock, mooring and tow lines or polyester 3-strand for running rigging on traditional cruising boats. Double Braid: A braided core inside a braided cover. This produces an easy-to-handle rope that is strong and durable. Double braid lines are used in running rigging and dock lines.
Huge Inventory of Rope and Sailboat Hardware. Rigging and Lifeline Shop. Splicing Shop. Expert Knowledge. [email protected]. (305) 758 1074.
Sailing line and rope including line kits, pre cut line, custom rigging, and line by the foot from Marlow, New England Ropes, Robline, Samson, and more. Free Shipping Over $99 - 366 Day Returns - Expert Advice. Menu. Search. Close Search. Call Us +1-503-285-5536; ... Sailboat Line & Rigging - Halyards, Sheets, ...
Our selection of sailboat lines and rigging will keep you covered from bow to stern. Our halyard rope and other sailboat sheets are durable and high performing. WE SHIP WORLDWIDE: More Info. Toggle menu. FREE SHIPPING* US Continental (min order $98) International (min order $750)
There are actually four ropes that exist on a sailboat: Bolt Rope. Foot Rope. Tiller Rope. Bell Rope. A bolt rope is a rope sewn into the luff and foot of the sail to aid in securing the sail to the spars. Bolt ropes help reinforce and strengthen the sail, giving it a very firm attachment to the spar that will help it set much better.
UPGRADE YOUR SAILING LINES. We offer the some of the best lines in the sailing and boating industry. From our High Performance Running Rigging to our Value Performance Running Rigging lines, we have something to fit every budget and need. Need a custom dock line? We've got you covered. All of our dock lines are hand spliced to ensure the best ...
Shop a comprehensive selection of sailboat rigging ranging from specialty wire rope and terminals to swaging tools and rigging pins. Whether replacing worn running rigging lines or updating aging standing rigging wires, we provide everything required - from turnbuckles and toggles to swagers and crimpers - as parts of a sailboat rigging.
Whether you are refitting your sailboat or re-stocking your tow ropes, Strand Core has the marine wire rope size and construction you need. Strand Core offers type 302 / 304 and type 316 stainless products for both fresh and salt water applications. Sizes range from 3/32" to 5/8", in 1x19, 7x7, 6x19, and 6x37 constructions.
West Marine Rigging Services can create a custom anchoring solution for your boat including rope-to-chain spliced rodes for windlasses. Select from double-braid, single-braid, 8-plait, or three-strand nylon line and Proof-Coil, High-Test, or Grade 70 chain. We're also experts in mooring pendants for either seasonal or transient use, and anchor ...
Rigging & Sail Making Tools. Rigging. ... With over 10,000 skus of rope and hardware on top of a full service splicing and rigging shop, there is no rope or rigging project too big or too small. We work with retail customers one on one, and supply large companies across the globe. Whether you're just trying to pick a new main halyard or need ...