
- Search Used Yachts For Sale
- Search Boats By Brand
- Search Boats By Type
- Search By Location
- Search By Price
- What's My Boat Worth?
- Search Boats Just Listed
- Small Yachts
- Custom Sport Fishing Boats
- Finance A Boat
- Amer Yachts
- Cabo Yachts
- French Yachts
- Gulfstream Yachts
- Hatteras Yachts
- Solaris Yachts
- Sunpower Yachts
- Sunreef Yachts
- Vela Boatworks
- Virtus Yachts
- Why List With United?
- Why Own A Boat Or Yacht?
- Custom Website For Your Yacht
- United Sold Boats
- Buy A Yacht With Crypto
- Find a Yacht Broker Near Me
- Search For Broker By Name
- Meet The United Support Team
- Our History
- Fort Lauderdale Boat Show
- Stuart Boat Show
- Miami Boat Show
- Palm Beach Boat Show
- Other Boat Shows
- Yachting News
- Yacht Closing Services
- River Forest Yachting Centers

Search All Yachts

Burger Yachts For Sale
Let me take you on a trip to a place where dreams are made, beauty is born and standards are excelled in every way! Where may we be, you ask? Step inside to the world of Burger Yachts. This proud American builder has a legacy of customized designs, world-class quality, and sea-worthiness. Today, there are many available Burger Yachts for sale on the brokerage market.

Learn More About Burger And Find Your Next Boat
This impressive eight-acre, modern, full - service shipyard, is nestled moments away from the ocean, giving you easy access for your yacht’s sea trials and, only a few miles away from Wis-consin’s major airport in Manitowoc. You’ll be quite in awe at the yard’s eight heated construction bays with overhead cranes. Everything ever needed to build the world-class Burger beauty up to 260 feet (80 meters) is all contained here including shops for mechanical/hydraulic and metal systems fabrication, plumbing, machining, HVAC and electrical. A 50,000 square foot state-of–the-art joiner facility equipped with CNC is also right on site. The company offices can be found in a 20,000 square foot corporate design and engineering location.
List Of Burger Yachts On The Brokerage Market
- Page 1 of 1
You’ll find ample space for every type of Burger project - from new construction to repair, maintenance and refit projects. To make the cut of a Burger shipyard expert, you’ll see each is adept in his area’s efficiency and quality work and amongst his peers is looked upon as a highly skilled engineer and/or craftsmen to ensure the yacht you’re stepping into is second to none!
One additional true fact about this choice you are consider: should you become part of the ex-clusive Burger yacht owner’s clan, you’ll know you have joined one of the most exclusive fleet of yachts in the world.
Burger Boat Company was founded in 1863, and is known for designing and building distinctive, custom aluminum and/or steel yachts. Valuing tradition, yet happy to welcome those innovations that would provide excellent value to their exclusive brand, your yacht will be known for it’s ex-quisite craftsmanship to reflect your very own style, while combining state-of-the-art technology.
In admiring the finished project, it will be clear to see how Burger reflects the loyalty and passion it’s employees have for each and every owner.
The Burger Design Team chooses the best in the business to ensure every yacht and commer-cial vessel they introduce is of spectacular quality, excelling in all areas of reliability, quality of fit and finish, and, most importantly, safety.
Having launched seven new yachts recently, with the largest coming in at 153 feet - named IN-GOT, don’t be surprised to learn that two of these new launches are measuring in at 42 feet in length - for those desiring a more manageable ride that can be operated without a crew!
BLUE, is a 48 Cruiser featuring a stunning De Basto Designs interior; while BLUE BOAT HOME Is the first totally customized, unique Burger 48 Cruiser. Burger went all out in conjunction with the designer and discriminating owner to develop this very special addition.
Looking for a commercial vessel, Burger has recently launched quite a few from 62 to 98 feet. One of the two 98 footers (30M), named CHICAGO’S LEADING LADY is the first steel vessel they’ve built, since launching BRODIE VI. A special, ‘Chicago’s First Lady Cruises’ build, she shows similar to the traditional Presidential Yacht, Sequoia with it’s mahogany panels and brass details—a 349 passenger, USCG certified type K vessel.
Burger’s new projects on the horizon range from a 214 foot tri-deck to a popular 112 Raised Pi-lothouse Motoryacht. Step aboard and I’ll show you around! Enter aboard into her expansive main salon and dining area, where you’re stewardess can make you a drink. This space is ideal for any entertaining or relaxing that’s on the menu. Continue on, to take a peek at her full beam main deck owner’s stateroom with his and hers en suite baths and lots of closet space. You’ll en-joy the welcoming feel her main entry foyer provides as well. Step into her comfortably chic guest staterooms. Four in total and all with en suite baths. Looking for an optional guest configu-ration, then you would steer towards the alternative that provides you with a VIP and two guest staterooms or even a gym.
The galley is spacious and provides efficiency for any master chef to whip up a meal that would rival the finest restaurant. Come with me now to her spacious pilot house and have a seat on her settee, where you can munch on some snacks at her table and join in on the Captain’s cruising action. Now for some outside fun, follow me from the pilot house to her generously sized, open sundeck where you’ll have your choice to either sunbathe, catch up on your favorite novel in the shade or take in the ever changing views accompanied by your favorite hors d’oeuvres. Step down forward into the crew area to visualize where your six crew members will feel well taken care of in their lounge and galley area. For those with lots of goodies to bring on each trip, you’ll appreciate the generous storage Burger thought of in advance including a hidden store room you can access at the aft end of the sundeck.
Want to feel the ride…that won’t be a problem as she’s powered by CAT C32’s with a cruising speed of 18 knots —topping out at approximately 22 knots.
As we hop off this stunning example of class and performance that rivals any yacht of the same size, you’ll now know why Burger’s wish come true is to be internationally recognized as the fin-est custom yacht builder in the world!
Interesting Boating Links
Worldwide yacht sales.
- 5 Million Dollar Yacht
- Yachts For Sale California
- Midnight Express Boats
- Boats For Sale NYC
- 10 Million Dollar Yacht
- Downeast Yacht Owners
- 100 Foot Yacht
- Yachts For Sale Seattle
- Boat Sales Beaufort SC
- Cost Of Owning A Luxury Yacht
- Sailboat Brokers Near Me
- Boats For Sale in Puerto Vallarta
- 50 Million Yacht
- Used Yachts NJ
Luxury Boats & Yachts
- $200000 Yacht
- 2 Million Dollar Yacht
- Center Consol Boats For Sale
- $300000 Boat
- Great Loop Boats For Sale
- 60 Ft Yacht For Sale
- Cabo Yachts For Sale
- Used Seakeeper For Sale
- Hinckley Boats For Sale
- Azimut Yachts Price
- Prestige Yachts For Sale Canada
- Yachts For Sale Under $500k
Popular Builders & Models
- Boston Whaler 350 Outrage
- Yachts For Sale Charleston Sc
- 44 Sundancer
- American Tug For Sale
- 60 Foot Hatteras For Sale
- Sea Ray 410
- 50 Sea Ray Sundancer For Sale
- Powercat For Sale
- Viking Convertible
- Sport Cruiser Boat
Trending Brands & Types
- Legacy Yachts
- Henriques Boats For Sale
- Outer Reef Yachts For Sale
- Vanquish Boats
- Hatteras Boats For Sale
- Luhrs Yachts
- Jarrett Bay Boats
- Silverton Boats For Sale
- Lobster Boats For Sale
Speak to A United Sales Professional About Burger Yachts
Burger Yachts for Sale
Burger yachts for sale | luke brown yachts.
Burger Boat Company, founded in 1863, has a long tradition of constructing an extensive variety of vessels to meet the highest expectations. Burger designs and builds custom yachts made of aluminum and/or steel in a community known for extraordinarily skilled professional shipbuilders who take great pride in the quality of their work. Each employee is a practitioner of traditional disciplines, yet is eager to embrace meaningful innovations dedicated to providing you with exquisite craftsmanship that reflects your personal style, while seamlessly integrating state-of-the-art technology. Burger employees continuously demonstrate the company’s core values: integrity, honesty and commitment. Commitment to these values is what fosters trust in Burger, from the beginning of the process until long after delivery. As a result, every Burger is a reflection of the passion and loyalty each employee has for its customers. The Burger Design Team works with many of the world’s most respected designers and naval architects to create exceptional custom built yachts and commercial vessels. Burger designs and builds custom yachts and commercial vessels that set the highest standards for safety, reliability and quality of fit and finish. In addition, Burger offers a comprehensive array of services including: custom furniture design and construction; specialty metal and joinery fabrications; refit, repair and maintenance. The shipyard is a short distance from the local airport making it easily accessible by private jet. Commercial airline service is available from Chicago, Illinois and Milwaukee or Green Bay, Wisconsin. Burger is also easily reached via limousine or the waterways of the Great Lakes.
RECENTLY SOLD BURGER YACHTS
LOA Manufacturer Year List Price Sold Price Location
105' Burger 2000 $3,495,000 (10/18) $2,000,000 (11/19) FL, USA
86' Burger 1979 $525,000 (09/18) $475,000 (02/19) FL, USA
75' Burger 1974 $795,000 (11/18) $475,000 (01/19) FL, USA
72' Burger 1976 $249,000 (07/19) $200,000 (12/19) MD, USA
60' Burger 1958 $199,00 (06/19) $179,900 (11/19) MD, USA
57' Burger 1963 $270,000 (10/18) $225,000 (12/19) MD, USA

CONTACT LUKE BROWN NOW TO GET STARTED SELLING OR BUYING YOUR YACHT TODAY!
- outback yachts
- president yachts
- everglades boats
- Reina boats
- buy with lby
- search yachts
- premier listings
- search by type
- search by brand
- list with lby
- we take trades
- our history
- testimonials
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
- Link to search page
- US: +1 (561) 833 4462
- US: +1 (206) 209-1920
- MC: +377 99 90 74 63
NADAN Yacht for Sale

NADAN Yacht for Sale - 151' Burger

Open Gallery

Contact Us For More Information
Detailed information, detailed description.
- ABS - 15-year survey
- Hauled yacht, checked, and serviced overboard valves
- Pulled shafts and checked shaft seals
- Inspected all tanks and painted freshwater tank
- Varnish and paint touch-ups
- Polish hull
- Service main engines and generators
- All recommended service on other equipment
- Fitted protection against a lightning strike
- A skylounge was added with bathroom, featuring large windows, interior mahogany panels and tongue and groove panelling, painted gloss white, with teak and holly flooring, designed by Ken Freivokh, perfectly complements the original interior/exterior styling and finish, as well as the exterior profile of this classic yacht
- Shortened the carbon fibre mast and installed electronics, teak faux painted
- Added Crow’s Nest and teak cladding all-around, under the upper deck’s cap rail
- Added teak cap rail on the upper deck
- Added height to the forward flag mast
- Modified the aft deck seating layout with 2 x new sofas and 2 x tables
- Shortened the upper aft deck above the transom seat
- Redesigned the main salon with faux leather panels with wood design, custom art deco sofas, arm chairs and tables
- New Novurania CAT 18 tender with 115 Hp Yamaha
- New Air MakeUp AC Handler
- New insulation on AC lines in all accessible areas
- New AC/DC neutral ground fault systems
- 3 x New pilothouse 19” monitors
- New GPS Map/Radar 12”
- New Samsung UHD TV 52” in Salon
The owner’s passion for the classic and neoclassic style cruisers led him to NADAN and her transformation. His specific vision and attention to detail was implemented to attain the timeless elegance and charm of the 1920's. The new skylounge and crow's nest compliment the yacht's fluid lines and pleasing proportions while reflecting the same commitment to perfection. NADAN's shallow draft enables her to cruise the Bahamas and inland waterways, which is very difficult to find in a vessel of this design. NADAN is in immaculate condition.
- Exquisite custom Burger quality
- 4 x Owners and guest staterooms
- Shallow 6 foot draft
- Economical with transatlantic range
- Recent completed ABS special survey
- Zero speed stabilization
what to include in a thesis proposal
Thesis Writing
Thesis Proposal
How to Write a Thesis Proposal - Sample Proposals and Tips!

People also read
Thesis Writing - An Ultimate Writing Guide With Tips & Examples
Thesis Introduction: A Step-by-Step Guide With Examples
Interesting Thesis Topics & Ideas To Get Started
Thesis Format Essentials: Structure, Tips, and Templates
Are you struggling with making a thesis proposal, not knowing where to start?
You're not the only one.
Creating a thesis proposal can feel confusing. But think of a thesis proposal as your guide for your academic research. It helps you plan your research and keeps you on the right path. If the thought of a thesis proposal has left you feeling unsure, don't worry.
This blog is here to help you understand how you can create a thesis proposal that serves your research project right!
So, let’s begin!
- 1. What is a Thesis Proposal?
- 2. What Does A Thesis Proposal Include?
- 3. How to Write a Thesis Proposal
- 4. Thesis Proposal Format
- 5. Sample Thesis Proposal
- 6. Thesis Proposal Writing Tips
What is a Thesis Proposal?
The thesis proposal is a type of detailed summary and outline of your thesis or research work. It provides a layout regarding how you will transform an unformed idea into a thoroughly researched concept.
Moreover, it also identifies the problem, questions, and methods you will use in your thesis. All students are required to submit this mind map to the supervisor. This is how they will get a comprehensive idea of the research journey.
A good proposal will prove that your thesis or dissertation is relevant and important. Similarly, it shows that you have adopted the right approach and tools to solve the problem.
- The following are the primary purposes of writing a thesis proposal.
- It shows that the chosen topic addresses a significant problem.
- It demonstrates an organized plan to collect or obtain data for solving the problem.
- It identifies data collection methods.
Lastly, it states the significance of the thesis indicating how it will contribute to the field.
What Does A Thesis Proposal Include?
A well-structured thesis proposal consists of several critical elements, each playing a distinct role. Here's a concise breakdown of the parts of thesis proposal:
Introduction (1 page)
This is where your proposal begins.
It opens with a clear definition of your research's topic area, followed by an explanation of its relevance and significance within the context of your field.
The introduction also establishes the scope of your research study by defining its boundaries and limitations.
Literature Review (7-8 pages)
The literature review is a substantial section, comprising four key components.
Firstly, it offers an overview of the existing body of literature related to your research topic. Secondly, it addresses theoretical frameworks and methodological research designs relevant to your area of study, demonstrating your familiarity with the field.
Thirdly, it emphasizes the gaps in the literature, showcasing areas that require further investigation and justifying your research.
Research Question (1-2 pages)
In this section, you formulate a specific research question that your study will seek to answer.
The research question serves as the focal point of your research. You also explain how your entire research design aligns with and is structured around this central question.
Methodological Design (1-2 pages)
The methodological design section is critical for outlining how you plan to conduct your research.
It encompasses several pivotal aspects. You describe your methodological approach ( qualitative , quantitative , or a combination). You detail your participant access strategy and the number of cases to be included.
You specify case selection criteria, research timeline, data collection methods, data coding, analytics, and other relevant factors.
References
This is your bibliography, listing all authors cited within your literature review. It validates your sources and provides a solid foundation for your proposed research.
Each of these components is crucial in creating a robust and structured framework for your thesis proposal.
How to Write a Thesis Proposal
Writing a thesis proposal is a structured process that involves several key steps, each of which plays a vital role in creating a successful proposal. Let's break it down:
Step 1 - Begin with Outlining
Start by outlining the information you've gathered. This step is crucial for both you and your supervisor. It provides a roadmap for your thesis.
By carefully outlining the parts of your proposal, you can guide yourself while drafting the document.
Step 2 - Know the Proposal Structure
Familiarize yourself with the structure of a proposal.
The major sections usually include an introduction, methodology, significance, data explanation, conclusions, and references. Understanding this structure is key to a well-organized proposal.
Step 3 - Plan Your Writing Process
It's important to organize your proposal meticulously. This helps you get a clear idea of how to write it. Many proposals get rejected because students don't plan their writing process. Plan the flow of your writing and stick to it. Here's a typical flow:
- Develop a proposal outline.
- Prepare visuals like charts or tables.
- Introduce the topic.
- Describe your chosen methodology.
- Explain why your research is significant.
- Present your data.
- Draw conclusions from your research.
- Cite your references.
Step 4 - Writing the Proposal Draft
Once you've planned the writing process, it's time to begin your final proposal draft. Use a formal writing style, but make sure to use simple words.
This makes it easier for your audience to read and understand. Also, use first-person references as needed, but consult your professors before writing a thesis statement.
Step 5 - Proofread Your Proposal
A good thesis proposal should be free of typos and other grammatical mistakes.
These errors can distract your readers from your actual problem statement. To ensure a polished proposal:
- Read the proposal aloud to identify grammar and spelling mistakes, along with any issues with sentence structure.
- Avoid proofreading immediately after writing; wait a day or two for a more objective view.
- Seek input from someone with a strong understanding of the material.
- Utilize an online spell checker for added accuracy.
Following these steps will help you craft a well-structured and error-free thesis proposal, increasing the likelihood of your proposal being accepted.
Refer to the following sample to understand the complete writing process.
Thesis Proposal Format
The format of the thesis paper proposal typically follows the below-given pattern.
- Title Page
The title page includes the research title, student and supervisor’s name, along with the submission date.
- Table of Contents
It gives a complete layout of the proposal by stating the headings and subheadings with their page numbers.
- Introduction
The thesis introduction highlights the historical background of your research. It also provides a brief overview of the thesis topic and the motivation behind choosing it.
- Statement of the Problem
It provides a clear statement that briefly defines the purpose of the study. Check out the below sample for a better understanding.
Sample Statement of the Problem in Thesis Proposal
- Theoretical Framework
Here, the research problem will be set within the framework of a theory. Moreover, it will also identify and define the terms conceptually.
Literature Review
It includes the review of the available literature on the topic to establish credibility. Keep in mind; this section must be at least 15 pages.
- Research Objectives
This section states the main objectives that you want to achieve in the research. Similarly, it will also mention the hypothesis and the expected outcome.
Methodology
It states the methodological approaches that will be used to achieve the objectives. It will also provide details about how the experiments will be conducted to test the hypothesis.
- Evaluation of Research Findings
It briefly discusses how the research findings and outcomes will be evaluated.
- Timetable for Completion of the Thesis
This section includes the dates for:
- Completion of research
- The first draft of the thesis
- Final draft
Cite all the primary and secondary sources in the reference list along with their codes. Also, choose a citation style after consulting with your professor.
- Other Instructions
The other format instructions include the following aspects.
- Word Count: 5000 words maximum.
- Font Style and Size: Times new roman, Arial - 12pt.
- Line Spacing: 1.5 for text, single-spaced for quotations.
- Margins: It should be set to 1.25 inches for left/right and 1 inch for top/bottom.
- Page Numbers : It must be in Roman numerals and placed at the bottom center of each page.
- Citation: APA, MLA, Chicago.
Here’s a thesis proposal outline that you can use as reference:

Need to know more about formatting your thesis? Explore this comprehensive blog to gain a deep understanding of thesis format !
Sample Thesis Proposal
Following are some examples and samples for you to get a detailed idea.
Thesis Proposal Sample
Thesis Proposal Example
Thesis proposal template.
Undergraduate Thesis Proposal Example
Master Thesis Proposal Example
Phd. Thesis Proposal
Architectural Thesis Proposal
Thesis Proposal Writing Tips
Here are some tips for writing a perfect thesis proposal.
- Know all the requirements before you start writing a proposal. It includes length, font, spacing, etc.
- Use simple words so that the readers can understand easily.
- Always check your proposal and carefully proofread for mistakes.
- Write answers and solutions to your problem in the conclusion as it provides a base for future research.
- Keep a record of your referencing from the start and triple check it before submitting the proposal.
- Plan, organize, and structure your proposal within a clearly defined deadline.
- Use pictures and graphs to illustrate background material, sample data, and analysis techniques.
Getting started on your thesis? Read here and choose from an extensive list of thesis topics !
So, you now have the key knowledge to create a strong and meaningful thesis proposal.
However, if you still find yourself facing challenges or require further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out.
Our reliable essay writing service is here to support you every step of the way.
With our experienced team of professionals, we guarantee to provide you with top-quality thesis help.
Whether you need us to deliver a complete thesis or a proposal, our thesis writing service is here for you 24/7. So, order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Writing a Thesis Proposal - Guide, Outline, Format & Tips
11 min read
Published on: Oct 16, 2021
Last updated on: Feb 6, 2024

Thesis Writing 101: Everything You Need to Know
100+ Thesis Topics That Will Make Your Research Stand Out
Thesis Format | Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis Introduction Like a Pro - Steps & Examples
Share this article
Are you feeling overwhelmed and stuck when it comes to crafting a compelling thesis proposal that will impress your committee?
As a graduate student, you know that your thesis proposal is the key to future career opportunities. However, with so much pressure and competition, it's easy to feel lost and unsure of where to start.
But don't worry!
In this blog post, we'll provide you with expert guidance and actionable tips on how to write a winning thesis proposal. From choosing the right topic to developing a persuasive argument, we'll walk you through the process step by step.
So if you're stuck and need some help writing your A-grade thesis proposal, check out this guide for the fundamentals on how to get started!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
On This Page On This Page -->
Thesis Proposal Definition
The thesis proposal is a detailed summary and outline of your research project. It outlines how you will develop an incomplete idea into a thoroughly researched concept.
The thesis proposal is a concise and written summary of your research project. It is like a blueprint for your project. It outlines how you will develop an incomplete idea into something valuable with thorough evidence.
Furthermore, it discovers methods, questions, and problems that will be used in your thesis.
The proposal typically includes the following:
- An Introduction to the research problem
- A review of relevant literature
- An explanation of the proposed methodology
- A discussion of the expected outcomes
- Significance of the study
Furthermore, it will help you discover methods and questions used in your thesis. This is how you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the research process.
Check out this video guide on what is a thesis proposal and how to write it for your better understanding!
Purpose of a Thesis Proposal
A good proposal will show the significance and relevance of your thesis or dissertation. It also indicates that you used the proper approach and tools to solve the problem.
The primary goals of writing a thesis proposal are as follows.
- It demonstrates that the chosen topic addresses a significant problem.
- It shows methods of data collection.
- It identifies a well-organized research plan for gathering or obtaining data to solve the problem.
- Finally, it expresses the thesis's significance, indicating how it will contribute to the field.
Have a look at this thesis topics blogs to explore ideas for your next paper.
How to Write a Thesis Proposal?
To write a thesis or a research proposal, simply follow the simple steps outlined below.
1. Make an Outline
Before you start writing your proposal, it's a good idea to create an outline. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure that you cover all the necessary points.
Your outline should include the following sections:
2. Understand the Proposal Structure
It is important to understand the parts of thesis proposal. A thesis proposal typically follows a specific structure. It should include:
3. Make a Writing Process Plan
Writing a thesis proposal can be a lengthy process, so it's a good idea to create a plan.
Determine how much time you have to work on the proposal and set specific goals for each day or week. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you finish the proposal on time.
4. Compose the Proposal Draft
Once you have your outline and plan, you can start your thesis proposal.
Begin by writing the sections that you feel most comfortable with, such as the introduction or literature review.
Similarly, make use of the first-person pronoun. However, before writing a thesis statement, you must consult your professors.
Don't worry about getting everything perfect on the first draft â you can always go back and make changes later.
5. Edit and Proofread Your Proposal
Once you have a complete draft, it's time to edit and proofread. Read through your proposal carefully and make sure it flows well and makes sense.
Check for spelling and grammar errors and ensure that your references are formatted correctly.
Follow these useful tips to avoid mistakes in your thesis proposal:
- Never proofread a proposal right after writing it. Instead, wait a day or two to look at it objectively.
- Use an online spell checker to assist you.
- Read the proposal aloud to identify grammar and spelling errors and incorrect sentence structure.
- Request someone to proofread who has a thorough understanding of your thesis topic.
Look at the sample below to understand the entire writing process of the thesis proposal.
How to Write a Thesis Proposal Sample Pdf
Thesis Proposal Outline
If you're a graduate student, you're likely familiar with the importance of a thesis proposal.
However, creating a strong and effective proposal can be a daunting task, especially if you're unsure of where to start.
This section will guide you through the process of creating a thesis proposal outline.
Introduction (1 page)
- What is the subject matter?
- What is the research study's scope?
- What is the topic's relevance or significance?
Learn to write an engaging introduction for your thesis with this thesis introduction blog!
Literature Review (7-8 pages)
- It allows you to identify a gap in the literature that has not previously been thoroughly researched.
- To grasp the idea, theoretical approaches and methodological research designs are used.
- It demonstrates that you are familiar with the research that has been done in this field.
- It provides an overview of the existing literature on your topic.
Research Question (1-2 pages)
It involves creating a specific research question. Furthermore, the writer creates the research study based on these questions.
Methodological Design (1-2 pages)
- What will your research's analysis be? (either qualitatively, quantitatively, or both)
- What will be your research methodology? (experiments, case studies, surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.)
- How are you going to code the data? inductive or deductive approach)
- What type of sampling research methods will you use? (probability and non-probability sampling methods)
- How many cases are you planning to include?
- How will you collect the information?
- How will you reach out to the participants?
- What will be the duration of your research study?
- What are your other work-related considerations?
It includes a bibliography and a list of the authors who contributed to your literature review.
Thesis Proposal Format
The thesis proposal format typically follows the pattern shown below.
The title page includes the title of the research, the submission date, the names of the student and supervisor.
- Table of Contents
The proposal is laid out in an easy-to-follow manner with headings and subheadings for each section.
The introduction to your paper gives a brief overview of the historical context and reasons for selecting the topic.
Provide a summary of the study's purpose in a clearly worded statement.
Sample Problem Statement in Thesis Proposal
- Theoretical Framework
The research problem will be posted within the framework of a theory to identify and define terms.
A literature review is a vital tool to provide credible information. It includes reviewing the relevant literature and creating credibility. Make sure this section is at least 15 pages long.
- Research Objectives
In this section, you should outline your research's goals. Similarly, it will state the hypothesis and expected outcome of your research.
The methodology section explains how to conduct experiments and analyze data to achieve the goals. Also, it tells how the experiments will test the hypothesis.
- Analysis of Research Findings
Here, the research findings and outcomes will be evaluated rigorously.
- Timetable for Thesis Completion
The following dates are included in this section:
- Completion of draft
- Initial draft
- Complete draft
- Thesis Proposal Defense
Include every primary and secondary source and their codes in the reference list. Also, you must consult with your professor before deciding on a citation style.
- Other Requirements
The following are some requirements for your proposed project you should follow:
- 5000 words is the maximum word count limit for your thesis proposal.
- Line spacing should be 1.5 for text and single-spaced for quotations.
- Set the margins to 1.25 inches on the right/left and 1 inch on the top and bottom.
- Write in Times New Roman or Arial font and use 12pt size.
- Ment sources in APA, Chicago, or MLA citation styles.
- Mention page numbers at the bottom center of each page in Roman numerals.
Look at the below PDF to learn about the thesis format template.
Need to explore the detailed guide on thesis format? Check our thesis format blog here!
Thesis Proposal Examples
Here are some thesis proposal examples to help you get a clear understanding.
Thesis Proposal Presentation
MBA Thesis Proposal
PhD. Thesis Proposal
Tips for Writing a Thesis Proposal
Writing a thesis proposal can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding experience.
Here are some tips to help you write a successful thesis proposal:
- Start early: Writing a thesis proposal takes time, so it's important to start early. This will give you enough time to research your topic, plan your proposal, and make revisions.
- Understand the requirements: Before you start writing, make sure you understand the requirements for your proposal. This includes the format, length, and any specific guidelines provided by your institution or advisor.
- Conduct a thorough literature review: A literature review is a critical component of any thesis proposal. It shows that you understand the existing research on your topic and can identify gaps that your research will fill.
- Clearly state your hypothesis: Your research question or hypothesis is the foundation of your proposal. It should be clear, concise, and focused.
- Choose appropriate research methods: The research methods you choose should be appropriate for your research question or hypothesis. They should also be feasible and ethical.
- Explain the significance of research: It's important to explain why your research is important and how it will contribute to the field. This will help convince your readers that your research is worth funding and conducting.
- Edit and proofread your proposal: Before submitting your proposal, make sure to edit and proofread it carefully. This will help you catch any errors or inconsistencies and ensure that your proposal is clear and well-written.
- Get feedback: It's always a good idea to get feedback on your proposal from colleagues, advisors, or other experts in your field. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improving your proposal.
In short, writing a thesis proposal demands your full attention and you need to proceed step by step. This way, you can ensure a smoother journey to completing your thesis.
However, due to time constraints and other personal challenges, it becomes very difficult even when you know how to do it. If you have an idea but are lost for words, you can get help from our amazing AI essay writing tool .
Need expert and professional help for more specific aspects of your thesis? We've got your back!
CollegeEssay.org offers budget-friendly proposal essay writing service to help you out. Our team has expert college essay writer from various disciplines, and we promise personalized and original writing assistance so can submit an excellent proposal on time.
Reach out to our academic writing service today!
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

Elite Editing
You write it. We right it.™

If you want to build a house, step one is not wandering over to the next vacant lot with a hammer, some nails, and a pile of boards. Your first step is probably finding an appealing place to build your house—an empty plot of land where the roads are good and where you can pretty easily connect the gas, electricity, and water. Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build.
If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint. It’s you figuring out how your thesis will fit into the space you’ve found, how you’ll build it, and whether it will stand up to the harsh winds of your thesis adviser’s opinions and the tremors of a difficult defense. A thesis proposal allows you to clearly define—and even more crucially, limit—the focus and scope of your research. Producing an excellent thesis blueprint means that you won’t accidentally find you’re trying to build a skyscraper when you should be aiming at a bungalow—and that you have all the supplies and equipment you need.
But how do you create a research proposal? How do you know what it should include? The style and length of your thesis proposal will vary a bit depending on your school’s requirements and the type of thesis you will eventually produce, but the fundamentals will always be the same, and those are what we’re going to cover here. So let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal.
Choosing a Topic
The first step (a step that you must take before figuring out how to write a thesis proposal or even a thesis proposal outline) is choosing a topic for your thesis. The point of embarking on this kind of project is that you’ll first find and then fill a gap in the established, preexisting research in your field. You’re looking for a manageable topic—something focused enough that you can cover it within your word limit but broad enough that you actually have something to write about.
Undergraduate theses are often less revolutionary and more about surveying or analyzing the existing research on a particular topic. This is appropriate because these projects are shorter in length—and you have much less time (typically months rather than years) to work on them. An undergraduate thesis can run anywhere from ten to thirty pages. A master’s thesis is typically forty to eighty pages and might present some original research, or it might be a significant reinterpretation of preexisting research.
A doctoral thesis is (naturally) the longest of these three, and the research it presents should be more groundbreaking and challenging to complete. That investment of time and mental energy is what’s going to earn you the right to demand that everyone call you “Doctor.”
Tips for Choosing a Thesis Topic
- Consider your interests. What makes you sit up and your brain feel fizzy? You’re about to spend a lot of time working on this topic. It had better be something that fascinates you.
- Explore open-ended questions. How or why questions offer you more scope and flexibility than what or who questions.
- Consider the time. How long will your project take to complete? Make sure you have enough time to get from here to there.
- Research any funding you’ll need. Will you need to travel or establish an experimental protocol? If so, can you get the funding for these projects? How do these affect your projected timeline? Save the long-view research for your later career, and find something you can finish.
- If it’s a controversial topic, choose wisely. Be realistic about whether you’re likely to encounter stiff resistance during your defense. Something that goes against all existing research will demand greater rigor and effort from you than something that challenges only a part of what is currently considered established knowledge.
- Make it publishable. Are all possible outcomes to your research interesting and academically publishable? Or is there a potential dead end that you can avoid by shifting your focus now?
- Think long term. How will the project affect (and improve) your marketability for the future? There is life after your thesis, after all. Where do you want to be, and how can your work now help get you there?
Structuring Your Thesis Proposal
A thesis proposal usually includes some or all of the following elements:
- Table of contents
- Thesis statement
- Literature review or annotated bibliography
- Approach/methods
- Preliminary results and discussion
- Work plan and schedule
- Research implications
The thesis proposal outline above shows one potential way to order the parts, but (and this is important) you won’t work on those elements in that order. For example, that table of contents? It’s probably the last thing you’ll work on. Similarly, you can’t write the abstract until you’ve written everything else.

Let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal in greater detail.
Title Page and Creating a Title
The title of your project is likely to be a brief statement of your research topic, approach, and intent. It will be far easier to write a title once you’ve written a thesis statement (see below) because it is likely to restate or incorporate your thesis statement.
Violence and Redemption in Modern Afghani Literature: A Marxist Analysis of Power Structures in The Kite Runner and The Wasted Vigil
Living the Fantasy: Addiction and Social Identity in World of Warcraft
Your title page will include this title, your name, your department and institution, your adviser, your adviser’s institution, and the date you’re submitting the proposal.
Writing an Abstract
An abstract is a short summary of your full proposal, usually about a page in length. It hits the highlights of the proposal as a whole, including your title, your thesis statement, a quick summary of your plan of research, and a statement about why this project matters.
Table of Contents
If you’re writing your table of contents, you’re minutes away from a celebratory “Woo-hoo!” because you’re almost finished. A table of contents will list all the headings and subheadings of your proposal with lovely indentations and the correct page numbers. If you’re using MS Word, and you’ve been formatting your headings in the appropriate styles, you can automatically generate a table of contents that will make everything look very pretty indeed.
Writing the Thesis Statement
It’s not a simple question: How do you write a good thesis statement? Your thesis statement may well be the hardest sentence (or two—three at the most) you ever have to write. Despairing tears or frustrated anger are not out of the question. However, once you formulate that thesis statement, you will be off and running because now you have a beautifully clear and specific goal to head for.
A thesis statement should clearly define the scope and intent of your project. It might be a hypothesis or a question, or it might be a firm statement. The hours of work that will become your thesis will then prove (or possibly disprove, though hopefully in a deeply productive way) your thesis statement, so it should be something provable—something that can in some way be measured.
Let’s look at some examples of how to write a good thesis statement.
Not so good:
Taking a year off between high school and college is a good idea.
A “good idea” is vague and indefensible. Good by whose standards? How can you prove that?
Students who take a year off between high school and college are more academically successful than their peers.
This is better because it limits the scope of the project to academics, but it’s still rather vague and unwieldy. It also doesn’t suggest what metrics will be used to judge “academically successful.”
Better still:
Students who take a year off between high school and college are significantly more likely than their peers to graduate within four years with a B average or better.
This thesis statement works because it is concrete and measurable. The data you collect will either clearly prove the statement or disprove it.
How does the internet affect social behavior?
Wow, that’s a huge question. Also, there is nothing to prove, measure, or evaluate. It’s a topic rather than a thesis. It might be what you’re generally interested in, but you have yet to find the aspect of this topic that you can effectively research.
The internet has changed how American teens approach gender.
At least this is a statement, but it’s still too vague. “Changed” how? And what does “approach” mean?
The social media profiles of American teens thirteen to eighteen years old reflect this demographic’s increasing comfort with fluid sexual and gender identities.
This thesis statement could probably still be improved, but it is getting toward something measurable and provable.
Writing a Thesis Proposal Introduction
Your introduction will do just that—introduce your readers to your topic and thesis. Don’t mistake this for an introductory paragraph, however. This is where you’ll summarize your project in the hopes of intriguing and engaging the committee that will either approve your thesis project or send you back to the drawing board. Your writing should be as clear, straightforward, and free from jargon as possible. You’ll contextualize your project within the broader scope of the topic, perhaps exploring the papers, research, or work that led to your formulation of your thesis. You’ll explain why your project excites you. You’ll illustrate your competence to embark on this project. Basically, you’ll sell your proposal.
Literature Review or Annotated Bibliography
You might be able to quickly cover the most relevant literature in your proposal introduction, but if there are many articles or books relevant to your research, your thesis proposal might include an annotated bibliography or a literature review (which is slightly more informal and conversational in approach). Here is where you’d not only list the most influential and crucial texts that underpin your research but also explain why they matter—that is, how they fit into your project. This is a way to show that gap in the research that you will be filling with your thesis project.
Explain Your Proposed Methods or Approach
Most thesis projects demand original research of some kind, and for degrees in the sciences (including the social sciences), that research may very well take the form of an experiment or raw data collection. Here is where you should describe your proposed methodology. What materials will you use? How will you collect your data? How will you analyze the data once it’s collected? Are you taking a qualitative or quantitative approach? Why? Will you need outside funding (for travel or other costs), and how do you propose to acquire that funding? Do you need space and equipment to conduct your research?
Provide Preliminary Results
It may be that you have already been testing the viability of your thesis project with some preliminary research (which is not a bad idea). If so, here is where you should provide the results of that research and your tentative interpretation of those results. Clearly show how this work fits into your larger project—and how it proves that you’re heading down a productive road of inquiry.
Design a Work Plan
Even if your particular program or professor doesn’t require you to include a work plan in your thesis proposal, you should still make one. There’s nothing more likely than a schedule—with deadlines!—to keep you on track and get your thesis done on time.
This section should
- lay out your plan,
- list the various stages of your project,
- set deadlines for the completion of each stage, and
- detail any work you’ve already completed.
In addition, your work plan should take into account any challenges (personal, practical, or institutional) that may affect the completion of the study.
Discuss Research Implications
Here, you are striving to answer this question: Why does this project matter in this place and at this time? It’s actually a wonderful exercise in focusing your own thoughts and evaluating the worth of your proposed project. Are you remedying a misunderstanding that might affect how to treat a particular medical condition? Are you exploring the dynamics of a culture that is (socially or politically) especially relevant at the moment? Are you providing new insight into a classic work of literature or music that will reinvigorate teachers and academics? Your research might have implications for the entire world or it might be of interest only to other specialists in your subject, but that really doesn’t matter. The point is to figure out and clearly state how your research will enhance the sum total of knowledge.
Notes and Bibliography
All statements in this thesis proposal need to be supported with data, whether that data is derived from your own research or gleaned from a third party. Using whatever citation style is most appropriate to your field, you should give credit to all your sources, primary or secondary. Note that this is separate from your literature review in that you’re only going to cite the sources you’ve used in your proposal.
Thesis Proposal Defense / Thesis Proposal Presentation
Your college or university may require you to appear in person at a thesis proposal defense or to make a thesis proposal presentation. In both cases, however, you’ll be presenting your proposal to your thesis committee (and possibly others) and then potentially answering their questions about your project. While this might seem alarming, this event is actually an excellent opportunity to pick your committee’s brain about possible obstacles or objections you will need to overcome while working on your project. Better to know right now that they’d rather you took a quantitative approach than do all the work and then discover their preference. It will also help focus you since knowing something is one level of understanding it—but explaining it to someone else can take your understanding to a much deeper level.
You should now have a much deeper understanding of how to write a thesis proposal. A clear, thorough, well-thought-out thesis proposal allows you to see the entire shape of your project before you invest huge amounts of time and energy into research that might end up leading nowhere. Your thesis proposal sets the stage for the success of your project as a whole, and it should reflect and predict the quality you intend to produce in your final thesis. That’s why your thesis proposal presentation also matters. In addition, remember that proofreading counts. It’s extremely important to carefully review your finished proposal for spelling, grammar, and structural errors.
With your thesis proposal completed and approved, you’re well on your way to embarking on what might be the most important project of your life to date. We wish you all the best with your studies, and if you decide you want an editor to cast an expert eye over any part—large or small—of your project, we here at Elite are happy to help!
Want more? Check out this post on credible online sources and how to find them.
Other Resources You Might Like

Crafting Timeless Content

Mastering the Art of Persuasive White Papers

Writing Effective Press Releases in a Digital Age
Get elite updates straight to your inbox..
- Content Writing
- Marketing and Sales Enablement
- Program Management
- AI Implementation
Who We Help
- Thought Leaders
- Cybersecurity
- Health Care
- Full-Time Careers
- Freelance Opportunities
- Press and Awards
- About Elite
In the News
- Elite Creative Makes the Inc. 5000 for the Third Year in a Row

What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
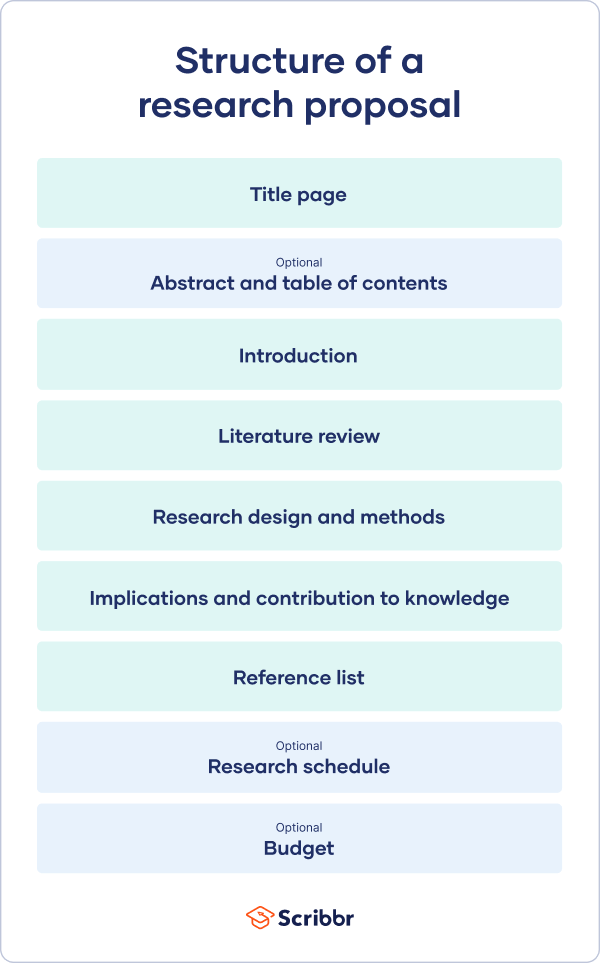
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
University Libraries
Writing a dissertation or thesis proposal, what is a proposal, what is the purpose of a proposal.
- Video Tutorials
Select a Topic
- Research Questions
- Search the Literature
- Plan Before Reviewing
- Review the Literature
- Write the Review
- IRB Approval
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation or thesis.
In the graduate student timeline, the proposal comes after successfully passing qualifying or comprehensive exams and before starting the research for a dissertation or thesis.
Each UNT department has slightly different proposal requirements, so be sure to check with your advisor or the department's graduate advisor before you start!
- Examples of Proposals from UTexas More than 20 completed dissertation proposals are available to read at the UT Intellectual Entrepreneurship website.
- Dissertation Proposal Guidelines This document from the Department of Communication at the University of Washington is a good example of what you might be expected to include in a proposal.
The purpose of a proposal is to convince your dissertation or thesis committee that you are ready to start your research project and to create a plan for your dissertation or thesis work. You will submit your proposal to your committee for review and then you will do your proposal defense, during which you present your plan and the committee asks questions about it. The committee wants to know if your research questions have academic merit and whether you have chosen the right methods to answer the questions.
- How to Prepare a Successful Dissertation Proposal Defense Some general tips for a proposal defense from synonym.com
Need help? Then use the library's Ask Us service. Get help from real people face-to-face, by phone, or by email.
- Next: Resources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.unt.edu/Dissertation-thesis-proposal
Additional Links
UNT: Apply now UNT: Schedule a tour UNT: Get more info about the University of North Texas
UNT: Disclaimer | UNT: AA/EOE/ADA | UNT: Privacy | UNT: Electronic Accessibility | UNT: Required Links | UNT: UNT Home
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How to Write the Perfect Thesis Proposal

Before you begin your thesis or dissertation, you will have to prepare a proposal. A thesis proposal is a roadmap to your actual research. It outlines the topic and acts as a guide to understand why the issues you wish to address in your thesis, warrant research.
The first step is to understand how to write a thesis proposal. There are a few simple steps that you can follow:
- Zero down on your topic: You may have a sense of what you wish to write about. However, you need to make sure that the topic is of interest in your field. It should answer important questions and must have a good scope for content collection.
- Example – You may want to write on genocides in history and Norman Naimark is one of your favorite authors.
- Make a working title: The length of your working title should be more than the final title. It should also be more descriptive so as to have a better discussion with your professor or committee.
Example – Actual title – ‘Genocides in History’. Working title – ‘Genocides in History that Shaped the World’
- Review the available literature: This will help you know about the existing research on your topic and help determine the scope for further research.
- Make an outline of your proposal: Your thesis proposal sample must list all the important points that you wish to include in your proposal.
Example – include all preliminary research, create appendices for secondary information, literature review and more.
- Create headings: Each section of your thesis proposal should be broken down into sub-topics. This helps present vital information in a better manner.
Example – when you are writing the subtopics for the methodology make a list of books that you will refer to, why you think the topic is important and how your will approach various subjects.
- Put it all together: Use the thesis proposal format mentioned below and put together your thesis proposal. Make sure you include your timeline, theoretical approach, and methodology as well.

Structure of a Thesis Proposal
There is a set thesis proposal structure that students must adhere to while writing their proposal. You can also refer to a thesis proposal template for better understanding:
Title page: Every thesis proposal example will include a title page which includes a descriptive title. It also includes information like the name of the author, name of the mentor, date, name of the institution etc. The title must reflect the subject, the proposed method of research and the lessons that one will learn from it. Abstract: In the beginning of every sample thesis proposal, you will notice a short 200 word paragraph summarizing the thesis. This is known as the abstract. It includes the title, the key statement, the methods used to address the subject and the implications of the research once completed. Table of Contents: This is one of the most important elements of the thesis proposal. It will provide a complete thesis proposal outline, listing all the headings and subheadings. Introduction: The introduction must be catchy and impressive. This will urge your reader to explore your ideas further. The background of the topic and a broad perspective of the research must be provided in this introduction. Key questions: The questions that you wish to answer in the thesis must be listed. When a reader views these questions in the thesis proposal example, it will show the direction that you intend to take with your research. Literature review: The literature review provides a description of all the sources that you wish to use in your research. This shows the information that you have already accumulated for your research. It also indicates the future goals of the thesis. Methodology: This section describes all the methods that you wish to make use of in the thesis paper in order to answer the key questions. Conclusion: When you are writing a thesis proposal, pay attention to the conclusion. This section indicates the possible research of your research, the contributions it will make to your field and the expected accuracy of your results. Thesis proposal summary: This is the section where the goals of your proposal are stated in brief. Bibliography: You must provide a list of all the references that you will make use of for your research. Remember that the bibliography must be written according to the writing style required for your thesis, be it APA or MLA writing style.
How Long Should a Thesis Proposal Be?
A thesis proposal should not be more than 8 pages long.
The idea of the thesis proposal is to make the purpose of the research clear. It should provide a clear idea about how you wish to go about your research. There is no need to delve into the details when you are writing the proposal. These eight pages exclude the bibliography.
Tips on How to Write a Good Thesis Proposal
Here are five tips to help you make a convincing thesis proposal:
Your thesis proposal must be solid, yet flexible. Try to incorporate as many important elements as possible to prove that the subject you have chosen warrants further research. However, be open to changes and feedback. That is the whole idea of the proposal. Make sure you choose a subject that excites you. This will urge you to dig deeper and gather as much information as possible. Your subject should be a good balance between novelty and already established ideas about the subject. Do you have enough material to prepare the thesis in the given period of time? This is the most important question that you should answer. The questions listed in your thesis proposal should be open-ended, yet well defined. Allow some scope for discussion and debate. Avoid straightforward, “Yes and No” questions. Choose subjects that will help you develop marketable skills. Think of subspecialties in your field. Select a subject that will help you explore these subspecialties in your field. This will help you develop skills that will help you land better jobs and open more opportunities for you in the future. This approach is most likely to convince your professor and university committee about the scope of your thesis.
If you are looking for writing help or are confused about how to write a thesis proposal sample, get in touch with us today . We help students across various areas of study create the best proposals that make a good impression.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- How it works
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal with Structure & Steps
Published by Anastasia Lois at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
“A dissertation proposal is a stepping stone towards writing the final dissertation paper. It’s a unique document that informs the reader of the aim & objectives of dissertation research and its course of action.”
The main purpose of a proposal paper is to showcase to your supervisor or dissertation committee members that your dissertation research will add value to existing knowledge in your area of study.
Although the exact structure of a dissertation proposal may vary depending on your academic level, academic subject, and size of the paper, the contents remain pretty much the same.
However, it will still make sense to consult with your supervisor about the proposal formatting and structuring guidelines before working on your dissertation proposal paper.
You may lose out on scoring some important marks if your proposal paper does not follow your department’s specific rules. Here are some tips for you on how to structure a dissertation proposal paper.
Tips on Completing a Dissertation Proposal in Due Time
Consult your supervisor or department to find out how much time you have to complete your dissertation proposal . Each graduate program is different, so you must adhere to the specific rules to avoid unwelcome surprises.
Depending on the degree program you are enrolled in, you may have to start working on your chosen topic right away, or you might need to deal with some assignments and exams first.
You can learn about the rules and timelines concerning your dissertation project on the university’s online portal. If you are still unsure, it will be best to speak with your department’s admin clerk, the program head, or supervisor.
Look for Proposal Structural Requirements in the Guidelines
Most academic institutions will provide precise rules for structuring your dissertation proposal in terms of the document’s content and how to arrange it. If you have not figured out these requirements, you must speak with your supervisor to find out what they recommend. Typical contents and structure of a dissertation proposal include the following;
- Background/Rationale
- Introduction (Justifying your Research)
- Research Questions or Hypothesis (Research aim and objectives)
- Proposed Methodology
- Opportunities and Limitations
Project Schedule
Have an unhelpful dissertation project supervisor? Here is some advice to help you deal with an uncompromising dissertation advisor.
How Long is a Dissertation Proposal?
The length of your dissertation proposal will depend on your degree program and your research topic. PhD-level dissertation proposals are much longer in terms of word count than Bachelors’s and Master’s level proposals.
- Bachelor’s level dissertation proposals are about 5-6 pages long.
- Masters and Ph.D. level proposals’ length varies from 15-25 pages depending on the academic subject and degree program’s specifications.
- If the word count or page length expectation is not mentioned in the dissertation handbook or the guidelines on the university’s website, you should check with your supervisor or program coordinator for a clear understanding of this particular requirement.
The proposals we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources

Dissertation Proposal Formatting
Formatting your dissertation proposal will also depend on your program’s specific guidelines and your research area. Find the exact guidelines for formatting cover sheets and title pages, referencing style, notes, bibliography, margin sizes, page numbers, and fonts. Again if you are unsure about anything, it is recommended to consult with your project advisor.
Find out About the Approval Criteria
The process of writing your dissertation proposal paper and getting acceptance from the committee of members of your supervisor is tricky.
Consult your department’s academic assistant, supervisor, or program chair to learn about all the process stages. Here are a couple of points you will need to be aware of:
- You might be required to have your chosen research topic approved by your academic supervisor or department chair.
- Submit your proposal and have it formally signed and approved so you can continue with your research.
You may find the dissertation proposal writing process perplexing and challenging if this is the first time you are preparing such a document. All the essential elements of a dissertation proposal paper need to be present before submitting it for approval.
Any feedback received from the tutor or the supervising committee should be taken very seriously and incorporated into your planning for dissertation research. Do not start working on your final dissertation paper until your supervisor has accepted the proposal.
To help you organise your dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have detailed guidelines for structuring a dissertation proposal. Irrespective of the degree program you are developing your dissertation proposal for, you will find these guidelines equally important.
Our expert academics can produce a flawless dissertation proposal on your chosen topic. They can also suggest free topics in your area of study if you haven’t selected a topic. Order free topics here or get a quote for our proposal writing service here.
Selecting an appropriate topic is the key to having your research work recognised in your field of study. Make sure your chosen topic is relevant, interesting, and manageable.
Ideally, you would want to research a topic that previous researchers have not explored so you can contribute to knowledge on the academic subject.
But even if your topic has been well-researched previously, you can make your study stand out by tweaking the research design and research questions to add a new dimension to your research.
How to Choose a Suitable Research Topic
Here are some guidelines on how to choose a suitable research topic.
List all the topics that you find interesting and relevant to your area of study. PhD and MaMasters’sevel students are already well aware of their academic interests.
Bachelor students can consider unanswered questions that emerged from their past academic assignments and drove them to conduct a detailed investigation to find answers.
Follow this process, and you’ll be able to choose the most appropriate topic for your research. Not only will this make your dissertation unique, but it also increases the chances of your proposal being accepted in the first attempt.
- Think about all your past academic achievements and associations, such as any research notes you might have written for your classes, any unsettled questions from your previous academic assignments that left you wondering, and the material you learned in classes taught by professors.
- For example , you learned about how natural gas is supplied to households in the UK in one of your coursework assignments and now eagerly wish to know exactly how natural gas is processed at an industrial scale.
ORDER YOUR PROPOSAL NOW
Conduct initial research on your chosen topic(s). This will include reading authentic text material on the topic(s) to familiarise yourself with each potential topic. Doing so will help you figure out whether there really is a need to investigate your selected topics further.
Visit your university’s library or online academic databases such as ProQuest, EBSCO, QuickBase to find articles, journals, books, peer-reviewed articles, and thesis/dissertation papers (by other students) written on your possible research topic .
Ignore all academic sources that you find methodologically flawed or obsolete. Visit our online research topics library to choose a topic relevant to your interests .
Consult your academic supervisor and show them your list of potential topics. Their advice will be crucial for deciding whether the topic you are interested in is appropriate and meets your degree program requirements.
It is recommended to set up an appointment with your supervisor to see them in person to discuss your potential topics, even though you can do the same in email too.
- If the topics you are interested in are too broad or lack focus, your supervisor will be able to guide you towards academic sources that could help narrow down your research.
- Having several topics in your list of potential topics will mean that you will have something to fall back onto if they don’t approve your first choice.
Narrow the Focus of your Research – Once a topic has been mutually agreed upon between you and your academic supervisor, it is time to narrow down the focus. Hence, your research explores an aspect of the topic that has not been investigated before.
Spend as much time as possible examining different aspects of the topic to establish a research aim that would truly add value to the existing knowledge.
- For example, you were initially interested in studying the different natural gas process techniques in the UK on an industrial scale. But you noticed that the existing literature doesn’t count for one advanced gas processing method that helps the industry save millions of pounds every year. Hence, you decide to make that the focus of your research.
- Your topic could be too broad as you start your research, but as you dig deep into your research, the topic will continue to narrow and evolve. TIP – It is better to work on a topic that is too broad rather than on something there is not enough text material to work with.
Structure of a Dissertation Proposal
The key elements of a great dissertation proposal are explained in detail under this section ‘structure of a dissertation proposal’. Once you’ve finalised your topic, you need to switch to writing your dissertation proposal paper quickly. As previously mentioned, your proposal paper’s exact structure may vary depending on your university/college requirements.
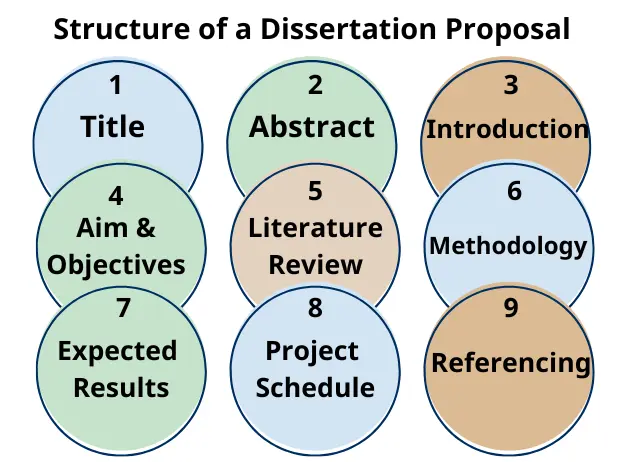
A good dissertation proposal title will give the reader an insight into the aim/idea of your study. Describe the purpose and/or contents of your dissertation proposal paper in the fewest possible words.
A concise and focused title will help you gain the attention of the readers. However, you might need to adjust your title several times as you write the paper because your comprehensive research might continue to add new dimensions to your study.
- Your title must be as categorical as possible. For example, instead of “Natural Gas Processing Techniques in the UK”, use a more specific title like “Investigating various industrial natural gas processing technologies employed in the UK” so the reader can understand exactly what your research is about.
Write a brief executive summary or an abstract of your proposal if you have been asked to do so in the structural guidelines. Generally, the abstract is included in the final dissertation paper with a length of around 300-400 words.
If you have to write an abstract for your proposal, here are the key points that it must cover;
- The background to your research.
- Research questions that you wish to address.
- Your proposed methods of research, which will either test the hypothesis or address the research problem.
- The significance of your research as to how it will add value to the scientific or academic community.
Get Help With Your Assignment!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try.

This is your first chance to make a strong impression on the reader. Not only your introduction section should be engaging, contextually, but it is also supposed to provide a background to the topic and explain the thesis problem .
Here is what the first paragraph of the introduction section should include:
- Explain your research idea and present a clear understanding as to why you’ve chosen this topic.
- Present a summary of the scope of your research study, taking into account the existing literature.
- Briefly describe the issues and specific problems your research aims to address!
In the next paragraphs, summarise the statement of the problem . Explain what gap in the existing knowledge your research will fill and how your work will prove significant in your area of study.
For example, the focus of your research could be the stage of carbon monoxide removal from natural gas. Still, other similar studies do not sufficiently explore this aspect of natural gas processing technology.
Here is a comprehensive article on “ How to Write Introduction for Dissertation Paper .”
Aim & Objectives
This is the most critical section of the proposal paper . List the research questions or the research objectives your study will address. When writing this particular section, it will make sense to think of the following questions:
- Are there any specific findings that you are expecting?
- What aspects of the topic have you decided not to investigate and why?
- How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge in your field?
Literature Review
The literature review section is your chance to state the key established research trends, hypotheses , and theories on the subject. Demonstrate to the reader that your research is a unique contribution to your field because it explores the topic from a new angle.
In a dissertation proposal, you won’t be expected to provide an extensive list of all previous research studies on the topic. Still, all the key theories reported by other scholars should be briefly referred to.
Take into consideration the following when writing the literature review section:
- The gaps identified in the previous research studies on the topic which your own research aims to fill. State the limitations of previous studies, whether lacking sufficient evidence, invalid, or too broad.
- The key established research trends, theories, and hypotheses as reported by other researchers.
- Any specific arguments and/or methodologies that previous scholars used when investigating your topic.
Our expert dissertation proposal editors can improve the quality of your proposal paper to the First Class standard. Complete this short and simple order form here so we can get feedback from our writers.
A focused and well-defined methodology in a proposal paper can help you explain to your readers how you plan to conduct your research and why your chosen research design can provide reliable answers to your research questions.
The choice of research design and analytical approach will depend on several factors, including but not limited to your area of study and research constraints.
Depending on your topic and the existing literature, you will need to decide whether your dissertation will be purely descriptive or use primary (quantitative/qualitative data) as part of the research design.
Any research limitations and ethical issues that you expect to deal with should be clearly stated. For example, you might not be able to use a large sample size of respondents due to financial constraints. Small sample size can undermine your research significance.
How to Write a First Class Dissertation Proposal or Research Proposal.
“If you’re unable to pull off a first-class proposal, we’re here to help. We at ResearchProspect make sure that our writers prepare a flawless dissertation proposal for you. Our highly qualified team of writers will also help you choose a relevant topic for your subject area. Get in touch with us today, and let us take care of all your dissertation worries! Learn more about our dissertation proposal writing service.
Some Masters and PhD level degree programs require students to include a project timeline or timetable to give readers an idea of how and when they plan to complete different stages of the project.
Project timeline can be a great planning tool, mainly if your research includes experiments, statistical analysis , designing, and primary data collection. However, it may have to be modified slightly as you progress into your research.
By no means is it a fixed program for carrying out your work. When developing the project timeline in your proposal, always consider the time needed for practical aspects of the research, such as travelling, experiments, and fieldwork.
Referencing and In-Text Citations
Underrated, but referencing is one of the most crucial aspects of preparing a proposal. You can think of your proposal as the first impression of your dissertation.
You would want everything to be perfect and in place, wouldn’t you? Thus, always make sure that your dissertation consists of all the necessary elements.
You will have to cite information and data that you include in your dissertation. So make sure that the references that you include are credible and authentic.
You can use well-known academic journals, official websites, past researches, and concepts presented by renowned authors and writers in the respective field.
The same rule applies to in-text citations. Make sure that you cite references accurately according to the required referencing style as mentioned in the guidelines.
References should back statistics, facts, and figures at all times. It is highly recommended to back every 100-200 words written with at least one academic reference. The quantity of references does not matter; however, the quality does.
These are the basic elements of a dissertation proposal. Taking care of all these sections will help you when you are confused about structuring a dissertation proposal. In addition to these steps, look for different dissertation proposal examples on your research topic. A sample dissertation proposal paper can provide a clear understanding of how to go about the “pro”osal stage” of”the dissertation project.
“If you’re unable to pull off a first-class proposal, we’re here to help. We at ResearchProspect make sure that our writers prepare a flawless dissertation proposal for you. Our highly qualified team of writers will also help you choose a relevant topic for your subject area. Get in touch with us today, and let us take care of all your dissertation worries! Learn more about our dissertation proposal writing service .”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dissertation proposal in research.
A dissertation proposal in research outlines the planned study. It includes research objectives, methods, scope, and significance. It’s a blueprint that demonstrates the feasibility and value of the research, helping gain approval before proceeding with the full dissertation.
How do you write a dissertation proposal?
A dissertation proposal outlines your research topic, objectives, methodology, and potential significance. Start with a clear title, state your research question, detail the methods you will use to answer it, and highlight the contribution it will make to the field. Ensure it is well-researched, concise, and compelling to gain approval.
How long is a dissertation proposal?
A dissertation proposal’s length varies by field and institution. Typically, it ranges from 10 to 20 pages, but can be longer for complex topics. It includes an introduction, research question, literature review, methodology, and potential significance. Always consult department guidelines or advisors to ensure appropriate length and content.
What are the types of dissertation proposals?
Dissertation proposal types largely depend on the research’s nature and methodology. Common types include empirical (collecting data from the real world), non-empirical (theory or literature-based), and narrative (case studies). Each type dictates a different approach to data collection, analysis, and presentation, tailored to the subject and field of study.
You May Also Like
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
Repository of ten perfect research question examples will provide you a better perspective about how to create research questions.
Here we explore what is research problem in dissertation with research problem examples to help you understand how and when to write a research problem.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Graduate School
How to Write a Master's Thesis Proposal
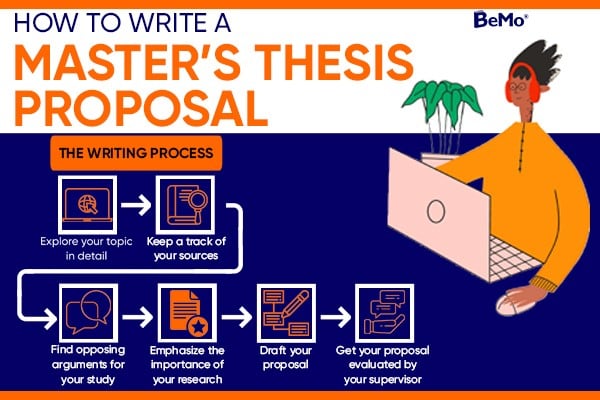
How to write a master’s thesis proposal is one of the most-asked questions by graduate students. A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis. Your proposal should serve as a foundational blueprint on which you will later build your entire project. To have the perfect thesis proposal, you need to have original ideas, solid information, and proper presentation. While it is a good idea to take assistance from thesis writing services , you still need to personally understand the elements that contribute to a master’s thesis proposal worthy of approval. In this blog, we will discuss the process of writing your master’s thesis proposal and give you tips for making your proposal strong. Stay tuned!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 8 min read
How to decide the goals for your master's thesis.
If you are pursuing a master’s or a PhD , you will be undertaking a major research paper or a thesis. Thus, writing a thesis proposal becomes inevitable. Your major objective for pursuing a master’s degree is to improve your knowledge in your field of study. When you start your degree, you delve deeper into different concepts in your discipline and try to search for answers to all kinds of questions. If you come across a question that no one can answer, you can select that question as your research thesis topic.
A master's thesis proposal will have multiple sections depending on your decided layout. These sections will continuously support your argument and try to convince the reader of your core argument. The structure will also help you arrange the various parts of the paper to have a greater impact on the readers. A paper should always begin with you giving a brief summary of the topic and how you have come across it. The introduction is particularly important because it will give the readers a brief idea about the topic of discussion and win their interest in the matter.
After the summary has been given, slowly you need to progress into the body of the thesis proposal which would explain your argument, research methodology, literary texts that have a relation to the topic, and the conclusion of your study. It would be similar to an essay or a literary review consisting of 3 or 4 parts. The bibliography will be placed at the end of the paper so that people can cross-check your sources.
Let's take a look at the sections most master's thesis proposals should cover. Please note that each university has its own guidelines for how to structure and what to include in a master’s thesis proposal. The outline we provide below is general, so please make sure to follow the exact guidelines provided by your school:
Restate your primary argument and give us a glimpse of what you will include in the main master\u2019s thesis. Leave the reader wanting more. Your research proposal should talk about what research chapters you are trying to undertake in your final thesis. You can also mention the proposed time in which you will complete these chapters. ","label":"Conclusion and proposed chapters","title":"Conclusion and proposed chapters"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
A thesis proposal needs to be convincing enough to get approval. If the information is not enough to satisfy the evaluation committee, it would require revision. Hence, you need to select and follow the right methodology to make your argument convincing. When a research proposal is presented, the reader will determine the validity of your argument by judging the strength of your evidence and conclusions. Therefore, even writige:ng a proposal will require extensive research on your part. You should start writing your thesis proposal by working through the following steps.
Interested in a summary of the points covered below? Check out this infographic:
Exploring your topic in detail
You need to delve deeper into your chosen topic to see if your idea is original. In the process of this exploration, you will find tons of materials that will be supportive of your argument. When choosing your research topic and the problem you want to explore, you should always consider your primary research interest (yes, the one which you had mentioned in your research interest statement during grad school applications) for a better master’s thesis. You have a high probability of performing better in an area that you have always liked as compared to any other research area or topic.
Reviewing the literature
You have to include all the sources from where you have formed your argument and mention them in the thesis proposal. If you neglect to mention important source texts, the reader may consider it to be plagiarism. Furthermore, you want to keep track of all your research because it will be easier to provide references if you know the exact source of each piece of information.
Finding opposing arguments for your study
You should also mention any texts that would counter your argument and try to disprove their claims in the thesis. Make sure to use evidence if you try to disprove the counterarguments you face.
Emphasizing the importance of your research
At the end of the thesis proposal, you need to convince the reader why your proposal is important to your chosen field of study, which would ultimately help you in getting your topic approved. Thus, it is essential to outline the importance of your research thoroughly.
Drafting your proposal
After doing proper research, you should go ahead and draft your proposal. Remember you will not get it right in just one draft, it will take at least 50 attempts to come up with a satisfactory proposal. You should proofread your draft several times and even have a fellow student review it for you before sending it further to your research supervisor.
Getting your proposal evaluated by your supervisor
After you have written sufficient drafts, you need to get your proposal evaluated by your research supervisor. This is necessary to meet the graduate research requirements. It will ensure the clarity and correctness of your proposal. For your supervisor to evaluate your proposal, you should complete the research methodology part along with sufficient proposed work.
Since your supervisor will play a crucial role in your master's research thesis, you must choose a supervisor who can be your ultimate guide in writing your master's thesis. They will be your partner and support system during your study and will help you in eliminating obstacles to achieving your goal.
Choosing the ideal supervisor is a pretty daunting task. Here’s how you can go about the process:
You should approach your professor with an open mind and discuss the potential goals of your research. You should hear what they think and then if you both mutually agree, you can choose them as your supervisor for your master\u2019s thesis. "}]">
Length of a Master’s Thesis Proposal
The length of a master’s thesis proposal differs from university to university and depends on the discipline of research as well. Usually, you have to include all the above-mentioned sections, and the length is around 8 pages and can go up to 12-15 pages for subjects such as the liberal arts. Universities might also define the number of words in the guidelines for your master’s thesis proposal and you have to adhere to that word limit.
Are you debating between pursuing a Masters or a PhD? This video has details that can help you decide which is best for you:
How to Format a Research Thesis Proposal Correctly?
Now that you know how to write a thesis proposal, you must make it presentable. Although your school might give your specific instructions, you can keep in mind some of the general advice:
- You can use some basic font like Times New Roman and keep the font size to 10 or 12 points.
- The left margin should be 1.5 inches and all other margins should be 1 inch each.
- You should follow double-spacing for your content.
- The first line of paragraphs should be indented 0.5 inches and the paragraphs should be left or center aligned.
Tips to Write a Strong Master's Thesis Proposal
When you are writing your master’s thesis proposal, you should keep these tips in mind to write an excellent master’s thesis proposal with all the correct elements to get approval from the evaluating committee:
Select your research objectives wisely
You should be clear on what you wish to learn from your research. Your learning objectives should stem from your research interests. If you are unsure, refer to your grad school career goals statement to review what you wanted out of grad school in the first place. Then, choose your objectives around it.
Write a clear title
The title of your research proposal should be concise and written in a language that can be understood easily by others. The title should be able to give the reader an idea of your intended research and should be interesting.
Jot down your thoughts, arguments, and evidence
You should always start with a rough outline of your arguments because you will not miss any point in this way. Brainstorm what you want to include in the proposal and then expand those points to complete your proposal. You can decide the major headings with the help of the guidelines provided to you.
Focus on the feasibility and importance
You should consider whether your research is feasible with the available resources. Additionally, your proposal should clearly convey the significance of your research in your field.
Use simple language
Since the evaluation committee can have researchers from different subject areas, it is best to write your proposal in a simple language that is understandable by all.
Stick to the guidelines
Your university will be providing the guidelines for writing your research proposal. You should adhere to those guidelines strictly since your proposal will be primarily evaluated on the basis of those.
Have an impactful opening section
It is a no-brainer that the opening statement of your proposal should be powerful enough to grasp the attention of the readers and get them interested in your research topic. You should be able to convey your interest and enthusiasm in the introductory section.
Peer review prior to submission
Apart from working with your research supervisor, it is essential that you ask some classmates and friends to review your proposal. The comments and suggestions that they give will be valuable in helping you to make the language of your proposal clearer.
You have worked hard to get into grad school and even harder on searching your research topic. Thus, you must be careful while building your thesis proposal so that you have maximum chances of acceptance.
If you're curious how your graduate school education will differ from your undergraduate education, take a look at this video so you know what to expect:
Writing the perfect research proposal might be challenging, but keeping to the basics might make your task easier. In a nutshell, you need to be thorough in your study question. You should conduct sufficient research to gather all relevant materials required to support your argument. After collecting all data, make sure to present it systematically to give a clearer understanding and convince the evaluators to approve your proposal. Lastly, remember to submit your proposal well within the deadline set by your university. Your performance at grad school is essential, especially if you need a graduate degree to gain admission to med school and your thesis contributes to that performance. Thus, start with a suitable research problem, draft a strong proposal, and then begin with your thesis after your proposal is approved.
In your master’s thesis proposal, you should include your research topic and the problem statement being addressed in your research, along with a proposed solution. The proposal should explain the importance and limitations of your research.
The length of a master’s thesis proposal is outlined by the university in the instructions for preparing your master’s thesis proposal.
The time taken to write a master’s thesis proposal depends upon the study which you are undertaking and your discipline of research. It will take a minimum time of three months. The ideal time can be around six months.
You should begin your master’s thesis proposal by writing an introduction to your research topic. You should state your topic clearly and provide some background. Keep notes and rough drafts of your proposal so you can always refer to them when you write the first real draft.
The basic sections that your master’s thesis proposal should cover are the problem statement, research methodology, proposed activities, importance, and the limitations of your research.
A master’s thesis proposal which clearly defines the problem in a straightforward and explains the research methodology in simple words is considered a good thesis proposal.
You can use any classic font for your master’s thesis proposal such as Times New Roman. If you are recommended a specific font in the proposal guidelines by your institution, it would be advisable to stick to that.
The ideal font size for your master’s thesis proposal will be 10 or 12 points.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
How to Write a Great Thesis Proposal The Easy Way

- 1. What Is A Thesis Proposal?
- 2. Thesis Proposal Template
- 3.1. Craft Your Abstract
- 3.2. Choose Topic and Working Title
- 3.3. Create Your Introduction
- 3.4. Write the Thesis Research Questions
- 3.5. Present Your Literature Review
- 3.6. Write Down the Methodology
- 3.7. Provide Your Timeline
- 3.8. Craft A Conclusion
- 4. Thesis Proposal Example
- 5. Thesis Proposal FAQ
What Is A Thesis Proposal?
A thesis proposal is the link-bridge to the main thesis, laying out the plan of how you will conduct the research. This way, the professors (assessment committee) will know that you are on the right path and got the right tools to get to the final destination.
The first step is developing a thesis proposal outline, commonly referred to as a thesis proposal template, which will help you do your project. It provides a clear thesis proposal format so that you can easily know what to do at what stage. Your proposal should be structured on a number of key elements, each of which should assist you to define the main project.
- Abstract . This is a summary of the entire proposal.
- Define the topic of the proposal. The topic is the title of the project and gives the reader a general idea of what the thesis is all about.
- Write the introduction . The introduction helps to bring out the main issues in the thesis as well as its significance.
- Craft your research questions. These are the questions that you will be seeking to answer in the thesis.
- Review the related literature. This is a comprehensive analysis of existing literature on the topic you are working on.
- Methods . These are the theoretical approaches and methods that will be used to do the study.
- Timeline . In this part, you outline the time required for doing your study.
- Conclusion . This is the last part of your proposal and is used to give the anticipated results from the study.
A thesis proposal requires comprehensive research, preparation, and a well-defined final destination. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft thee best proposal for your thesis.
“ The differences in communication styles between men and women have been a topic of interest in the research world for many years. These differences may lead to miscommunication, conflict, and even dissatisfaction between couples. This study analyzes the communication styles among genders, more specifically among married couples. It questions how differences in communication styles between married couples married five years or less affect marital satisfaction. …”
Discuss the topic with your supervisor. Your supervisor can help you to refine the topic further, and give you the assurance that you are headed in the right direction. He/she will also assist you in grasping the complexities to anticipate along the way and the best way to approach them. See a good thesis proposal example topic.
“ A Detailed History of Halloween and King of Gourds: A Study of Horror Symbolism”
“ The first spooky faces were carved on pumpkins by rats, although considered inferior, mimics were later done by people. When rats brought the dangerous Black Death, people started connecting pumpkins to plague. Pumpkins were also used to scare off the spirits of the dead person to prevent further deaths. Soon after, Jack o lanterns were adopted across the globe as common Halloween talismans. ”
“ What effect does daily use of Facebook have on the Attention span of adolescents?” “What effect do legal approaches have on people who drink and drive in the UK?”
“ Noller (1980) comprehensively compared the effectiveness of women and men as nonverbal communicators. Being an effective communicator involves both encoding and decoding messages. Noller argued that w omen have a natural tendency to be more expressive. He added that men tend to make more errors than women when encoding messages.”
Theoretical approaches. Analytical framework. Formulas and equations. Experiments. Philosophies.
“Pumpkins are crucial Jungian symbols used to indicate the desire of the subconscious mind to control and change the feeling of horror and fear of the people’s desire to understand the unknowable. This study will expand the field of pumpkinology, while fellowship with rats will further be expanded. This will herald a new era of plague-less companionship.”
Check out this thesis proposal sample from our dissertation proposal writing services to get an idea of how a good thesis proposal is supposed to look and to give you a better idea of what to do.
Significant advances in technological capacity have brought the world closer. While this is a positive aspect, it has also introduced a new kind of problem. Cyber-attacks are common features in the present internet age. Individuals and governments are at risk of being targeted, leading to studies involved in alleviating possible breakdown of society owing to its dependence on technology. The paper aims at determining the United States’ preparedness for cybercrime by looking at the nation’s best law enforcement agencies, the CIA and the FBI. By understanding the inner workings of these bodies with relation to cybercrime, the research aims at eliciting an understanding of issues that have been dealt with and showcasing emerging issues that threaten existing cybersecurity measures in a bid to improve them. Cybercrime has shown considerable advancement over the past, necessitating nationwide attention, where the Federal government should use its resources to ensure it is always up to date on matters concerning cybersecurity. In this way, the avenues used by cybercriminals are destroyed.
The significant advancement made in internet technology has yielded a lot of aid in the development of certain aspects of the world relating to information technology. Ranging from medical studies to an intricate internet monetary system (Bitcoin has grown significantly over the past few years) internet development is at the core of modern civilization. As such, issues relating to the internet are of particular concern, especially to developed nations such as the U.S.A. In recent years, a new form of crime has developed due to the growth in internet usage. Cybercrime is a relatively new threat in the American system. Nations such as China and Russia have evidenced an inclination towards technological development, therefore, it is important to determine America’s preparedness for issues that deal with cyber-attacks. The issue can be seen to have dire consequences for economies as cybercriminals have in the past hacked into American corporations (incidences have been blamed on Russia and China). Well-established protocols should be put in place to deal with the growing threat that cannot be alleviated by traditional means of defense. The paper aims at determining if the U.S. is prepared in case of future cyberattacks as cybercriminals continue to increase on a global scale.
Therefore, cybercrime can be deemed as the newest threat to the development of nations in the internet era, which leads to the purpose of this study. It entails an intricate knowledge of writings on the issue and methods that can be used to determine the level of risk faced by an organization or government with regard to cyber attacks. In this way, the researcher aims at ascertaining the relevance of U.S.A. security against cybercrime.
Many scholars argue that governments, as seen by efforts of agencies such as FBI, have limited interest in developing countermeasures for cyber threats. While these institutions confer that the next leading global giants will undoubtedly have the best virtual network connectivity, most of them do not consider cybercrime as serious. In recent years, the United States (U.S) government has come up with various legislations regarding crime committed on cyberspace. While they have elicited some kind of response from the public, enacted legislation is inadequate in curbing cybercriminals. A good example of the limited focus on cyber security is evidenced in the restrictions placed on the FBI with regard to an iPhone that had potentially useful information due to a confidentiality clause.
Such issues should be considered when coming up with legislation concerning cybercrime. Nevertheless, such an issue showcased instances where the public views technological advancements of the government in curbing crime as the FBI hacked the suspect’s phone. It is important to note that a large portion of legislation targeting cyber criminals has been developed after individuals have committed a crime. This is particularly visible in the nation’s interest in cyberspace which developed after leaked information revealed that the Chinese government had hacked government systems in the U.S.A. for an unknown period of time. As such, the FBI has failed in this regard to protect citizens from cybercriminals. A large number of crimes dealing with the internet have led to leaked information concerning individuals such as social security numbers and credit card information. Therefore, loss of such information has led to an increase in crime where identity theft plays a crucial role in highlighting cyber-crime effects. Nevertheless, governments continue to downplay the importance of cyber security, since there is no clearly accepted definition of cyber warfare, cyberattacks and cybercrime. This leads to hackers being provided the opportunity to continue with their tasks unhindered, allowing them to progress faster than the law in this respect.
Furthermore, it is necessary to point out the diversity of cybercrime to better develop the issue. Cybercrime targets anyone without any form of consideration for age, sex, or financial status. A young child whose information has been stolen could be the victim in a social security fraud case. In this case, individuals use the child’s documents to open up new lines of credit thereby giving criminals revenue to conduct their activities which negatively affects the individuals in the future and the country. For such a victim, it is difficult to determine the source of the hack since most people realize these issues when they require credit such as when applying for a loan. In the same way, an organization may be threatened with leakage of information regarding a particular product that could potentially lead to loss of revenue. Multiplier effects of such hacks are immense, cutting across the economy as some people are at risk of losing their livelihoods.
Therefore, new laws enacted to protect people against cybercrime have led to a unanimous agreement by nations. This concerns the role of cyber security in eradicating cybercrime, showcasing its importance in a country. Mohammed and Mariani also agree as they emphasize for governments to adopt better measures of cybersecurity. To deter criminals, nations need to understand the implications of cybercrime in the communities involved. Rather than wait for a criminal occurrence to develop good countermeasures, they should invest a sizeable quantity of resources to the attainment of peak cybersecurity measures.
Theoretical Framework/Approach
A large number of studies related to cybercrime have focused on the ability of a country to mitigate cybercrime based on existing research and technological capabilities. However, this study aims to develop an understanding of the American system with regard to its readiness to deal with this form of crime. In this respect, the research will focus on the government’s primary law enforcement agency tasked with interior security (F.B.I) and their ability to prevent cybercriminals from operating in the U.S. It is important to ascertain the agency’s level of development in terms of computer expertise. Moreover, the CIA is tasked with external protection of the nation. The study will thus include measures taken by the CIA. in their pursuit of a nation without cybercriminals.
However, the key to determining the relevance of a nation’s systems in curbing cybercrime is the legislature where it needs to come up with severe penalties for perpetrators of these acts. As such, individuals who wish to become hackers will be less receptive to the allure of hacking as they consider the penalty as extremely high. This requires a nation to develop strong foreign policies dealing with cybercrime. Such systems act as a deterrent to foreign nationals who would wish to hack a country such as America due to the potential legal ramifications. In this manner, the number of white hat hackers is likely to increase thus contributing to a nation’s systems to counter cybercrime. As a large pool of individuals possesses skills that could potentially aid a government to prevent future attacks, it is important to look at the criminal system and how it deals with cybercriminals. Some of these individuals possess a significant number of skills that could improve cybersecurity when used in a positive manner. Therefore, rather than work against people with good computer skills, the government will work with them to boost the nation’s cyber security. This reduces the number of people in the prison system and provides the government with a proper labor force to maintain cyber security.
Nevertheless, it is necessary to consider the impact of integrating criminals into the justice system since it might have detrimental effects. These may arise because of nationalism. Individuals who hack American systems are less likely to be of American descent. Therefore, providing them with access to sensitive information could be disastrous if they continue exhibiting radical tendencies. However, for an agency or bureau to develop proper measures of security, there is a need to understand the mindset of cybercriminals. Offering these individuals incentives such as monetary compensation and reduced jail sentences could help mitigate against the aforementioned issues.
Research Design & Methods
The research will differ from the majority of studies by concentrating on non-experimental methods, specifically correlational research where the focus is on reduction of cybercrime in the nation as security systems continue to improve. With a certain focus on the American system, the study will encompass various studies in an attempt to find a connection between them. In this way, it will be possible to determine the manner in which the U.S. has survived a myriad of cyber attacks based on existing technology. Furthermore, this approach aids in showcasing a trend of the manner in which cybercrime is developing in contemporary societies. As such, the CIA and FBI come into focus. They are deemed the paramount institutions established by the U.S. in dealing with threats, both externally and internally and thus a review of the processes employed by both institutions is helpful in gauging American readiness for cyber warfare.
In recent years, various internet-based institutions have taken over the global markets. Bitcoin threatens the very existence of conventional financial instruments as it continues on an upward trend. Other actors such as Google have grown considerably over the past decade to become giant corporations. As such, the internet continues to broaden in its application to normal day life. It is, therefore prudent that the US government improve its cyber security to protect its organizations.
Moreover, it is impossible to come up with an accurate depiction of the nation’s state in terms of cybersecurity. This is because information regarding systems used by the CIA and FBI is highly classified. As such, the study can only base its arguments on technologies used by the F.B.I., that is, those that they evidence to the public as opposed to the one’s they do not reveal. It is also important to gauge the direction in which government institutions have gone in their attempts to deviate cybercriminals from criminal behavior. A recent issue concerning the hack of an iPhone belonging to the San Bernadino shooter is proof of the advancement in hacking technology within the government. It is possible to come up with an insightful view of the focus placed by governments, particularly the American government concerning cyber security by looking at budget records and trends in recent past. A rise in the value assigned to local agencies to deal with cyber threats shows increased interest in cyber security.
Cybercrime plays a huge role in modern societies. Many nations have claimed that whomever leads in technological capacity wields a large power. As such, while governments focus on physical threats, the study intends to ascertain their readiness for a cyber attack. With the U.S. as the primary source of information, the paper aims at developing an understanding into the digital world and ways that the government has, and should, use resources in creating impenetrable cyber security systems.
Seek Thesis Proposal Help
At this point, it is important to point out that writing a thesis proposal is never easy. Indeed, many are university students who get stuck even before getting started. But you cannot give up because the proposal is the gateway to crafting a great thesis. Therefore, you should seek writing help from professionals.
The experts have been writing thesis proposals and other tasks that students fund tough to handle. In addition to being experts in different fields, they know what works and what does not. So, they are your best bet to crafting a great proposal and, finally, the best thesis to impress the evaluation committee. We are the best master thesis writing service online, and are as reliable as it gets!
Thesis Proposal FAQ
- How long should a thesis proposal be? Although the length of a thesis proposal may differ from one university to another, the average length is about ten pages.
- What is the best formatting and citation for a proposal and thesis? Well, there is no standard formatting and citation method when it comes to writing proposals and thesis. However, your department will give the recommended formatting and citation style that students should use for their proposal. If your department does not provide a clear guideline on formatting and citation, consider checking the best sample thesis proposal to see how the best students did it.
- How long does it take to draft a thesis proposal? It depends on the type of research paper you are writing and the requirement for the proposal. You can dedicate an entire day to draft a proposal. But, the average amount of time you should spend on a thesis proposal should not exceed three days.
- Literature review
- Research methodology
- Ethical consideration
- Research timeline
- Is Writing a thesis proposal stressful? Definitely, writing a thesis proposal requires ample time for research and preparation to avoid being rejected. It might take your time but when you have an idea of what you’re working on, it isn’t too stressful.
- Best way on how to write a thesis proposal? It is very simple. Research. Doing a thorough research before starting your proposal makes the work easier. The secret to every thesis proposal or research paper that is properly written is the amount of research that went into producing the paper. Therefore, when starting your proposal, carry out an extensive research on your topic to build up more information.
- Is Writing a thesis proposal hard? Aside from researching, most times, putting together a thesis proposal even after extensive research can be a bit difficult. It could be the challenge of not knowing how to start or “how to put pen on paper”. Every researcher or student experiences this at the initial stage. But, the important thing to note is that you don’t need to get it right in your first draft. Just write. You can structure it later.

Make PhD experience your own
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.
Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
- Honors Undergraduate Thesis
- Program Resources
The Honors Undergraduate Thesis program requires students to submit a research proposal to the Office of Honors Research prior to advancing to the Thesis semester.
Generally, a scientific research proposal will include a brief introduction to the research topic, a literature review, and a methodology that will explain how the student plans to meet the objectives of the research. A proposal in the Arts and Humanities will generally include an introduction and a creative work (e.g. screenplays, short stories, artwork) or theoretical analysis.
Students will create a signature cover page for the thesis proposal that will list the entire committee and HUT Liaison. The Thesis proposal cover page template can be found here .
The following are examples of substantially researched, properly formatted research proposals and their respective signature pages. These examples should be used for reference only and not necessarily as templates. Students should his or her Thesis Chair and committee regarding the structure of the proposal, information that should be present, and documentation style.
A thesis proposal is a document that outlines the thesis topic, defines the issues that the thesis will address, and explains why the topic warrants further research. It should identify a problem and provide a proposed solution to that problem.
Proposals representative of the sciences (both hard sciences and social sciences) should generally include the following:
- A brief introduction, which will define the thesis topic and explain the purpose of the thesis.
- A literature review that outlines the most relevant readings and theories which pertain to the thesis topic.
- A methodology section, which should include the research questions, hypotheses, participants, materials, and procedures.
- A bibliography or reference list. Most of the sources should be from peer reviewed articles or books. As with other academic papers, the use of internet sources should be limited.
For students conducting more theoretical or comparative analyses, the structure could also take the form of chapters that define and specify each concept, and a concluding chapter that brings all of these ideas together.
For students in the arts, a proposal and thesis may take the form of a creative project. In this instance, the proposal may include:
- A brief introduction, which includes the thesis statement, general intent of project, what the project should accomplish, and justification for considering the project a legitimate endeavor.
- A literature review, which includes any supporting literature that justifies the intention of the project.
- A method for accomplishing the project. Include any necessary background or equipment needed for the project, where the project will be conducted, and a proposed timeline for completion.
- A bibliography or reference list.
An alternative structure would be for students who are writing their own short stories, novellas, or screenplays.
Here, the thesis should include a clear mastery of the skill set by producing chapters of the novella, poetry selections, or the working/final screenplay. [/accordion-item][/accordion]
Burnett School of Biomedical Sciences Biomedical Sciences
College of Arts and Humanities Art History History English-Creative Writing English-Literature Philosophy
College of Business Administration Finance
College of Nursing Nursing
College of Education and Human Performance Elementary Education English Language Arts Education
College of Engineering and Computer Science
Computer Engineering Mechanical Engineering
College of Health and Public Affairs Legal Studies Sports and Exercise Science
College of Nursing Nursing -->
College of Sciences Anthropology Chemistry Mathematics Physics International & Global Studies Psychology Sociology
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
How to write a thesis proposal
I. Framework II. Structure of a thesis proposal III. Order in which to write the proposal IV. Tips V. Resources
I. Framework
- An environmental issue is identified.
- Other people's work on the topic is collected and evaluated.
- Data necessary to solving the problem are either collected by the student, or obtained independently.
- Data are analyzed using techniques appropriate to the data set.
- Results of the analysis are reported and are interpreted in light of the initial environmental issue.
- the thesis topic addresses a significant environmental problem;
- an organized plan is in place for collecting or obtaining data to help solve the problem;
- methods of data analysis have been identified and are appropriate to the data set.
II. Structure of a thesis proposal
- Work plan including time table
- Implications of research
- List of references
- contains short, descriptive title of the proposed thesis project (should be fairly self-explanatory)
- and author, institution, department, resreach mentor, mentor's institution, and date of delivery
- the abstract is a brief summary of your thesis proposal
- its length should not exceed ~200 words
- present a brief introduction to the issue
- make the key statement of your thesis
- give a summary of how you want to address the issue
- include a possible implication of your work, if successfully completed
- list all headings and subheadings with page numbers
- indent subheadings
- this section sets the context for your proposed project and must capture the reader's interest
- explain the background of your study starting from a broad picture narrowing in on your research question
- review what is known about your research topic as far as it is relevant to your thesis
- cite relevant references
- the introduction should be at a level that makes it easy to understand for readers with a general science background, for example your classmates
- in a couple of sentences, state your thesis
- this statement can take the form of a hypothesis, research question, project statement, or goal statement
- the thesis statement should capture the essence of your intended project and also help to put boundaries around it
- this section contains an overall description of your approach, materials, and procedures
- what methods will be used?
- how will data be collected and analyzed?
- what materials will be used?
- include calculations, technique, procedure, equipment, and calibration graphs
- detail limitations, assumptions, and range of validity
- citations should be limited to data sources and more complete descriptions of procedures
- do not include results and discussion of results here
- present any results you already have obtained
- discuss how they fit in the framework of your thesis
- describe in detail what you plan to do until completion of your senior thesis project
- list the stages of your project in a table format
- indicate deadlines you have set for completing each stage of the project, including any work you have already completed
- discuss any particular challenges that need to be overcome
- what new knowledge will the proposed project produce that we do not already know?
- why is it worth knowing, what are the major implications?
- cite all ideas, concepts, text, data that are not your own
- if you make a statement, back it up with your own data or a reference
- all references cited in the text must be listed
- cite single-author references by the surname of the author (followed by date of the publication in parenthesis)
- ... according to Hays (1994)
- ... population growth is one of the greatest environmental concerns facing future generations (Hays, 1994).
- cite double-author references by the surnames of both authors (followed by date of the publication in parenthesis)
- e.g. Simpson and Hays (1994)
- cite more than double-author references by the surname of the first author followed by et al. and then the date of the publication
- e.g. Pfirman, Simpson and Hays would be:
- Pfirman et al. (1994)
- cite newspaper articles using the newspaper name and date, e.g.
- ....this problem was also recently discussed in the press (New York Times, 1/15/00)
- do not use footnotes
- list all references cited in the text in alphabetical order using the following format for different types of material:
- Hunt, S. (1966) Carbohydrate and amino acid composition of the egg capsules of the whelk. Nature , 210, 436-437.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (1997) Commonly asked questions about ozone. http://www.noaa.gov/public-affairs/grounders/ozo1.html, 9/27/97.
- Pfirman, S.L., M. Stute, H.J. Simpson, and J. Hays (1996) Undergraduate research at Barnard and Columbia, Journal of Research , 11, 213-214.
- Pechenik, J.A. (1987) A short guide to writing about biology. Harper Collins Publishers, New York, 194pp.
- Pitelka, D.R., and F.M. Child (1964) Review of ciliary structure and function. In: Biochemistry and Physiology of Protozoa , Vol. 3 (S.H. Hutner, editor), Academic Press, New York, 131-198.
- Sambrotto, R. (1997) lecture notes, Environmental Data Analysis, Barnard College, Oct 2, 1997.
- Stute, M., J.F. Clark, P. Schlosser, W.S. Broecker, and G. Bonani (1995) A high altitude continental paleotemperature record derived from noble gases dissolved in groundwater from the San Juan Basin, New Mexico. Quat. Res. , 43, 209-220.
- New York Times (1/15/00) PCBs in the Hudson still an issue, A2.
- it is acceptable to put the initials of the individual authors behind their last names, e.g. Pfirman, S.L., Stute, M., Simpson, H.J., and Hays, J (1996) Undergraduate research at ......
III. Order in which to write the proposal
- Make an outline of your thesis proposal before you start writing
- Prepare figures and tables
- Figure captions
- Discussion of your data
- Inferences from your data
- Bibliography
- "Pictures say more than a thousand words!" Figures serve to illustrate important aspects of the background material, sample data, and analysis techniques.
- A well chosen and well labeled figure can reduce text length, and improve proposal clarity. Proposals often contain figures from other articles. These can be appropriate, but you should consider modifying them if the modifications will improve your point.
- The whole process of making a drawing is important for two reasons. First, it clarifies your thinking. If you dont understand the process, you cant draw it. Second, good drawings are very valuable. Other scientists will understand your paper better if you can make a drawing of your ideas. A co-author of mine has advised me: make figures that other people will want to steal. They will cite your paper because they want to use your figure in their paper.
- Make cartoons using a scientific drawing program. Depending upon the subject of your paper, a cartoon might incorporate the following:
- a picture of the scientific equipment that you are using and an explanation of how it works;
- a drawing of a cycle showing steps, feedback loops, and bifurcations: this can include chemical or mathematical equations;
- a flow chart showing the steps in a process and the possible causes and consequences.
- Incorporate graphs in the text or on separated sheets inserted in the thesis proposal
- Modern computer technology such as scanners and drafting programs are available in the department to help you create or modify pictures.
Grammar/spelling
- Poor grammar and spelling distract from the content of the proposal. The reader focuses on the grammar and spelling problems and misses keys points made in the text. Modern word processing programs have grammar and spell checkers. Use them.
- Read your proposal aloud - then have a friend read it aloud. If your sentences seem too long, make two or three sentences instead of one. Try to write the same way that you speak when you are explaining a concept. Most people speak more clearly than they write.
- You should have read your proposal over at least 5 times before handing it in
- Simple wording is generally better
- If you get comments from others that seem completely irrelevant to you, your paper is not written clearly enough never use a complex word if a simpler word will do
V. Resources/Acknowlegements
The senior seminar website has a very detailed document on " How to write a thesis " which you might want to look at. Most of the tips given there are relevant for your thesis proposal as well. Recommended books on scientific writing Some of the material on this page was adapted from: http://www.geo.utep.edu/Grad_Info/prop_guide.html http://www.hartwick.edu/anthropology/proposal.htm http://csdl.ics.hawaii.edu/FAQ/FAQ/thesis-proposal.html http://www.butler.edu/honors/PropsTheses.html

Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page. Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes: The proposed title of your project; Your name
Step 2 - Know the Proposal Structure. Familiarize yourself with the structure of a proposal. The major sections usually include an introduction, methodology, significance, data explanation, conclusions, and references. Understanding this structure is key to a well-organized proposal.
Step 3. Planning your writing. The best way to put together an organized thesis proposal is to determine how you will write it before you get started. Many thesis proposals are rejected simply because students fail to plan their writing and instead try to hack everything together in a piecemeal approach.
A guide to writing a winning research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, with 5 essential ingredients: title/topic, introduction, scope, literature review and design/methodology. Learn how to structure your proposal with a 5-section format and tips for each section.
The following are some requirements for your proposed project you should follow: 5000 words is the maximum word count limit for your thesis proposal. Line spacing should be 1.5 for text and single-spaced for quotations. Set the margins to 1.25 inches on the right/left and 1 inch on the top and bottom.
Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build. If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint. It's you figuring out how your thesis will fit into the space you've found, how you'll build it, and whether it will stand up to the harsh winds of your thesis adviser's opinions and the tremors of a difficult ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography. Like any academic text, it's important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal. Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing ...
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes: The proposed title of your project; Your name; Your supervisor's name; Your institution and department; Tip If your proposal is very long, you may also want to include an abstract and a table of contents to help your reader navigate your work ...
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation ...
Example - include all preliminary research, create appendices for secondary information, literature review and more. Create headings: Each section of your thesis proposal should be broken down into sub-topics. This helps present vital information in a better manner. Example - when you are writing the subtopics for the methodology make a ...
Typical contents and structure of a dissertation proposal include the following; Title. Statement of the Problem. Background/Rationale. Introduction (Justifying your Research) Research Questions or Hypothesis (Research aim and objectives) Literature Review. Proposed Methodology.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
The thesis proposal should include: a background theory a working hypothesis a methodology which should be organized under chapter headings a body of work for analysis a bibliography If your thesis will be presented in an alternate format (such as performance), be sure to include this in your proposal. Some graduate programs require students to ...
A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis.
Abstract. This is a summary of the entire proposal. Define the topic of the proposal. The topic is the title of the project and gives the reader a general idea of what the thesis is all about. Write the introduction. The introduction helps to bring out the main issues in the thesis as well as its significance.
A Thesis Proposal is a document that sets forth what is to be studied as a thesis project, why and in what way. It contains a number of important sections. The purpose of the proposal is to communicate the plan for the work to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies via the First Reader (principal thesis advisor) and a Second Reader.
1. Title Page: Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization's name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines. 2. Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
A proposal in the Arts and Humanities will generally include an introduction and a creative work (e.g. screenplays, short stories, artwork) or theoretical analysis. Students will create a signature cover page for the thesis proposal that will list the entire committee and HUT Liaison. The Thesis proposal cover page template can be found here.
The dissertation proposal is required for all doctoral students. It addresses 1) why the research is relevant, 2) the focus of the research, and 3) how the research will be conducted. Students prepare a written document and give an oral presentation to the supervisory committee. This template is to serve as a general outline for…
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Abstract. the abstract is a brief summary of your thesis proposal. its length should not exceed ~200 words. present a brief introduction to the issue. make the key statement of your thesis. give a summary of how you want to address the issue. include a possible implication of your work, if successfully completed.
write a term paper of enhancement of memory

resume sample undergraduate
- Frank Magazine
- Denison History
- Virtual Tours
- Alaskan Yachts
- Azimut Yachts
- Back Cove Yachts
- Beneteau Yachts
- Benetti Superyachts
- Bertram Yachts
- Boston Whaler
- Broward Yachts
- Buddy Davis Sportfish
- Burger Yachts
- Cabo Yachts
- Carver Motoryachts
- Center Console
- Chris-Craft Yachts
- Cruisers Yachts
- DeFever Trawlers
- Dufour Sailboats
- Fairline Yachts
- Feadship Yachts
- Ferretti Yachts
- Formula Yachts
- Fountaine Pajot Cats
- Grady-White
- Grand Banks Trawlers
- Hargrave Yachts
- Hatteras Yachts
- Hinckley Picnic Boats
- Horizon Yachts
- Hydra-Sports
- Intrepid Boats
- Jarrett Bay Sportfish
- Jeanneau Yachts
- Kadey-Krogen Trawlers
- Lazzara Yachts
- Luhrs Sportfish
- Marlow Yachts
- Maritimo Yachts
- Marquis Yachts
- McKinna Motoryachts
- Meridian Yachts
- Midnight Express
- Mochi Craft
- Neptunus Motoryachts
- Nordhavn Trawlers
- Nordic Tugs
- Ocean Alexander Yachts
- Offshore Yachts
- Oyster Sailing Yachts
- Pacific Mariner Yachts
- Palmer Johnson Yachts
- Pershing Yachts
- Prestige Yachts
- Princess Yachts
- Pursuit Yachts
- Riva Yachts
- Riviera Yachts
- Sabre Downeast
- San Lorenzo Yachts
- Sea Ray Boats
- SeaVee Central Consoles
- Selene Trawlers
- Scout Yachts
- Sunseeker Yachts
- Tiara Yachts
- Trinity Superyachts
- Viking Yachts
- Westport Yachts
78 Burger 1965 Yacht for Sale
Asking price: $495,000.
- Yachts for sale
- motoryachts
- 78' Burger
Last updated Jan 31, 2024
78' Burger 1965
VERY MOTIVATED SELLER OPEN TO ALL OFFERS OR TRADES
LONG-TERM DOCK SLIP IS AVAILABLE FOR NEW OWNER AT NICE LIVE-ABOARD MARINA IN FORT PIERCE WITH A SPECTACULAR VIEW, PLENTY OF PARKING, AND VERY NICE MANAGEMENT PERSONNEL
Located in Fort Pierce, Florida. This yacht is a magnificent example of quality and heavy duty construction. She was totally refit top to bottom, inside and out from 2004 to 2012 by her current owner, with 40 plus years of experience in the marine industry. Her beautiful mahogany interior has been refinished with Awlcraft 2000 and Awlbrite. Super high gloss finish throughout. Aft deck area is all teak. Same Awlgrip finish. All interior mahogany cabinets and woodwork were stripped and refinished, most of them had been painted over the years but fortunately they were made with very thick solid 1 inch mahogany and easier to refinish compared to all veneer and plywood boats of later years.
Remodeled heads, with new sinks, tile, and fixtures. All new mattresses in every stateroom. New watercooled, 4 ton AC unit on bridge cools pilothouse and aft deck. All new seastrainers and AC pumps, and thru-hulls installed in 2016. Exterior was stripped to bare aluminum, windows removed and replaced with factory rubber. Exterior hull and topsides were faired with west system fillers, Awlgrip primer and Awlgrip topcoat. All decks and superstructure were faired out with no expense spared she has smooth lines and has no waves as do most aluminum yachts. Deck and exterior hardware were carefully installed with a special isolating technique using isolators made from delrin and nylon to help prevent corrosion due to unlike metals touching. Very time consuming but worth every penny. No one takes the time to do this when they refit these aluminum boats.
Too many upgrades to list, must come see this amazing vessel to appreciate all that has been done. This was not a normal refit, it went way beyond that of normal refits. I used all my years of working on these yachts to make this one a true Gem. FantaSea has been used very little since its restoration. Some exterior wood trim etc. needs refinished again. Rails are good, but exterior just needs spruced back up some, buffing/polishing and britework. She also needs a new bimini top thanks to Irma.
FantaSea has only had two owners in its 57 years. She is a heavy duty ship that has been a pleasure to own and refit. She is ready to have a great new life with a new owner.
Denison Yachting is pleased to assist you in the purchase of this vessel. This boat is centrally listed by National Yacht Sales.
Denison Yacht Sales offers the details of this yacht in good faith but can’t guarantee the accuracy of this information nor warrant the condition of this boat for sale. This yacht for sale is offered subject to prior sale, price change, or withdrawal from that yacht market without notice. She is offered as a convenience by this yacht broker to its clients and is not intended to convey direct representation of a specific yacht for sale.
INQUIRE ABOUT 78' BURGER
Have questions about this yacht? Fill out the form below and our team of experts will contact you soon.
Your privacy is important to us. Find out how we protect it. Privacy Policy

First-Time Yacht Buyer?
Read our guide to learn the process for buying this 78' Burger
78' Burger HIGHLIGHTS
- Yacht Details: 78' Burger 1965
- Location: Fort Pierce, FL
- Engines: Detroit
- Last Updated: Jan 31, 2024
- Asking Price: $495,000
- Max Draft: 4' 3''
78' Burger additional information
- Beam: 16' 0''
- Hull Material: Aluminum
- Fuel Tank: 1 x 2100|gallon
- Fresh Water: 1 x 500|gallon
Schedule a Tour of 78' BURGER Yacht
Contact our team to schedule a private showing.
SIMILAR YACHTS FOR SALE View All
90' schooner 1962, camden, me, us, 88' ferretti yachts 2006, fort lauderdale, fl, us, 87' mangusta 2003, formia, italy, 83' custom 2003, istanbul, turkey, 82' abeking & rasmussen 1960, 81' burger 1967, lake champlain, vermont, chittenden, estados unidos, us, 81' burger 1982, fort myers, fl, us, other burger yachts for sale view all, 127' burger 2003, west palm beach, fl, us, 63' burger 1961, wickford, ri, us, 63' burger 1965, redondo beach, ca, us, 63' burger 1962, curacao, netherlands antilles, yachts a luck, 80' burger 1988, holland, mi, us, 84' burger 2000, burger yachts sales report, price watch.
Love this yacht? Get notified on price reductions and other related updates.
Our Newsletter
Stay informed on all things yachting, including notable sales, industry updates, events, and boating tips with our newsletters.
motoryachts News
Read the latest motoryachts news and stay up to date on related events.
RELATED SERVICES

LOGIN OR REGISTER
Hi, welcome back.
Login and pick up from where you left off.
Creating an account allows you to save and compare your favorite yachts.
By creating an account you agree to the terms of use and our privacy policy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Burger boats for sale on YachtWorld are offered at a swath of prices from $174,500 on the relatively lower-priced models, with costs up to $22,500,000 for the most advanced and biggest yachts. What Burger model is the best? Some of the best-known Burger models currently listed include: 60, 82, Raised Pilothouse, 106 Raised Pilothouse and 48 ...
Every new Burger yacht reflects the yacht builder's heritage and the personality and cruising requirements of each yacht owner. Shipyard Stats. Founder: Henry Burger; Size: Up to 79 feet; Type: Luxury superyachts, motor yachts, sailing yachts; Scroll down to find new and used Burger Yachts for sale on the world's most trusted MLS for yachts ...
Freedom Yacht for Sale is a 86 superyacht built by Burger in 1979. Currently she is located in West Palm Beach and awaiting her new owners. ... OWNER WANTS BOAT SOLD NOW !.....BRING OFFERS ... OTHER Burger YACHTS FOR SALE View All. Checkers 85' Burger 2001 $2,900,000 Destin, FL, US 63' Burger 1962 ...
BURGER MODELS AVAILABLE. Burger offers a diverse range of models and concepts, from the collaborative venture with Evan K. Marshall, the Burger 142' Atrium Motor Yacht, to the 120' Raised Pilothouse Motor Yacht, along with the adventure-ready 112', 115', 122' Raised Pilothouse Motor Yachts. The flagship 144' Tri-Deck Motor Yacht combines a ...
Burger went all out in conjunction with the designer and discriminating owner to develop this very special addition. Looking for a commercial vessel, Burger has recently launched quite a few from 62 to 98 feet. One of the two 98 footers (30M), named CHICAGO'S LEADING LADY is the first steel vessel they've built, since launching BRODIE VI.
Silver Seas Yacht for Sale is a 107 superyacht built by Burger in 1998. Currently she is located in Fort Lauderdale and awaiting her new owners. ... and the third was an ocean racing sailor who owned three prior Burgers himself. The current owner performed an 8-year restoration on his prior Burger. Upon taking ownership of SILVER SEAS, he ...
Impetuous Yacht | 127' Burger 2003. Rolls Royce of American Yacht Builders - Top Pedigree Burger Yacht. Yacht equipped for wheel chair access including gangway, master stateroom, main deck and skylounge, swim platform lift and 3 cranes to lift on and off yacht in strategic locations throughout. Elevator to all levels.
Burger boats for sale on YachtWorld are listed for a swath of prices from $54,500 on the lower-cost segment, with costs up to $22,500,000 for the most luxurious yachts. What Burger model is the best? Some of the most widely-known Burger models presently listed include: Motoryacht, 106 Raised Pilothouse, 60, 63′ Classic Motor Yacht and 64 ...
Burger boats for sale on Boat Trader are available for a range of prices, valued from $55,600 on the lower-end all the way up to $7,900,000 for the most advanced boats. Higher performance models now listed are rigged with motors up to 3,100 horsepower, while shorter, more affordable more functional models may have as little as 700 horsepower ...
Burger's offerings include semi-custom mega-yachts in two collections for the discriminating owner, as well as the 48 Cruiser, an affordable option for those who want a smaller option. ... Back to Used Burger Yachts for Sale. Burger Yachts by length. Burger 70' to 80' Burger 80' and above. Burger Yachts by price. Burger $600,000 to $900,000 ...
Burger is also easily reached via limousine or the waterways of the Great Lakes. RECENTLY SOLD BURGER YACHTS. LOA Manufacturer Year List Price Sold Price Location. 105' Burger 2000 $3,495,000 (10/18) $2,000,000 (11/19) FL, USA.
SOVEREIGN is a 100' (30.48m) Burger motor yacht delivered in 1966, refit in 2020 with many upgrades throughout the last few years. Accommodation includes 4 staterooms sleeping 8 guests with 4 crew in 3 cabins. Denison Yacht Sales offers the details of this yacht in good faith but cannot guarantee or warrant the accuracy of this information nor ...
Explore NADAN yacht for sale; through beautiful photos and a full walk-through description of this impressive Burger 151' 3" Motor Yacht. Primary Navigation. Purchase. Worldwide Yachts For Sale; Featured Yachts For Sale; ... NADAN sleeps 9 in the Owner's party in 4 cabins with one Pullman berth, plus crew accommodations for up to 7 in 4 ...
Description. Freedom is a well appointed luxury yacht from the Burger Yacht Builders. Her interior finishes were recently upgraded by the word renowned designer "The Red Rickshaw" throughout this fine vessel. Freedom is ready to cruise the world, she has four watertight bulkheads, a full keel with a maximum speed of 20 knots.
Impressions; At 91 meters in length, Lady Lara is an ultramodern superyacht with sweeping curves and an elegantly balanced profile. Dynamic, sculpted features carry through her ex
Motor Yacht CHECKERS is an 85' (25.91m) yacht for sale, built and launched by yacht builder Burger and delivered in 2001 with a refit in 2023. This vessel sleeps up to 6 guests in 3 staterooms and has accommodations for 2 crew in 1 cabin. Please see Other Details below for complete specifications. Denison Yachting is pleased to assist you in ...
1966 Burger Classic. US$2,100,000. ↓ Price Drop. Worth Avenue Yachts | Palm Beach, Florida. <. 1. >. * Price displayed is based on today's currency conversion rate of the listed sales price. Boats Group does not guarantee the accuracy of conversion rates and rates may differ than those provided by financial institutions at the time of ...
118 WallyPower, christened Galeocerdo, is a 118-foot (36 m) luxury motor yacht with a maximum speed of 60 knots (69 mph; 110 km/h), designed by Lazzarini Pickering Architetti, produced by Wally Yachts. [1] The yacht is narrow and angular in design with black glass housing, driven by three Vericor TF50 gas turbines generating 5,600 horsepower .....
Find Pershing 115 boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of Pershing boats to choose from.... Astonishingly, Pershing boss Tilli Antonelli didn't think 7,400 hp would be quite enough for some owners, so each 115 is built with a central molded-in stern pod, ready to accommodate a TF50 gas turbine.
Yachts A Luck Yacht | 80' Burger 1988. YACHTS A LUCK (ex. Corinne) - was proudly launched on November 21st, 1987.... Built in Wisconsin by Burger Boat Company She is a fine example of a highly customized 80 foot aluminum raised pilothouse cruiser.The interior of YACHTS A LUCK is matched teak with a custom stain finish.
40' MTI. ( (SOLD)) Luxury 2009 40 MTI with the Tilt Trailer.$399K This boat is a one-owner powerboat used only in freshwater. Powered with two Mercury 700s stage 3 motors with original 150 HR this boat is nice. "Don't miss out" For viewing please make an appointment with us @ Rockstarboats.com (928)208-8460..... These powerboats use the following propulsion options: outboard engine.
This yacht for sale is offered subject to prior sale, price change, or withdrawal from that yacht market without notice. She is offered as a convenience by this yacht broker to its clients and is not intended to convey direct representation of a specific yacht for sale. Yacht for Sale is a 78 superyacht built by Burger in 1965.